|
Temple Of Reason
A Temple of Reason () was, during the French Revolution, a state atheist temple for a new belief system created to replace Christianity: the Cult of Reason, which was based on the ideals of reason, virtue, and liberty. This "religion" was supposed to be universal and to spread the ideas of the revolution, summarized in its "" motto, which was also inscribed on the Temples. Services The symbols of Christianity were covered up, and the symbols of the Cult of Reason replaced them. In the Churches of Reason, there were specially created services meant to replace the Christian liturgy. For instance, at the Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, on 10 November 1793, a special ritual was held for the "Feast of Reason": the nave had an improvised mountain on which stood a Greek temple dedicated to Philosophy and decorated with busts of philosophers. At the base of the mountain was located an altar dedicated to Reason, and in front of it was a torch of Truth. The ceremony included the crowd payi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple De La Raison, St Martin, Ivry-la-Bataille
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in English, while those of other religions are not, even though they fulfill very similar functions. The religions for which the terms are used include the great majority of ancient religions that are now extinct, such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. Among religions still active: Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir or Kovil), Buddhism (whose temples are called Vihāra, Vihar), Sikhism (whose temples are called Gurdwara, gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baháʼí Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baháʼí House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are often called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
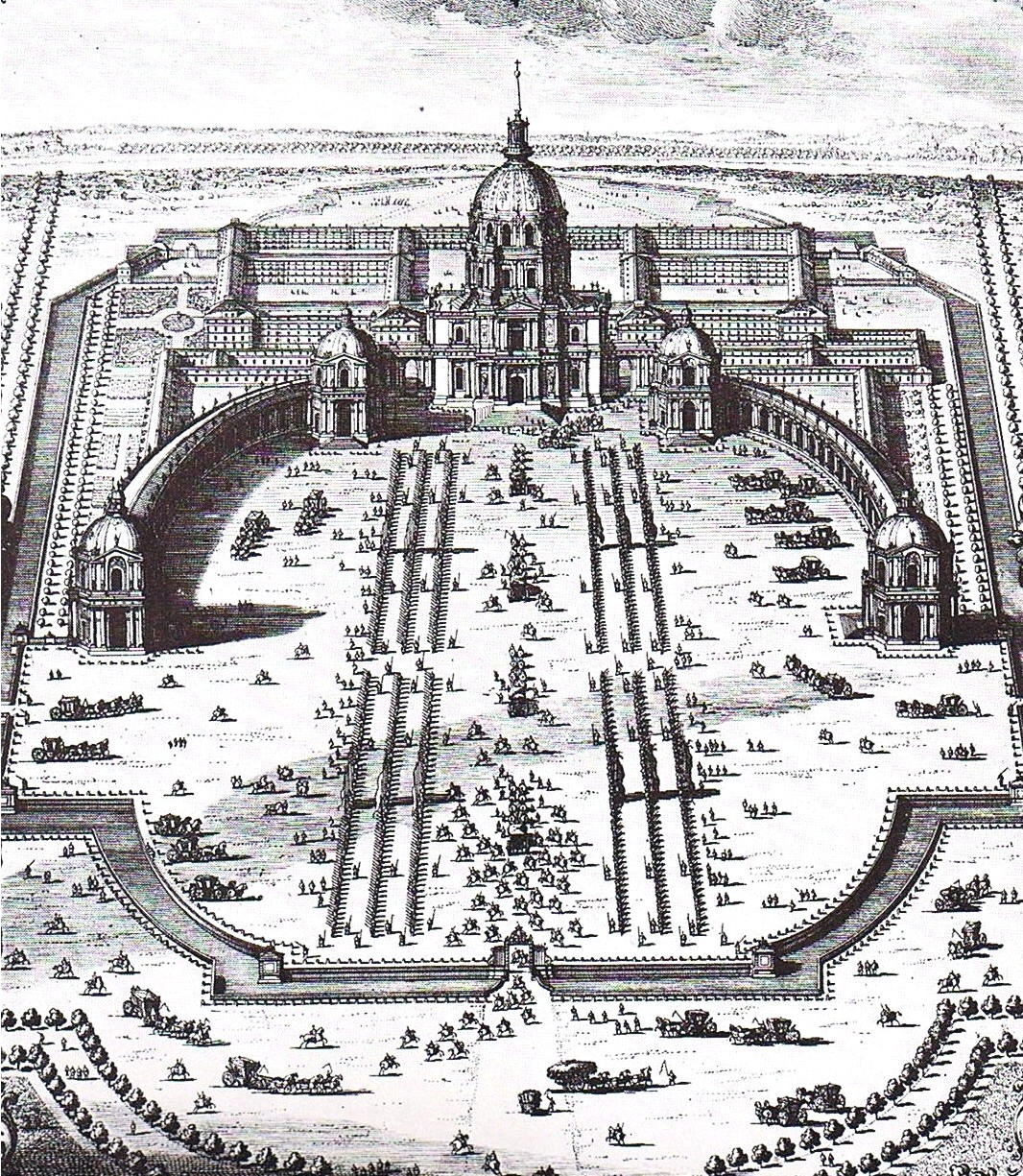
Les Invalides
The Hôtel des Invalides (; ), commonly called (; ), is a complex of buildings in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France, containing museums and monuments, all relating to the military history of France, as well as a hospital and an old soldiers' retirement home, the building's original purpose. The buildings house the Musée de l'Armée, the museum of the Army of France, the Musée des Plans-Reliefs, and the Musée d'Histoire Contemporaine. The complex also includes the Cathedral of Saint-Louis-des-Invalides, the national cathedral of the French military. It is adjacent to the Royal Chapel known as the , the tallest church building in Paris at a height of 107 meters. The latter has been converted into a shrine to some of France's leading military figures, most notably the tomb of Napoleon. History Louis XIV initiated the project by an order dated 24 November 1670 to create a home and hospital for aged and disabled () soldiers, the veterans of his many military campaigns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion And The French Revolution
Religion is a range of social- cultural systems, including designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relate humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements—although there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. It is an essentially contested concept. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacredness, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). and a supernatural being or beings. The origin of religious belief is an open question, with possible explanations including awareness of individual death, a sense of community, and dreams. Religions have sacred histories, narratives, and mythologies, preserved in oral traditions, sacred texts, symbols, and holy places, that may attempt to explain the origin of life, the universe, and other phenomena. Religiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Davidson
Samuel Davidson (September 18061 April 1898) was an Irish biblical scholar. Life He was born at Kellswater, County Antrim, the son of Abraham Davidson, into a Scots-Irish presbyterian. He was educated at the village school, under James Darragh, and then in Ballymena till 1824; and then became a student at the Royal Belfast Academical Institution, destined for the presbyterian ministry. His college course included periods in Londonderry and Liverpool, and was completed in 1832. In November 1833 Davidson was licensed to preach by the Ballymena presbytery. In 1835 the Synod of Ulster made him the first professor of biblical criticism at Belfast College, and he held the post till 1841. Congregationalist Becoming a Congregationalist, Davidson accepted in 1842 the chair of biblical criticism, literature and oriental languages at the Lancashire Independent College, in Manchester. In the summer of 1844 Davidson paid the first of a series of visits to Germany, and made the acquai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hartwell Horne
Thomas Hartwell Horne (20 October 1780 – 27 January 1862) was an English theologian and librarian. Life He was born in London and educated at Christ's Hospital until he was 15 when his father died and he had to work. He then became a clerk to a barrister, and used his spare time to write. Horne was initially affiliated with the Wesleyans but later joined the Church of England. He was admitted to holy orders without the usual preliminaries, because of his published work. In 1833 he obtained a benefice in London and a prebend in St Paul's Cathedral. Horne was a librarian in 1814 at the Surrey Institution, which was dissolved in 1823. He was admitted sizar to St John's College, Cambridge in 1819. In 1824 he joined the staff at the British Museum and was senior assistant in the printed books department there until 1860. He prepared a new system for cataloguing books at the museum but it was never used there.Colin Lee, ‘Currer, Frances Mary Richardson (1785–1861)’, Oxfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cult Of The Supreme Being
Cults are social groups which have unusual, and often extreme, religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals. Extreme devotion to a particular person, object, or goal is another characteristic often ascribed to cults. The term has different, and sometimes divergent or pejorative, definitions both in popular culture and academia and has been an ongoing source of contention among scholars across several fields of study. Beginning in the 1930s, new religious movements became an object of sociological study within the context of the study of religious behavior. Since the 1940s, the Christian countercult movement has opposed some sects and new religious movements, labeling them cults because of their unorthodox beliefs. Since the 1970s, the secular anti-cult movement has opposed certain groups, which they call cults, accusing them of practicing brainwashing. Groups labelled cults are found around the world and range in size from small localized groups to some in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deism
Deism ( or ; derived from the Latin term '' deus'', meaning "god") is the philosophical position and rationalistic theology that generally rejects revelation as a source of divine knowledge and asserts that empirical reason and observation of the natural world are exclusively logical, reliable, and sufficient to determine the existence of a Supreme Being as the creator of the universe. More simply stated, Deism is the belief in the existence of God—often, but not necessarily, an impersonal and incomprehensible God who does not intervene in the universe after creating it, solely based on rational thought without any reliance on revealed religions or religious authority. Deism emphasizes the concept of natural theology—that is, God's existence is revealed through nature. Since the 17th century and during the Age of Enlightenment, especially in 18th-century England, France, and North America, various Western philosophers and theologians formulated a critical reject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reign Of Terror
The Reign of Terror (French: ''La Terreur'', literally "The Terror") was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the French First Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and Capital punishment in France, numerous public executions took place in response to the Federalist revolts, revolutionary fervour, Anti-clericalism, anticlerical sentiment, and accusations of treason by the Committee of Public Safety. While terror was never formally instituted as a legal policy by the Convention, it was more often employed as a concept. Historians disagree when exactly "the Terror" began. Some consider it to have begun in 1793, often giving the date as 5 September or 10 March, when the Revolutionary Tribunal came into existence. Others cite the earlier September Massacres in 1792, or even July 1789 when the first killing of the revolution occurred. Will Durant stated that "strictly, it should be dated from the Law of Suspects, September 17, 1793, to the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; ; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognised as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre fervently campaigned for the voting rights of universal manhood suffrage, all men and their unimpeded admission to the National Guard (France), National Guard. Additionally, he advocated the right to petition, the right to bear arms in self-defence, and the abolition of the Atlantic slave trade. A radical Jacobin leader, Robespierre was elected as a deputy to the National Convention in September 1792, and in July 1793, he was appointed a member of the Committee of Public Safety. Robespierre faced growing disillusionment due in part to the politically motivated violence associated with him. Increasingly, members of the Convention turned against him, and accusations came to a head on 9 Thermidor. Robespierre was arrested and with around 90 othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Jacques-sur-Coudenberg
The Church of St. James on Coudenberg (; ) is a Catholic church on the historic Place Royale/Koningsplein, in the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. It is dedicated to Saint James, one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. The Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical church was designed by the architects Gilles-Barnabé Guimard and Louis Montoyer and built from 1776 to 1787, replacing two neighbouring places of worship. In the 19th century, a dome and bell tower, as well as a coloured fresco, were added to it. The complex was designated a Heritage registers in Belgium, historic monument in 1959. Nowadays, it ranks as royal parish church, and since 1986, as cathedral of the Military Ordinariate of Belgium. This site is served by Brussels-Central railway station, as well as by the Brussels Metro, metro stations Parc metro station (Brussels), Parc/Park (on lines Brussels Metro line 1, 1 and Brussels Metro line 5, 5) and Trône/Troon metro station, Trône/Troon (on lines Brussels Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troyes Cathedral
Troyes Cathedral () is a Catholic church, dedicated to Saint Peter and Saint Paul, located in the town of Troyes in Champagne, France. It is the episcopal seat of the Bishop of Troyes. The cathedral, in the Gothic architectural style, has been a listed since 1862. History Earlier cathedrals According to local church tradition, Christianity was carried to Troyes in the third century by the Bishop of Sens, Savinien, who sent Saint Potentien and Saint Sérotin to the town to establish the first church. The house where they lived is believed to have stood on the same site as the cathedral; and excavations in the 19th century found traces of Gallo-Roman building under the sanctuary. A 5th-century bishop of Troyes, Lupus was credited with saving Troyes from destruction by Huns by leading a delegation of clerics to appeal to Attila, in 451. An enamel of Lupus healing a deaf young woman is displayed in the cathedral; the old cathedral is visible in the background. The first church w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reims Cathedral
Notre-Dame de Reims (; ; meaning "Our Lady of Reims"), known in English as Reims Cathedral, is a Catholic cathedral in the French city of the same name, the seat of the Archdiocese of Reims. The cathedral was dedicated to the Virgin Mary and was the traditional location for the coronation of the kings of France. The cathedral is considered to be one of the most important works of Gothic Architecture. A major tourist destination, it receives about a million visitors annually. It became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1991. The cathedral is thought to have been founded by the bishop Nicasius in the early 5th century. Clovis was baptized a Christian here by Saint Remigius, the bishop of Reims, about a century later. He was the first Frankish king to receive this sacrament. Construction of the present cathedral began in the 13th century and concluded in the 14th century. A prominent example of High Gothic architecture, it was built to replace an earlier church destroyed by fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |