|
Tapinosaurus
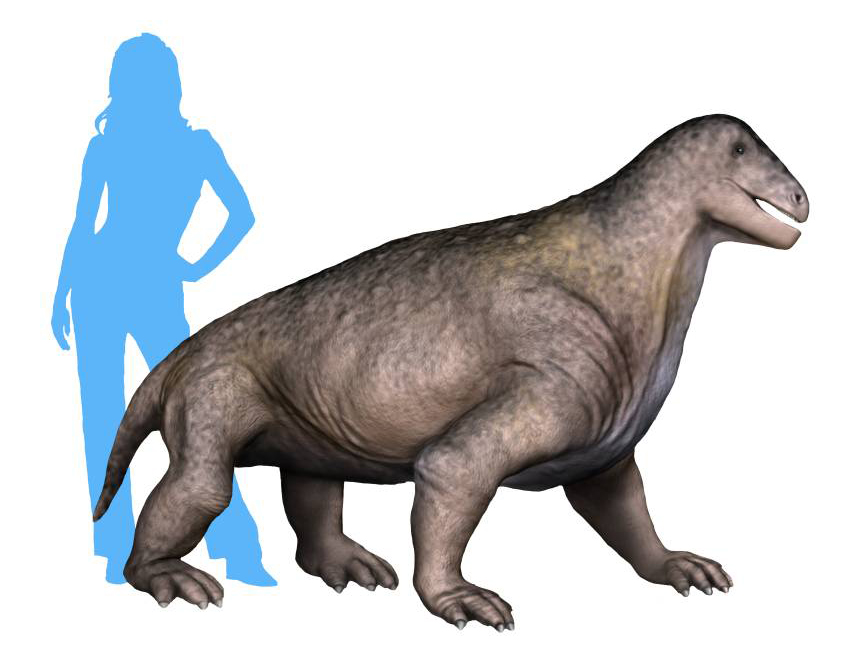
''Tapinocephalus'' ("humble head") is an extinct genus of large herbivorous dinocephalians that lived during the Middle Permian Period. These stocky, barrel-bodied animals were characterised by a massive bony skull roof and short weak snout. It is thought that, like the rest of the members of its family, the animals engaged in head-butting intraspecific behavior, possibly for territory or mates. The fossil remains (skull and postcranial elements) of ''Tapinocephalus'' are known from the Lower, Middle, and Upper part of the ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone ( Capitanian age) of the Lower Beaufort Beds of the South African Karoo. Only the type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ..., ''T. atherstonei'' is now considered valid for this genus. In life, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/ epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Group
The Beaufort Group is the third of the main subdivisions of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. It is composed of a lower Adelaide Subgroup and an upper Tarkastad Subgroup. It follows conformably after the Ecca Group and unconformably underlies the Stormberg Group. Based on stratigraphic position, lithostratigraphic and biostratigraphic correlations, palynological analyses, and other means of geological dating, the Beaufort Group rocks are considered to range between Middle Permian ( Wordian) to Early Triassic (Anisian) in age. Background During the period when sedimentation of the Beaufort Group rocks took place, the Ecca sea had retreated to the northeastern Karoo Basin. All sediment deposition at this time took place in a terrestrial, although in a predominantly fluvial or alluvial environment that was seasonally arid. This environment covered a vast area and deposition was influenced by a retroarc foreland basin. This foreland system was caused by crustal uplift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian Synapsids Of Africa
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Therapsid Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalians
The Tapinocephalia are one of the major groups of dinocephalian therapsids and the major herbivorous group. Tapinocephalia has been found to consist of three clades: Styracocephalidae, Titanosuchidae, and the very successful Tapinocephalidae. Notable tapinocephalians include '' Moschops'', '' Tapinocephalus'', and '' Titanosuchus''. Description Unlike anteosaurs and estemmenosuchids, tapinocephalians are primarily an African group. The estemmenosuchids and pareiasaurs may have occupied this paleo-bovine niche in the north. Only one tapinocephalian, '' Ulemosaurus'', is known from Russia. Earlier tapinocephalians were carnivorous or omnivorous. One such group was Titanosuchidae, which consisted of long-tailed predators that hunted herbivorous therapsids Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gillian King
Gillian may refer to: Places * Gillian Settlement, Arkansas, an unincorporated community People Gillian (variant Jillian) is an English feminine given name, frequently shortened to Gill. It originates as a feminine form of the name Julian, Julio, Julius, and Julien. It is also in use as a surname. Notable people with the name include: First name * Gillian Alexy (born 1986), Australian actress * Gillian Allnutt (born 1949), English poet * Gillian Anderson (born 1968), American actress * Gillian Apps (born 1983), Canadian ice hockey player * Gillian Armstrong (born 1950), Australian film director * Gillian Attard (born 1983), Maltese actress * Gillian Avery (born 1926), British children's novelist and literary historian * Gillian Ayres (born 1930), English painter * Gillian Bailey (born 1955), British academic and actress * Gillian Barge (1940–2003), English actress * Gillian Baverstock (1931–2007), British author * Gillian Baxter, British writer * Gillian Beer (born 1935), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieuwe Dirk Boonstra
Lieuwe Dirk Boonstra (1905 – 1975) was a South African palaeontologist whose work focused on the therapsida, mammal-like reptiles of the Middle ( Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone) and Late Permian, whose fossil remains are common in the South African Karoo. He was the author of a large number of papers on Therapsids and Pareiasaurs, and described and revised a number of species. Work In 1927 Boonstra was appointed Assistant Palaeontologist of the South African Museum and promoted to Palaeontologist in 1931. He remained at the museum until his retirement in 1972. He was the sole curator of the museum's Karoo vertebrate fossil collection for 45 years. Awards He was awarded the Queen Victoria Scholarship by the University of Stellenbosch and received the Havenga prize The Havenga Prize (''Havengaprys'' in Afrikaans) is a prize awarded annually by the ''Suid-Afrikaanse Akademie vir Wetenskap en Kuns'' (South African Academy for Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Therapsids
This list of therapsids is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the Therapsida excluding mammals and purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomina dubia''), or were not formally published ('' nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered therapsids. The list currently contains 510 generic names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synonym, and all other instances are junior synonyms. Senior syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phocosaurus
''Phocosaurus'' is an extinct genus of tapinocephalian therapsid. See also * List of synapsids These lists of synapsids collectively include every genus that has ever been included in the clade Synapsida- the mammals and their evolutionary precursors. The lists includes accepted genera along with those now considered invalid, doubtful (''nom ... References The main groups of non-mammalian synapsids at Mikko's Phylogeny Archive Dinocephalians Synapsids {{paleo-therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moschops
''Moschops'' (Greek for "calf face") is an extinct genus of therapsids that lived in the Guadalupian epoch, around 265–260 million years ago. They were heavily built plant eaters, and they may have lived partly in water, as hippopotamuses do. They had short, thick heads and might have competed by head-butting each other. Their elbow joints allowed them to walk with a more mammal-like gait rather than crawling. Their remains were found in the Karoo region of South Africa, belonging to the ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone. Therapsids, such as ''Moschops'', are synapsids, the dominant land animals in the Permian period, which ended 252 million years ago. Description ''Moschops'' were heavy set dinocephalian synapsids, measuring in length, and weighing on average and in maximum body mass. They had small heads with broad orbits and heavily-built short necks. Like other members of Tapinocephalidae, the skull had a tiny opening for the pineal organ. The occiput was broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalus
''Tapinocephalus'' ("humble head") is an extinct genus of large herbivorous dinocephalians that lived during the Middle Permian The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Pale ... Period (geology), Period. These stocky, barrel-bodied animals were characterised by a massive bony skull roof and short weak snout. It is thought that, like the rest of the members of its family (biology), family, the animals engaged in head-butting agonistic behavior, intraspecific behavior, possibly for territory (animal), territory or mates. The fossil remains (skull and postcrania, postcranial elements) of ''Tapinocephalus'' are known from the Lower, Middle, and Upper part of the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone ( Capitanian, Capitanian age) of the Beaufort Group, Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(2).jpg)