|
Tall Chief
Tall Chief (ca. 1840–1918) was a hereditary chief of the Quapaw Tribe and a peyote roadman. He served in this position after his father, Lame Chief, died in 1874, until his own death in 1918 at around 78 years old. Tall Chief was the last individual to be selected in the traditional manner from a hereditary chief line among the Quapaw people. Tall Chief also facilitated the introduction of the Peyote Religion among the Quapaw and Osage people. Early life Tall Chief was born around 1840 in Indian Territory along the Neosho River in what is now Kansas at a Quapaw village referred to as Hu-cha-pa Tah-wha. His father was a hereditary Chief named Ka-hi-ka te-dah, or Lame Chief, and his mother was named Mi-ska no-zhe, or White Sun Standing; both of Tall Chief's parents were Quapaw. Tall Chief's given name was Wa-zhi Hunka which in the Quapaw language refers to an eagle in Quapaw tradition which led the people to the earth. Tall Chief would translate this name as "Sacred Angel Bird" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Territory
Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who held aboriginal title, original Indian title to their land as an independent nation. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the Indian Territory in the American Civil War, American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of Cultural assimilation of Native Americans#Americanization and assimilation (1857–1920), assimilation. Indian Territory later came to refer to an Territories of the United States#Formerly unorganized territories, unorganized territory whose general borders were initially set by the Nonintercourse Act of 1834, and was the successor to the remainder of the Missouri Territory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peyote Roadman
The Native American Church (NAC), also known as Peyotism and Peyote Religion, is a syncretic Native American religion that teaches a combination of traditional Native American beliefs and elements of Christianity, especially pertaining to the Ten Commandments, with sacramental use of the entheogen peyote. The religion originated in the Oklahoma Territory (1890–1907) in the late nineteenth century, after peyote was introduced to the southern Great Plains from Mexico. Today, it is the most widespread indigenous religion among Native Americans in the United States (except Alaska Natives and Native Hawaiians), Canada (specifically First Nations people in Saskatchewan and Alberta), and Mexico, with an estimated 300,000 adherents. History Historically, many denominations of mainstream Christianity attempted to convert Native Americans to Christianity in the Western Hemisphere. These efforts were partially successful, because the religious practices, including those of the Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quapaw, Oklahoma
Quapaw, officially the Town of Quapaw, is a town in Ottawa County, Oklahoma, United States, which serves as the capital of the Quapaw Nation. Located about northeast of Miami, it is part of the Joplin, Missouri metropolitan area. Incorporated in 1917,Mickey Johnson, ''Quapaw,'' Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture. Accessed March 15, 2015 Quapaw's population was 811 in 2020. History In 1891, Kansas farmer Isaac Bingham moved his family south into Ottawa County, then part of land assigned to the Quapaw Nation. It became part of the state of Oklahoma in 1907 after admission. The family founded a community and opened several businesses. Q ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiatook, Oklahoma
Skiatook (Skī·ǎ·tōōk ''or'' Skī·ǎ·tǒǒk versus Skī·tōōk ''or'' Skī·tǒǒk) is a city in Osage County, Oklahoma, Osage and Tulsa County, Oklahoma, Tulsa counties in the U.S. state of Oklahoma located in the northeastern part of the state, approximately 20 miles north and west of Tulsa, Oklahoma, Tulsa. Due to its location on the border between Osage County, Oklahoma, Osage County and Tulsa County, Oklahoma, Tulsa County, Skiatook has been referred to as "the Gateway to the Osage." The town includes the state highway junction of Oklahoma State Highway 11 and Oklahoma State Highway 20. The population was 8,450 at the 2020 census, an increase of 14.24 percent over the figure of 7,397 recorded in 2010 United States census, 2010. History 19th century Battle of Chustenahlah The Battle of Chustenahlah was fought just west of Skiatook, on December 26, 1861, during the American Civil War. The battle began when Confederate States of America, Confederate Col. James M. McIn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Chief
A tribal chief, chieftain, or headman is a leader of a tribe, tribal society or chiefdom. Tribal societies There is no definition for "tribe". The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia. Tribal societies are sometimes categorized as an intermediate stage between the band society of the Paleolithic stage and civilization with centralized, super-regional government based in Cities of the Ancient Near East, cities. Anthropologist Elman Service distinguishes two stages of tribal societies: simple societies organized by limited instances of social rank and prestige, and more stratified society, stratified societies led by chieftains or tribal kings (chiefdoms). Stratified tribal societies led by tribal kings are thought to have flourished from the Neolithic stage into the Iron Age, albeit in competition with Urban area, urban civilisations and empires beginning in the Bronze Age. In the case of tribal societies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
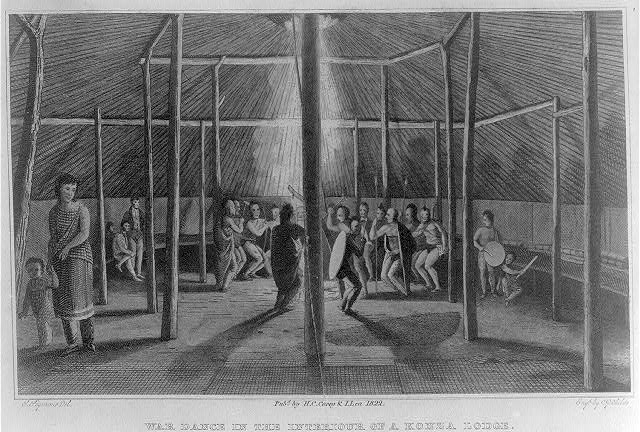
Quapaw
The Quapaw ( , Quapaw language, Quapaw: ) or Arkansas, officially the Quapaw Nation, is a List of federally recognized tribes in the United States, U.S. federally recognized tribe comprising about 6,000 citizens. Also known as the Ogáxpa or “Downstream” people, their ancestral homelands are traced from what is now the Ohio River, west to the Mississippi River to present-day St. Louis, south across present-day Arkansas and eastern and southern Oklahoma. The government Trail of Tears, forcibly removed them from Arkansas Territory in 1834. The Oklahoma Tribal Statistical Area, tribal Capital city, capital is Quapaw, Oklahoma, Quapaw, Oklahoma. Etymology The Quapaw broke from the other Dhegiha tribes and migrated down the Mississippi River into present-day Arkansas many generations before European contact. After that, the tribe began to refer to themselves Ogáxpa, which means the “Downstream” people." This was the name of their primary village or tribal band. Historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Church
The Native American Church (NAC), also known as Peyotism and Peyote Religion, is a Syncretism, syncretic Native American religion that teaches a combination of traditional Native Americans in the United States, Native American beliefs and elements of Christianity, especially pertaining to the Ten Commandments, with sacramental use of the entheogen peyote. The religion originated in the Oklahoma Territory (1890–1907) in the late nineteenth century, after peyote was introduced to the southern Great Plains from Mexico. Today, it is the most widespread indigenous religion among Native Americans in the United States (except Alaska Natives and Native Hawaiians), Canada (specifically First Nations in Canada, First Nations people in First Nations in Saskatchewan, Saskatchewan and First Nations in Alberta, Alberta), and Mexico, with an estimated 300,000 adherents. History Historically, many denominations of mainstream Christianity attempted to convert Native Americans to Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osage Nation
The Osage Nation ( ) () is a Midwestern Native American nation of the Great Plains. The tribe began in the Ohio and Mississippi river valleys around 1620 A.D along with other groups of its language family, then migrated west in the 17th century due to Iroquois incursions. The term "Osage" is a French version of the tribe's name, which can be roughly translated as "calm water". The Osage people refer to themselves in their Dhegihan Siouan language as (). By the early 19th century, the Osage had become the dominant power in the region, feared by neighboring tribes. The tribe controlled the area between the Missouri and Red rivers, the Ozarks to the east and the foothills of the Wichita Mountains to the south. They depended on nomadic buffalo hunting and agriculture. The 19th-century painter George Catlin described the Osage as "the tallest race of men in North America, either red or white skins; there being ... many of them six and a half, and others taller than seven f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neosho River
The Neosho River is a tributary of the Arkansas River in eastern Kansas and northeastern Oklahoma in the United States. Its tributaries also drain portions of Missouri and Arkansas. The river is about long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed May 31, 2011 Via the Arkansas, it is part of the Mississippi River watershed. Its name is an Osage word meaning "clear water." The lower section is also known as the Grand River. Course The Neosho's headwaters are in Morris County, Kansas, and it flows southeast through Kansas. In Ottawa County, Oklahoma, the river turns south-southwest for the remainder of its course through Oklahoma. It meets the Arkansas River near the city of Muskogee, about a mile downstream of the confluence of the Arkansas River and the Verdigris River. The area of convergence of the three rivers Arkansas, Verdigris and Neosho is called "Three Forks." In Oklahoma the Neosho ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named after the Kansas River, in turn named after the Kaw people, Kansa people. Its List of capitals in the United States, capital is Topeka, Kansas, Topeka, and its List of cities in Kansas, most populous city is Wichita, Kansas, Wichita; however, the largest urban area is the bi-state Kansas City metropolitan area split between Kansas and Missouri. For thousands of years, what is now Kansas was home to numerous and diverse Plains Indians, Indigenous tribes. The first settlement of non-indigenous people in Kansas occurred in 1827 at Fort Leavenworth. The pace of settlement accelerated in the 1850s, in the midst of political wars over the Slavery in the United States, slavery debate. When it was officially opened to settlement by the U.S. governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
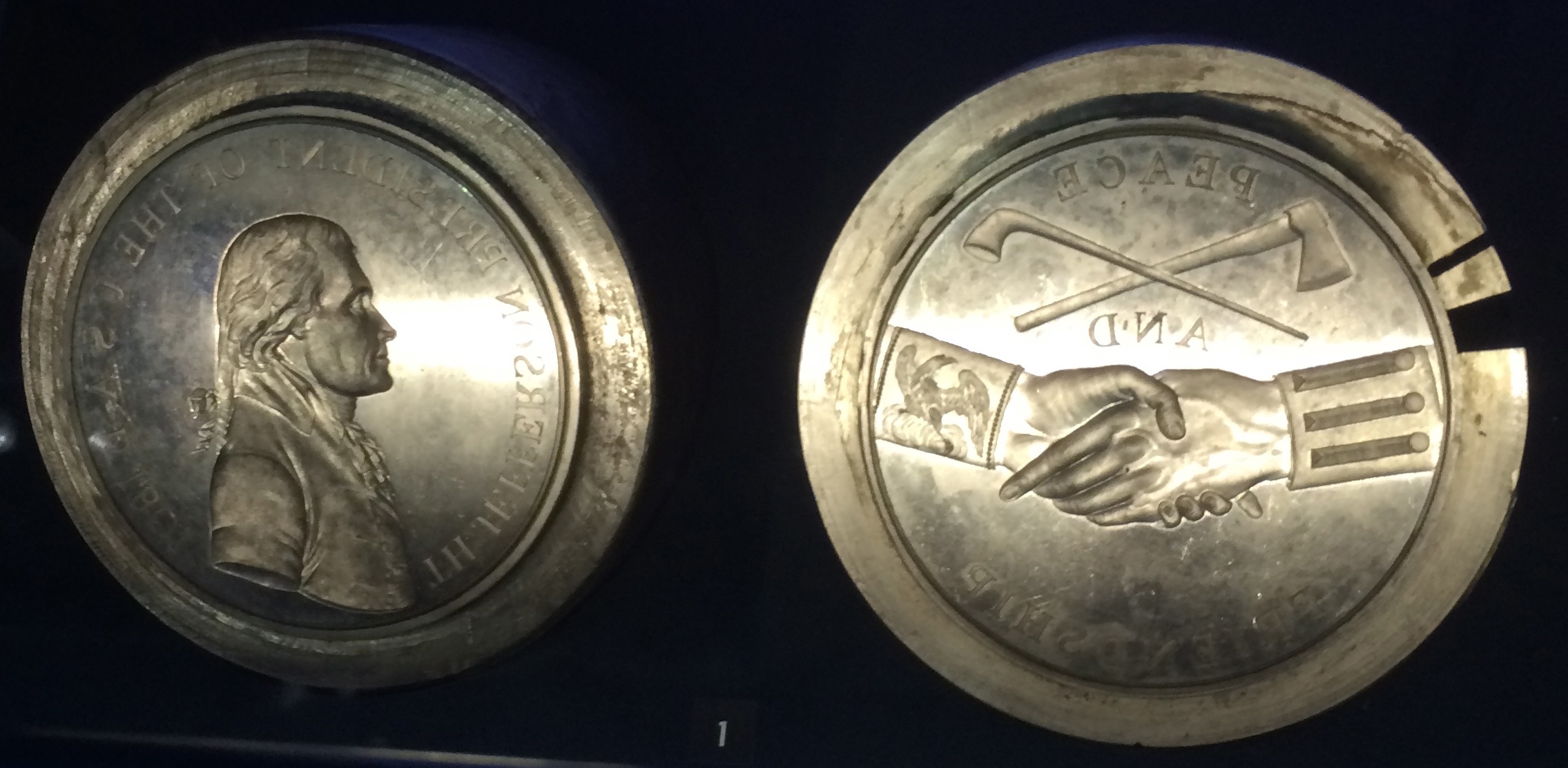
Indian Peace Medal
Indian peace medals refer to ovular or circular medals awarded to tribal leaders throughout colonial America and early United States history, primarily made of silver or brass and ranging in diameter from about one to six inches.Reilly, Kent (2011). "Displaying the Source of the Sacred: Shell Gorgets, Peace Medals, and the Accessing of Supernatural Power." Ed. Robert Pickering. ''Peace Medals: Negotiating Power in Early America''. Tulsa, OK: Gilcrease Museum. p. 9. Medals were often perforated and worn suspended around the neck of the recipient. Controversy remains surrounding the use and impact of peace medals in furthering diplomatic relationships between Native Americans and the federal government. Many Indian peace medals today are archived in museums, libraries, and cultural centers. Early peace medals During the colonization of America, European nations issued the earliest peace medals to build alliances and negotiate with tribes, dating as far back as the seventeenth cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wilson (Caddo)
"John Wilson the Revealer of Peyote" (c.1845–1901) was a Caddo medicine man who introduced the Peyote plant into a religion, became a major leader in the Ghost Dance, and introduced a new peyote ceremony with teachings of Christ. John Wilson's Caddo name was Nishkû'ntu, meaning "Moon Head." Though he was of half-Lenape descent, quarter-blood French American, French, and quarter-blood Caddo, John Wilson spoke only the Caddo language and identified only as a Caddo. He is believed to have been born in 1845, when his band of Caddo were still living in Texas. They were driven into Indian Territory in 1859. Wilson, being interested in religion and only known as a medicine man, sought out a path to be a peyote roadman in 1880.Stewart 86 As the Ghost Dance ceremonies regained popularity in Oklahoma, he became one of its most active leaders in the Indian Territory. During a two-week period, Wilson consumed peyote for spiritual reasons and said he was shown essential astronomical sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |