|
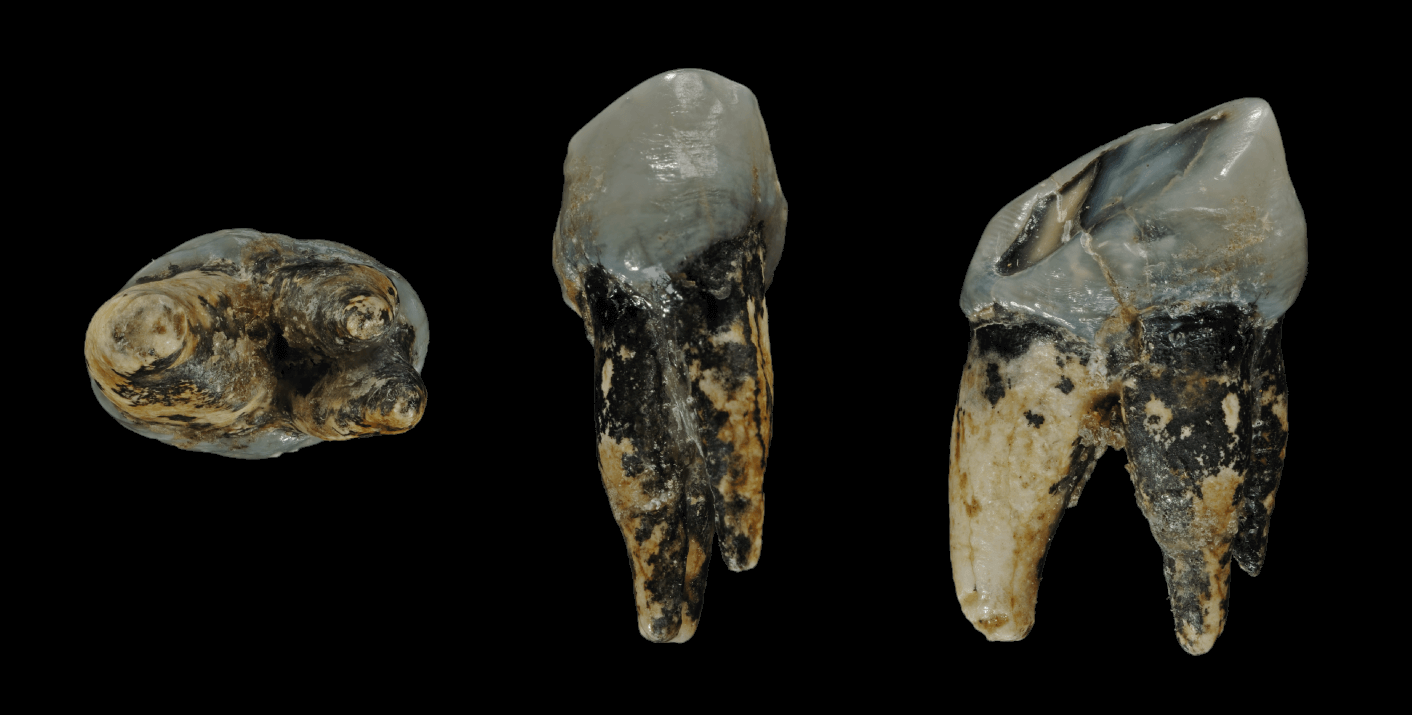
Talgai Skull
The Talgai Skull is a human fossil found on the Talgai Station, near Allora, Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. It has been dated indirectly, based on the radiocarbon date of a carbonate nodule found in stratigraphic proximity, at 13,500 years old. History The Talgai Skull was discovered in 1886 on Talgai Homestead, as the first fossil evidence of early human occupation in the area. It was found by fencing contractor, William Naish. It had been embedded in the wall of Dalrymple Creek, which had been scoured out by heavy rain. In 1896 the skull was sent to Sydney where it was examined by the trustees of the Australian Museum. The museum was interested in purchasing the fossil but could not agree on an acceptable price. Eventually the skull was returned to its owner. It remained at the homestead until 1914 when Professor Edgeworth David, Professor of Archaeology at Sydney University visited Talgai and presented a theory that the skull was 20,000 years old and provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Fossil
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of Hominini, hominin fossils and Skeleton, remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the Chimpanzee–human last common ancestor, human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missing Link (human Evolution)
"Missing link" is a non-scientific term for a hypothetical or recently-discovered transitional fossil. It is often used in popular science and in the media for any new transitional form. The term originated to describe the hypothetical intermediate form in the evolutionary series of anthropoid ancestors to anatomically modern humans ( hominization). The term was influenced by the pre-Darwinian evolutionary theory of the Great Chain of Being and the now-outdated notion (orthogenesis) that simple organisms are more primitive than complex organisms. The term "missing link" has been supported by geneticists since evolutionary trees only have data at the tips and nodes of their branches; the rest is inference and not evidence of fossils. However, it has fallen out of favor with anthropologists because it implies the evolutionary process is a linear phenomenon and that forms originate consecutively in a chain. Instead, last common ancestor is preferred since this does not have the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Talgai Skull
''The Talgai Skull: An Investigation Into the Origin of the Australian Aborigines'' is a 1968 Australian film about the Talgai Skull. It shared the 1968 AACTA Awards, Australian Film Institute Award for Best Documentary and won the Logie Awards of 1969, 1969 Logie Award for Best Documentary. References External links ''The Talgai Skull''at IMDb ''The Talgai Skull''at the National Library of Australia ''The Talgai Skull'' at the Melbourne International Film Festival 1968 documentary films 1968 films Documentary films about Aboriginal Australians Australian documentary films 1960s English-language films {{Australia-documentary-film-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Broadcasting Commission
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) is the national broadcaster of Australia. It is principally funded by direct grants from the Australian Government and is administered by a government-appointed board. The ABC is a publicly-owned body that is politically independent and fully accountable, with its charter enshrined in legislation, the ''Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983''. ABC Commercial, a profit-making division of the corporation, also helps to generate funding for content provision. The ABC was established as the Australian Broadcasting Commission on 1 July 1932 by an act of federal parliament. It effectively replaced the Australian Broadcasting Company, a private company established in 1924 to provide programming for A-class radio stations. The ABC was given statutory powers that reinforced its independence from the government and enhanced its news-gathering role. Modelled after the British Broadcasting Corporation ( BBC), which is funded by a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney Museum
The Museum of Sydney is a historical collection and exhibit, built on the ruins of the house of New South Wales' first Governor, Arthur Phillip, on the present-day corner of Phillip and Bridge Street, Sydney. Description The original house, which was Australia's first Government House, was built in 1788 and later abandoned. The foundations were exposed by archaeologists in 1983. The new museum building on the site was designed by Denton Corker Marshall architects. The museum was built as part of the Governor Phillip Tower development and is managed by the Historic Houses Trust of New South Wales. The Museum of Sydney explores colonial and contemporary Sydney through objects, pictures, and new digital media techniques. Panoramic views of Sydney— from 1788 until today— stretch across walls and video screens. Sydney's convict era is explored in a giant showcase of goods and chattels recovered from more than 25 archaeological digs. Origins of the name When it was commissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Museum
The Queensland Museum is the state museum of Queensland, dedicated to natural history, cultural heritage, science and human achievement. The museum currently operates from its headquarters and general museum in South Brisbane with specialist museums located in North Ipswich in Ipswich, East Toowoomba in Toowoomba, and in Townsville City in Townsville. The museum is funded by the Queensland Government. History The Queensland Museum was founded by the Queensland Philosophical Society on 20 January 1862,''"A Time for a Museum — The History of the Queensland Museum — 1862 to 1986"'', — Patricia Mather, published by the Queensland Museum, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, 2001 (originally published as ''"Volume 24"'' of ''"The Memoirs of the Queensland Museum"'') one of the principal founders being Charles Coxen, and had several temporary homes in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. The temporary homes included: The Old Windmill (1862–1869), Parliament House (1869� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSIRO
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research. CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO maintains more than 50 sites across Australia and in France, Chile and the United States, employing about 5,500 people. Federally funded scientific research began in Australia years ago. The Advisory Council of Science and Industry was established in 1916 but was hampered by insufficient available finance. In 1926 the research effort was reinvigorated by establishment of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which strengthened national science leadership and increased research funding. CSIR grew rapidly and achieved significant early successes. In 1949, further legislated changes included renaming the organisation as CSIRO. Notable developments by CSIRO have included the invention of atomic absorption spectroscopy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piltdown Man
The Piltdown Man was a paleoanthropological fraud in which bone fragments were presented as the fossilised remains of a previously unknown early human. Although there were doubts about its authenticity virtually from the beginning, the remains were still broadly accepted for many years, and the falsity of the hoax was only definitively demonstrated in 1953. An extensive scientific review in 2016 established that amateur archaeologist Charles Dawson was responsible for the fraudulent evidence. In 1912, Charles Dawson claimed that he had discovered the " missing link" between ape and man. In February 1912, Dawson contacted Arthur Smith Woodward, Keeper of Geology at the Natural History Museum, stating he had found a section of a human-like skull in Pleistocene gravel beds near Piltdown, East Sussex. That summer, Dawson and Smith Woodward purportedly discovered more bones and artifacts at the site, which they connected to the same individual. These finds included a jawbone, mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney University
The University of Sydney (USYD), also known as Sydney University, or informally Sydney Uni, is a public research university located in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in Australia and is one of the country's six sandstone universities. The university comprises eight academic faculties and university schools, through which it offers bachelor, master and doctoral degrees. The university consistently ranks highly both nationally and internationally. QS World University Rankings ranked the university top 40 in the world. The university is also ranked first in Australia and fourth in the world for QS graduate employability. It is one of the first universities in the world to admit students solely on academic merit, and opened their doors to women on the same basis as men. Five Nobel and two Crafoord laureates have been affiliated with the university as graduates and faculty. The university has educated eight Australian prime ministers, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allora, Queensland
Allora is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Allora had a population of 1,223 people. Geography Allora is on the Darling Downs in south-eastern Queensland, Australia, by road south-west of the state capital, Brisbane. The town is located on the New England Highway between Warwick and Toowoomba. History Giabal (also known as Paiamba, Gomaingguru) is an Australian Aboriginal language. The Giabal language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Toowoomba Regional Council, particularly Toowoomba south to Allora and west to Millmerran. The region surrounding this small farming community was first explored by Europeans in the 1840s. In 1854 the first Presbyterian services were held in Allora. The town was surveyed in 1859. Its name is believed to derive from an Aboriginal word ''"gnarrallah"'', meaning waterhole or swampy place. Following European settlement, the hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgeworth David
Sir Tannatt William Edgeworth David (28 January 1858 – 28 August 1934) was a Welsh Australian geologist and Antarctic explorer. A household name in his lifetime, David's most significant achievements were discovering the major Hunter Valley coalfield in New South Wales and leading the first expedition to reach the South Magnetic Pole. He also served with distinction in World War I. Early life David was born on 28 January 1858, in St. Fagans near Cardiff, Wales, the eldest son of the Rev. William David, a fellow of Jesus College, Oxford, a classical scholar and naturalist and his wife Margaret Harriette (née Thomson). His mother's cousin, William A. E. Ussher of the Geological Survey, first interested David in what was to be his life work. At the age of 12, David went to Magdalen College School, Oxford in 1870. In 1876 he gained a classical scholarship to New College, Oxford. While there he was lectured by the famous John Ruskin and William Spooner. In 1878 he s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Museum
The Australian Museum is a heritage-listed museum at 1 William Street, Sydney central business district, New South Wales, Australia. It is the oldest museum in Australia,Design 5, 2016, p.1 and the fifth oldest natural history museum in the world, with an international reputation in the fields of natural history and anthropology. It was first conceived and developed along the contemporary European model of an encyclopedic warehouse of cultural and natural history and features collections of vertebrate and invertebrate zoology, as well as mineralogy, palaeontology and anthropology. Apart from exhibitions, the museum is also involved in Indigenous studies research and community programs. In the museum's early years, collecting was its main priority, and specimens were commonly traded with British and other European institutions. The scientific stature of the museum was established under the curatorship of Gerard Krefft, himself a published scientist. The museum is located a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |