|
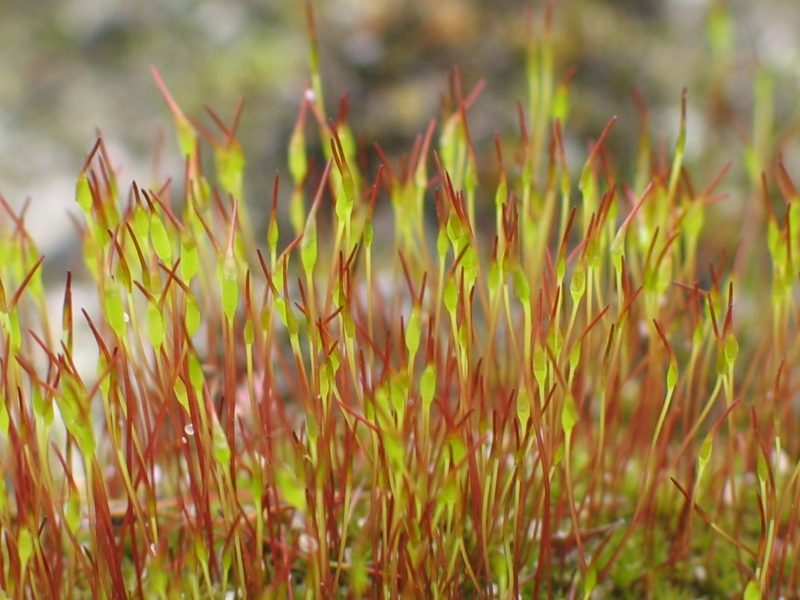
Takakia Ceratophylla
''Takakia ceratophylla'' is one of the two species of toothless mosses in the genus ''Takakia'', under the Takakiaceae family. This species was first described by William Mitten in 1861. ''Takakia ceratophylla'' is vulnerable and threatened by habitat loss due to human activities. Description ''Takakia ceratophylla'' was first described as a liverwort under the genus '' Lepidozia'' for nearly a century. Later rediscovered in Japan and claimed to be sharing traits from both the liverworts and mosses based on genetic sequences and morphological characters. Some features that are similar to mosses include the presence of columella, tapered foot, and calyptra; the elongation and twisting of the seta; and the absence of elaters. Whereas structures such as rhizoids, stomata in sporangium, operculum and peristome teeth are not differentiated in this species. Geographic range and habitat ''Takakia ceratophylla'' is terrestrial and can be found in China, India, Nepal, and the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takakia
''Takakia'' is a genus of two species of mosses known from western North America and central and eastern Asia. The genus is placed as a separate family, order and class among the mosses. It has had a history of uncertain placement, but the discovery of sporophytes clearly of the moss-type firmly supports placement with the mosses. Discovery ''Takakia'' was discovered in the Himalayas and described by William Mitten in 1861. It was originally described simply as a new liverwort species ('' Lepidozia ceratophylla'')Renzaglia, K. S., K. D. McFarland, & D. K. Smith. 1997. Anatomy and ultrastructure of the sporophyte of ''Takakia ceratophylla'' (Bryophyta). ''American Journal of Botany'' 84(10): 1337–1350. within an existing genus, and it was thus long overlooked. The discovery of similar odd plants in the mid-20th century by Dr. Noriwo Takaki (1915–2006) in Japan sparked more interest. The many unusual features of these plants led to the establishment in 1958 of the speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takakiopsida
''Takakia'' is a genus of two species of mosses known from western North America and central and eastern Asia. The genus is placed as a separate family, order and class among the mosses. It has had a history of uncertain placement, but the discovery of sporophytes clearly of the moss-type firmly supports placement with the mosses. Discovery ''Takakia'' was discovered in the Himalayas and described by William Mitten in 1861. It was originally described simply as a new liverwort species ('' Lepidozia ceratophylla'')Renzaglia, K. S., K. D. McFarland, & D. K. Smith. 1997. Anatomy and ultrastructure of the sporophyte of ''Takakia ceratophylla'' (Bryophyta). ''American Journal of Botany'' 84(10): 1337–1350. within an existing genus, and it was thus long overlooked. The discovery of similar odd plants in the mid-20th century by Dr. Noriwo Takaki (1915–2006) in Japan sparked more interest. The many unusual features of these plants led to the establishment in 1958 of the speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopy
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitherium
''Amphitherium'' is an extinct genus of stem cladotherian mammal that lived during the Middle Jurassic of England. It was one of the first Mesozoic mammals ever described. A recent phylogenetic study found it to be the sister taxon of ''Palaeoxonodon''. It is found in the Forest Marble Formation and the Taynton Limestone Formation. Etymology ''Amphitherium'' comes from the Greek ''amphi'' meaning 'on both sides', and ''therion'' meaning 'wild beast'. This was in reference to de Blainville's incorrect belief that the original fossil jaw of this animal was not a mammal, but something in between mammals and reptiles. History The first jaws of mammals from the Mesozoic - including ''Amphitherium'' - were found in the Stonesfield Slate, part of the Taynton Limestone Formation near Stonesfield in England.Rudwick, M.J.S. 2008Worlds Before Adam/ref> These were bought by a student of the British paleontologist William Buckland. Although he thought the jaws were mammalian, the anatomis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroid (botany)
A hydroid is a type of vascular cell that occurs in certain bryophytes. In some mosses such as members of the Polytrichaceae family, hydroids form the innermost layer of cells in the stem. At maturity they are long, colourless, thin walled cells of small diameter, containing water but no living protoplasm. Collectively, hydroids function as a conducting tissue, known as the hydrome, transporting water and minerals drawn from the soil. They are surrounded by bundles of living cells known as leptoids which carry sugars and other nutrients in solution. The hydroids are analogous to the tracheids of vascular plants but there is no lignin present in the cell walls to provide structural support. Hydroids have been found in some fossilised plants from the Rhynie chert, including ''Aglaophyton'', where they were initially mistaken for xylem tracheids. See also * Leptoid, a related sucrose-transporting vessel analogous to the phloem Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
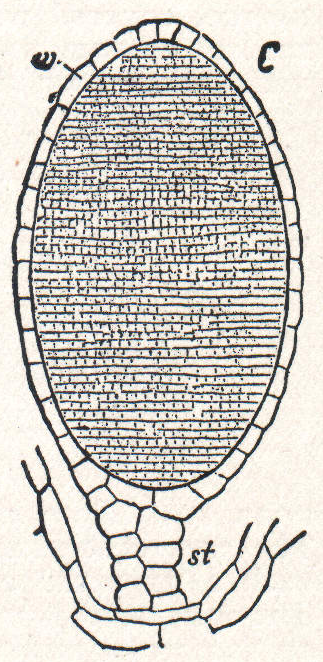
Sporophyte Of Takakia Ceratophylla
A sporophyte () is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual spores. This stage alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. Life cycle The sporophyte develops from the zygote produced when a haploid egg cell is fertilized by a haploid sperm and each sporophyte cell therefore has a double set of chromosomes, one set from each parent. All land plants, and most multicellular algae, have life cycles in which a multicellular diploid sporophyte phase alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. In the seed plants, the largest groups of which are the gymnosperms and flowering plants (angiosperms), the sporophyte phase is more prominent than the gametophyte, and is the familiar green plant with its roots, stem, leaves and cones or flowers. In flowering plants the gametophytes are very reduced in size, and are represented by the germinated pollen and the embryo sac. The sporophyte produces spores (hence t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non-homologous, differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition. Human anatomy In human anatomy, "cuticle" can refer to several structures, but it is used in general parlance, and even by medical professionals, to refer to the thickened layer of skin surrounding fingernails and toenails (the eponychium), and to refer to the superficial layer of overlapping cells covering the hair shaft ( cuticula pili), consisting of dead cells, that locks the hair into its follicle. It can also be used as a synonym for the epidermis, the outer layer of skin. Cuticle of invertebrates In zoology, the invertebrate cuticle or cuticula is a multi-layered structure outside the epidermis of many invertebrates, notably roundworms and arthropods, in which it forms an exoskelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archegonium
An archegonium (pl: archegonia), from the ancient Greek ''ἀρχή'' ("beginning") and ''γόνος'' ("offspring"), is a multicellular structure or organ of the gametophyte phase of certain plants, producing and containing the ovum or female gamete. The corresponding male organ is called the antheridium. The archegonium has a long neck canal or venter and a swollen base. Archegonia are typically located on the surface of the plant thallus, although in the hornworts they are embedded. Bryophytes In bryophytes and other cryptogams sperm reach the archegonium by swimming in water films, whereas in Pinophyta and Angiosperms the pollen are delivered by wind or animal vectors and the sperm are delivered by means of a pollen tube. In the moss '' Physcomitrella patens'', archegonia are not embedded but are located on top of the leafy gametophore (s. Figure). The Polycomb protein FIE is expressed in the unfertilized egg cell (right) as the blue colour after GUS staining reveals. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antheridium
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some fungi, for example ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to pollen grains and in most of these the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cells and spermatogenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and bacteria. Many eukaryotic organisms including plants, animals, and fungi can also reproduce asexually. In vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Komodo dragons and some monitor lizards can also reproduce asexually. While all prokaryotes reproduce without the formation and fusion of gametes, mechanisms for lateral g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |