|
Tajiks In China
In China, the terms "Tajik" and "Tajik nationality" () encompass three distinct ethnic subgroups: the Sarikoli language, Sarikolis, Wakhi people, Wakhis, and Tor Tajiks. The Sarikolis and Wakhis are ethnic Pamiris who live in the Pamir Mountains of Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County, in Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang. The Tor Tajiks are Tajiks, ethnic Tajiks who reside in the village of Tor, Xinjiang, Tor, also in Kashgar Prefecture. The Tajik nationality is one of List of ethnic groups in China, 56 nationalities or ethnicities officially recognized by the Chinese government. Name Despite their name, the majority of Tajiks in China are not ethnic Tajiks but ethnic Pamiris, a different Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group who speak the Eastern Iranian Pamiri languages. Early 20th-century CE travelers to the region referred to the group as "Mountain Tajiks", or by the Turkic exonym "Ghalcha". Sarikoli language, Sarikoli- and Wakhi language, Wakhi-speaking Tajiks were also referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashkurgan
Tashkurgan, historically known as Sarikol and Shitoucheng, is a town in the far west of China, close to the country's border with Tajikistan. It is seat of Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County, in the autonomous region of Xinjiang. Tajiksethnic Pamiris who live in the Pamir Mountains of Xinjiangmake up a little over half of Tashkurgan's population. Tashkurgan was a significant stop on the Silk Road, with roads leading to major centers of trade such as Kashgar. It also served as the capital of a number of ancient and pre-modern kingdoms. Etymology The town is named after a stone fortress to its north; Tashkurgan accordingly means "stone fortress" in the Turkic languages. The official English spelling (per the Chinese government) of the name is ''Taxkorgan'', while ''Tashkorgan'' appears occasionally in literature. The historical Chinese name for the town was ''Shitoucheng'' (), which literally means "stone city" in the context of a fortified city. The town was also historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashgar Prefecture
Kashgar, also known as Kashi, is a prefecture located in southwestern Xinjiang, China, located in the Tarim Basin region (roughly the southern half of Xinjiang). It has an area of and 4,496,377 inhabitants at the 2020 census with a population density of 35.5 inhabitants/km2. The capital of the prefecture is the city of Kashgar which has a population 506,640. Kashgar Prefecture borders the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan, Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan, Gilgit-Baltistan of Pakistan and Ladakh of India in the far south. History Kashgar, formerly referred to as Shule, served as the capital of the Shule Kingdom in the 2nd century B.C., inhabited by Indo-European tribes speaking Ancient Tocharian languages in the Tarim Basin. The earliest references to Shule emerged in the literature of the Han Dynasty. Shule served as the pivotal junction of the Silk Road in the northern Tarim Basin, facilitating access to the , Dayuan, and Kangju in Central Asia, and act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghurs
The Uyghurs,. alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia and East Asia. The Uyghurs are recognized as the titular nationality of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwest China. They are one of Ethnic minorities in China, China's 55 officially recognized ethnic minorities. The Uyghurs have traditionally inhabited a series of Oasis, oases scattered across the Taklamakan Desert within the Tarim Basin. These oases have historically existed as independent states or were controlled by many civilizations including History of China, China, the Mongol Empire, Mongols, the Tibetan Empire, Tibetans, and various Turkic polities. The Uyghurs gradually started to become Islamized in the 10th century, and most Uyghurs identified as Muslims by the 16th century. Islam has since played an important role in Uyghur culture and identity. An estimated 80% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Settlement Of The Tarim Basin
Turkic peoples began settling in the Tarim Basin in the 7th century. The area was later settled by the Turkic Uyghurs, who founded the Qocho Kingdom there in the 9th century. The historical area of what is modern-day Xinjiang in China consisted of the distinct areas of the Tarim Basin (also known as Altishahr) and Dzungaria. The area was first populated by the Tocharians and the Saka, who were Indo-Europeans and practiced Buddhism. The Tocharian and Saka peoples came under Xiongnu and then Chinese rule during the Han dynasty as the Protectorate of the Western Regions due to wars between the Han dynasty and the Xiongnu. The First Turkic Khaganate conquered this region in 560, and in 603, after a series of civil wars, the First Turkic Khaganate was separated into the Eastern Turkic Khaganate and the Western Turkic Khaganate, with Xinjiang coming under the latter. The region then became part of the Tang dynasty as the Protectorate General to Pacify the West after the Tang camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkification
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization () describes a shift whereby populations or places receive or adopt Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly applied to mean specifically Turkish rather than merely Turkic, meaning that it refers more frequently to the Ottoman Empire's policies or the Turkish nationalist policies of the Republic of Turkey toward ethnic minorities in Turkey. As the Turkic states developed and grew, there were many instances of this cultural shift. The earliest instance of Turkification took place in Central Asia, when by the 6th century AD migration of Turkic tribes from Inner Asia caused a language shift among the Iranian peoples of the area. By the 8th century AD, the Turkification of Kashgar was completed by Qarluq Turks, who also Islamization, Islamized the population. The Turkification of Anatolia occurred in the time of the Seljuk Empire and Sultanate of Rum, when Anatolia h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Iranian People
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European language family. The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe; from the Danubian Plains in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the steppes and the wooded steppes and even the semi-deserts f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Languages
The Scythian languages are a group of Eastern Iranic languages of the classical and late antique period (the Middle Iranic period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descendants. The dominant ethnic groups among the Scythian-speakers were nomadic pastoralists of Central Asia and the Pontic–Caspian steppe. Fragments of their speech known from inscriptions and words quoted in ancient authors as well as analysis of their names indicate that it was an Indo-European language, more specifically from the Iranic group of Indo-Iranic languages. Most of the Scythian languages eventually became extinct, except for modern Ossetian (which descends from the Alanic dialect of Scytho-Sarmatian), Wakhi (which descends from the Khotanese and Tumshuqese forms of Scytho-Khotanese), and Yaghnobi (which descends from Sogdian). Alexander Lubotsky summarizes the known linguistic landscape as follows: Classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
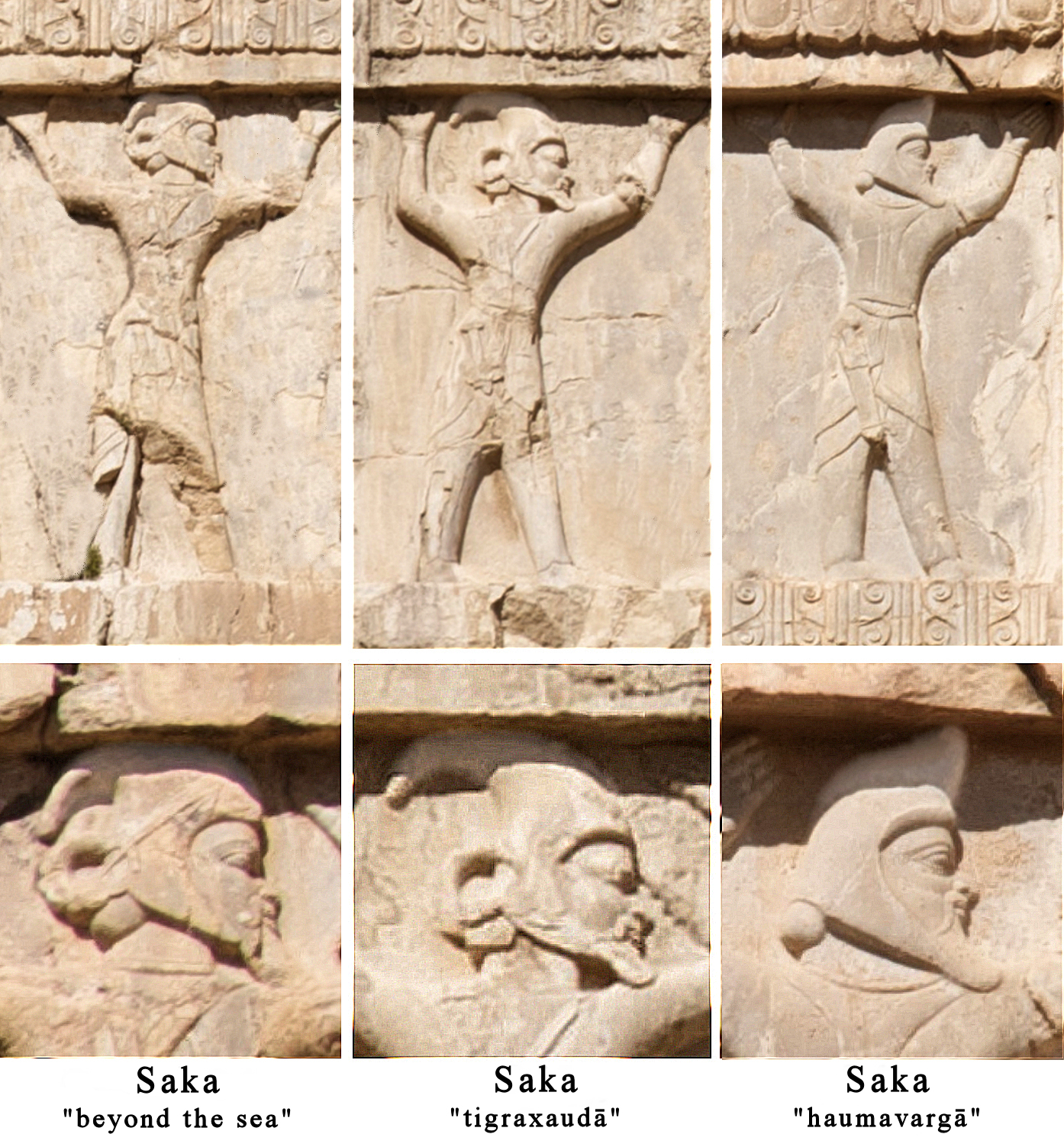
Saka
The Saka, Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples, Eastern Iranian peoples who lived in the Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin from the 9th century BC to the 5th century AD. "Modern scholars have mostly used the name Saka to refer specifically to Iranians of the Eastern Steppe and Tarim Basin" "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." The Saka were closely related to the Scythians, and both groups formed part of the wider Scythian cultures. However, they are distinguished from the Scythians by their specific geographical and cultural traits. The Saka la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakhis
The Wakhi people (, , ; ; ), also locally referred to as the Wokhik (), are an Iranian ethnic group native to Central and South Asia. They are found in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Pakistan, and China—primarily situated in and around Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor, the northernmost part of Pakistan's Gilgit−Baltistan and Chitral, Tajikistan's Gorno−Badakhshan Autonomous Region and the southwestern areas of China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. The Wakhi people are native speakers of the Wakhi language, an Eastern Iranian language. Name The Wakhi people refer to themselves as ''Khik'' and to their language as ''Khik zik''. The exonym ''Wakhī'', which is given to them by their neighbours, is based on ''Wux̌'', the local name of the region of Wakhan, deriving from *''Waxšu'', the old name of the Oxus River (Amu Darya), which is a major river formed by the junction of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers on the border between Tajikistan and Afghanistan. Demographics Ethn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate themselves, their place of origin, or their language. An exonym (also known as xenonym ) is an established, ''non-native'' name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used primarily outside the particular place inhabited by the group or linguistic community. Exonyms exist not only for historico-geographical reasons but also in consideration of difficulties when pronouncing foreign words, or from non-systematic attempts at transcribing into a different writing system. For instance, is the endonym for the country that is also known by the exonyms ''Germany'' and in English and Italian, respectively, and in Spanish and French, respectively, in Polish, and and in Finni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |