|
Taenarus
Cape Matapan (, Maniot dialect: Ματαπά), also called Cape Tainaron or Taenarum (), or Cape Tenaro, is situated at the end of the Mani Peninsula, Greece. Cape Matapan is the southernmost point of mainland Greece, and the second southernmost point in mainland Europe. It separates the Messenian Gulf in the west from the Laconian Gulf in the east. Cape Taenarum in classical antiquity was the site of the city of Taenarum (Ancient Greek: Ταίναρον), now in ruins. In ancient Greek mythology the eponymous founder-hero of the city was Taenarus (Ταίναρος), who was credited with establishing the city's important temple of Poseidon. Greeks used the proverb Tainarian evil (), meaning a great and unlawful evil affecting suppliants, for the Spartans killed the Helots who had fled into Tainaron and were suppliants in the temple of Poseidon. History Cape Matapan has been an important place for thousands of years. Near Taenarum, there is a cave that Greek legends clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taenarus (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Taenarus (Ancient Greek: Ταίναρος) was the eponym of Cape Taenarum, Mount Taenarum and the city Taenarus at Peloponnese. In different accounts, he is given as: *Taenarus, son of Zeus and brother of Calabrus and Geraestus. The three brothers were said to have sailed to Peloponnese and to have seized a portion of land there, where Taenarus founded a sanctuary of Poseidon known as "Taenarum".Stephanus of Byzantium, s.v. Tainaros' *Taenarus, son of Poseidon. *Taenarus, son of Elatus, himself son of Icarius, and Erymede, daughter of Damasiclus; was said to have had the city, the mountain, and the harbor named after him.Scholia ad Apollonius Rhodius, 1.102 Stephanus (who writes of him as a son rather than a grandson of Icarius) considers him to be a figure distinct from Taenarus, son of Zeus. Taenaran gateway: Taenarus, at the tip of the middle peninsula at the south of Peloponnese, was a conventional entrance to the underworld.Ovid, ''Metamorphoses'10. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helots
The helots (; , ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their exact characteristics, such as whether they constituted an Ancient Greek tribe, a social class, or both. For example, Critias described helots as "slaves to the utmost", whereas according to Pollux, they occupied a status "between free men and slaves". Tied to the land, they primarily worked in agriculture as a majority and economically supported the Spartan citizens. The proportion of helots in relation to Spartan citizens varied throughout the history of the Spartan state; according to Herodotus, there were seven helots for each of the 5,000 Spartan soldiers at the time of the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC. Thus the need to keep the helot population in check and to prevent rebellion were major concerns of the Spartans. Helots were ritually mistreated and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Matapan
Cape Matapan (, Maniot dialect: Ματαπά), also called Cape Tainaron or Taenarum (), or Cape Tenaro, is situated at the end of the Mani Peninsula, Greece. Cape Matapan is the southernmost point of mainland Greece, and the second southernmost point in mainland Europe. It separates the Messenian Gulf in the west from the Laconian Gulf in the east. Cape Taenarum in classical antiquity was the site of the city of Taenarum (Ancient Greek: Ταίναρον), now in ruins. In ancient Greek mythology the eponymous founder-hero of the city was Taenarus (Ταίναρος), who was credited with establishing the city's important temple of Poseidon. Greeks used the proverb Tainarian evil (), meaning a great and unlawful evil affecting suppliants, for the Spartans killed the Helots who had fled into Tainaron and were suppliants in the temple of Poseidon. History Cape Matapan has been an important place for thousands of years. Near Taenarum, there is a cave that Greek lege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cities and colonies. In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, Poseidon was venerated as a chief deity at Pylos and Thebes, with the cult title "earth shaker"; in the myths of isolated Arcadia, he is related to Demeter and Persephone and was venerated as a horse, and as a god of the waters.Seneca quaest. Nat. VI 6 :Nilsson Vol I p.450 Poseidon maintained both associations among most Greeks: he was regarded as the tamer or father of horses, who, with a strike of his trident, created springs (the terms for horses and springs are related in the Greek language).Nilsson Vol I p.450 His Roman equivalent is Neptune. Homer and Hesiod suggest that Poseidon became lord of the sea when, following the overthrow of his father Cronus, the world was divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taenarum (town)
Taenarum or Tainaron (Ταίναρον) or Taenarus or Tainaros (Ταίναρος), sometimes anglicized Tenarus, was a town of ancient Laconia, situated at the distance of 40 stadia, or , north of the isthmus of the Taenarian Peninsula (modern day Cape Matapan). A cavern near Tenarus was considered the entrance to the Greek underworld, through which Heracles dragged Cerberus in his 12th labor, and also through which Orpheus led Eurydice back among the living. Through this association the infernal world was often styled "Tenarus" among classicist writers. Green marble Taenarum was famous for a green marble much prized in the ancient world, as well as the purple snail that yielded the prized Lacedaemonian Purple dye. It was also famous for valuable marble (), known for its red and black elements. Seat of a bishop Taenarum was the seat of a bishop; no longer a resident see, it remains a titular see, suffragan of Corinth, in the Roman Catholic Church The Catholic Church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather than for political interests. Beginning in the 20th century, mercenaries have increasingly come to be seen as less entitled to protection by rules of war than non-mercenaries. The Geneva Conventions declare that mercenaries are not recognized as legitimate combatants and do not have to be granted the same legal protections as captured service personnel of the armed forces. In practice, whether or not a person is a mercenary may be a matter of degree, as financial and political interests may overlap. International and national laws of war Protocol I, Protocol Additional GC 1977 (APGC77) is a 1977 amendment Protocol (diplomacy), protocol to the Geneva Conventions. Article 47 of the protocol provides the most widely accepted internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
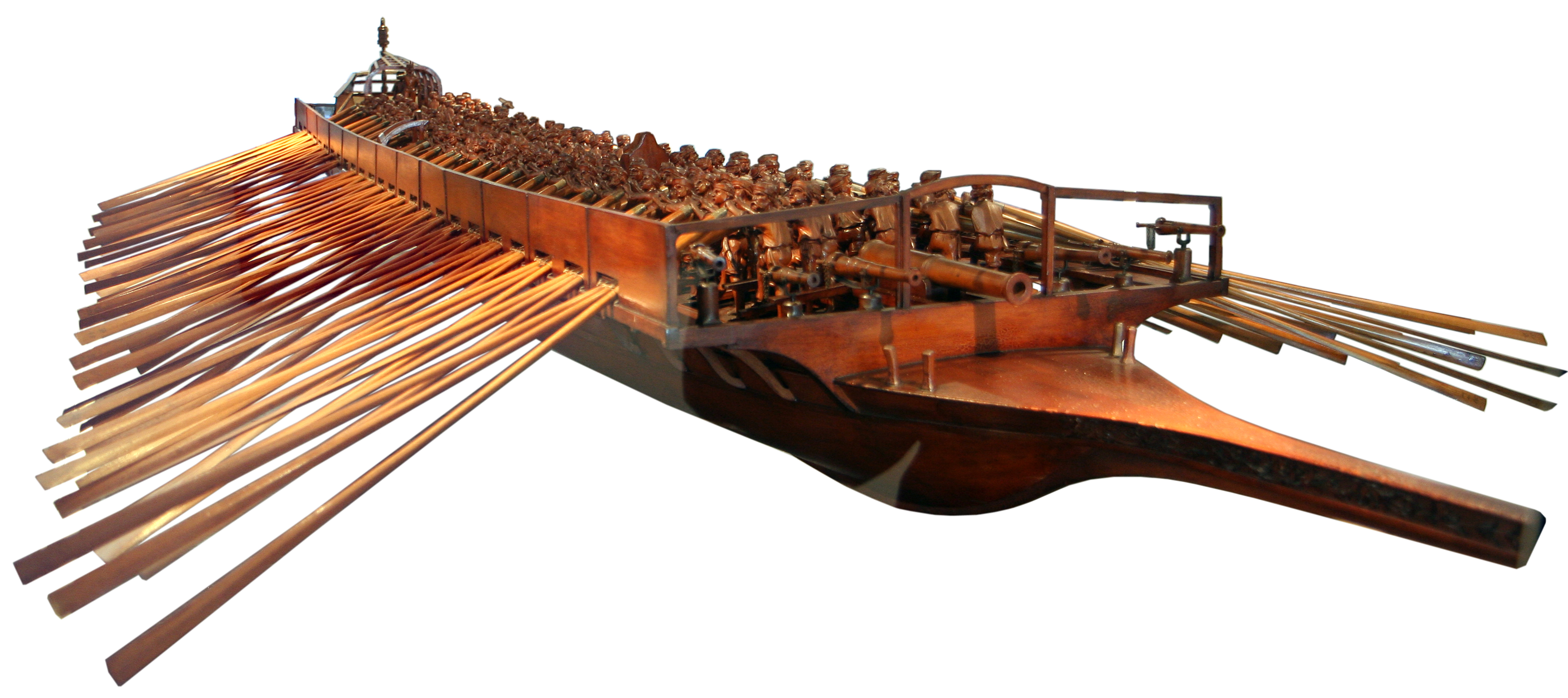
Venetian Navy
The Venetian navy () was the navy of the Venetian Republic which played an important role in the history of the republic and the Mediterranean world. It was the premier navy in the Mediterranean Sea for many centuries between the medieval and early modern periods, providing Venice with control and influence over trade and politics far in excess of the republic's size and population. It was one of the first navies to mount gunpowder weapons aboard ships, and through an organised system of naval dockyards, armouries and chandlers was able to continually keep ships at sea and rapidly replace losses. The Venetian Arsenal was one of the greatest concentrations of industrial capacity prior to the Industrial Revolution and responsible for the bulk of the republic's naval power. Driven at first by a rivalry with the Byzantine Empire, and later the maritime republics of Pisa and Genoa for primacy over trade with the Levant, the Venetian navy was at times technically innovative and yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Matapan 08
A cape is a clothing accessory or a sleeveless outer garment of any length that hangs loosely and connects either at the neck or shoulders. They usually cover the back, shoulders, and arms. They come in a variety of styles and have been used throughout history for many different reasons. Semantic distinction In fashion, the word "cape" usually refers to a shorter garment and "cloak" to a full-length version of the different types of garment, though the two terms are sometimes used synonymously for full-length coverings. A shoulder cape is thus sometimes called a "capelet". The fashion cape does not cover the front to any appreciable degree. In raingear, a cape is usually a long and roomy protective garment worn to keep one dry in the rain. History The first known usage of capes is unknown, but some early references we know of are from Ancient Roman military uniforms. Later on, capes were common in Middle Ages, medieval Europe, especially when combined with a Hood (headgear), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal was a Portuguese monarchy, monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also known as the Kingdom of Portugal and the Algarves after 1415, and as the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves between 1815 and 1822. The name is also often applied to the Portuguese Empire, the realm's overseas colonies. The nucleus of the Portuguese state was the County of Portugal, established in the 9th century as part of the ''Reconquista'', by Vímara Peres, a vassal of the Kingdom of Asturias, King of Asturias. The county became part of the Kingdom of León in 1097, and the Counts of Portugal established themselves as rulers of an independent kingdom in the 12th century, following the battle of São Mamede. The kingdom was ruled by the Portuguese House of Burgundy, Afonsine Dynasty until the 1383–85 Crisis, after which the monarchy passed to the Hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th century until the unification of Italy, which took place between 1859 and 1870, culminated in their demise. The state was legally established in the 8th century when Pepin the Short, king of the Franks, gave Pope Stephen II, as a temporal sovereign, lands formerly held by Arian Christian Lombards, adding them to lands and other real estate formerly acquired and held by the bishops of Rome as landlords from the time of Constantine onward. This donation came about as part of a process whereby the popes began to turn away from the Byzantine emperors as their foremost temporal guardians for reasons such as increased imperial taxes, disagreement with respect to iconoclasm, and failure of the emperors, or their exarchs in Italy, to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |