|
Venetian Navy
The Venetian navy () was the navy of the Venetian Republic which played an important role in the history of the republic and the Mediterranean world. It was the premier navy in the Mediterranean Sea for many centuries between the medieval and early modern periods, providing Venice with control and influence over trade and politics far in excess of the republic's size and population. It was one of the first navies to mount gunpowder weapons aboard ships, and through an organised system of naval dockyards, armouries and chandlers was able to continually keep ships at sea and rapidly replace losses. The Venetian Arsenal was one of the greatest concentrations of industrial capacity prior to the Industrial Revolution and responsible for the bulk of the republic's naval power. Driven at first by a rivalry with the Byzantine Empire, and later the maritime republics of Pisa and Genoa for primacy over trade with the Levant, the Venetian navy was at times technically innovative and yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Navy
The Byzantine navy was the Navy, naval force of the Byzantine Empire. Like the state it served, it was a direct continuation from its Roman navy, Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state than its earlier iteration. While the fleets of the Roman Empire faced few great naval threats, operating as a policing force vastly inferior in power and prestige to the Roman army, army, command of the sea became vital to the very existence of the Byzantine state, which several historians have called a "maritime empire". The first threat to Roman hegemony in the Mediterranean Sea was posed by the Vandals in the 5th century, but their threat was ended by the wars of Justinian I in the 6th century. The re-establishment of a permanently maintained fleet and the introduction of the dromon galley in the same period also marks the point when the Byzantine navy began departing from its late Roman roots and developing its own characteristic identity. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucentaur
The bucentaur ( ; ''bucintoro'' in Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian) was the pleasure barge, ceremonial barge of the Doge of Venice, doges of Venice. It was used every year on Ascension Day (''Festa della Sensa'') up to 1798 to take the doge out to the Adriatic Sea to perform the "Marriage of the Sea" – a ceremony that symbolically wedded Venice to the sea. Scholars believe there were four major barges, the first significant bucentaur having been built in 1311. The last and most magnificent of the historic bucentaurs made its maiden voyage in 1729 in the reign of Doge Sebastiano Mocenigo, Alvise III Sebastiano Mocenigo. Depicted in paintings by Canaletto and Francesco Guardi, the ship was long and more than high. A two-deck floating palace, its main salon had a seating capacity of 90. The doge's throne was in the stern, and the prow bore a figurehead representing Lady Justice, Justice with sword and scales. The barge was propelled by 168 oarsmen, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietro II Candiano
Pietro II Candiano ( – 939) was the nineteenth Doge of Venice between 932 and 939. He followed Orso II Participazio (912–932) to become Doge in 932. Career The Candiano family was the most important family of Venice during the tenth century.Lane, ''Venice'', p. 24. Pietro II's father Pietro I was the first Candiano to become doge in 887, but died soon after while fighting the Narentines. At the beginning of his term in 932, Pietro II cosigned a letter with Marinus Contarini, the Patriarch of Grado, which he sent to the Synod of Erfurt asking for the expulsion from Germany of the Jews who refused to convert to Christianity. The King of Germany Henri I—who presided over the Synod—did not follow his recommendation though.Blumenkranz, ''Juifs et chrétiens'', p. 102. With the weakening power of the Byzantine Empire in the Adriatic Sea, Venice asserted an independent policy of taking control the northern part of the sea. Pietro II began this expansion in the area, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
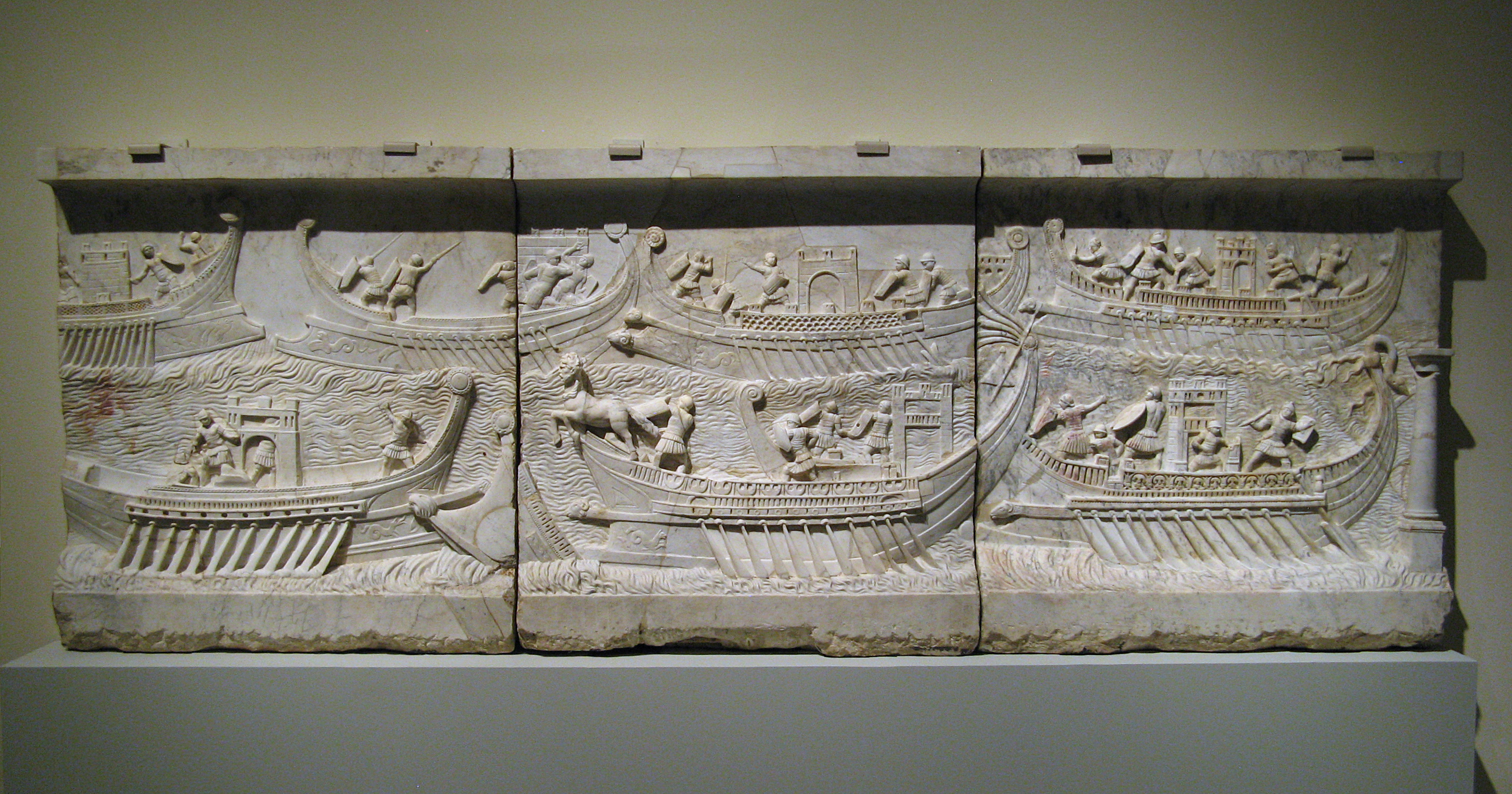
Greek Fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon system used by the Byzantine Empire from the seventh to the fourteenth centuries. The recipe for Greek fire was a closely-guarded state secret; historians have variously speculated that it was based on saltpeter, sulfur, or quicklime, but most modern scholars agree that it was based on petroleum mixed with resins, comparable in composition to modern napalm. Byzantine sailors would toss grenades loaded with Greek fire onto enemy ships or spray it from tubes. Its ability to burn on water made it an effective and destructive naval incendiary weapon, and rival powers tried unsuccessfully to copy the material. Name Usage of the term "Greek fire" has been general in English and most other languages since the Crusades. Original Byzantine sources called the substance a variety of names, such as "sea fire" (Medieval Greek: ), "Roman fire" ( ), "war fire" ( ), "liquid fire" ( ), "sticky fire" ( ), or "manufactured fire" ( ). History Incendiary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dromon
The dromon (from Greek δρόμων, , ), a type of galley, became the most important type of warship of the Byzantine navy from the 5th to 12th centuries AD, after which the Italian-style galley superseded it. It developed from the ancient liburnian, which was the mainstay of the Roman navy during classical antiquity. The Middle English word ''dromond'' and the Old French word ''dromont'' derive from the Greek word; these names identified any particularly large medieval ship. Evolution and features The appearance and evolution of medieval warships is a matter of debate and conjecture; until recently, no remains of an oared warship from either ancient or early medieval times had been found and information had to be gathered by analyzing literary evidence, crude artistic depictions and the remains of a few merchant vessels (such as the 7th-century Pantano Longarini wreck from Sicily, the 7th-century Yassi Ada ship and the 11th-century Serçe Limanı Shipwreck, Serçe Limanı ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateen Sails
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same overall category of sail. The lateen originated in the Mediterranean as early as the 2nd century AD, during Roman times, and became common there by the 5th century. The wider introduction of lateen rig at this time coincided with a reduction in the use of the Mediterranean square rig of the classical era. Since the performance of these two rigs is broadly similar, it is suggested that the change from one to the other was on cost grounds, since lateen rigs used fewer components and had less cordage to be replaced when it wore out. Arab seafarers adopted the lateen rig at a later datethere is some limited archaeological evidence of lateen rig in the Indian Ocean in the 13th century AD and iconographic evidence from the 16th century. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Ship
An auxiliary ship is a naval ship designed to support combatant ships and other naval operations. Auxiliary ships are not primary combatant vessels, though they may have some limited combat capacity, usually for purposes of self-defense. Auxiliary ships are extremely important for navy, navies of all sizes because if they were not present the primary fleet vessels would be unsupported. Thus, virtually every navy maintains an extensive fleet of auxiliary ships, however, the composition and size of these auxiliary fleets vary depending on the nature of each navy and its primary mission. Smaller coastal navies tend to have smaller auxiliary vessels focusing primarily on littoral and training support roles, while larger blue-water navy, blue-water navies tend to have larger auxiliary fleets comprising longer-range fleet support vessels designed to provide support far beyond territorial waters. Roles Replenishment One of the most direct ways that auxiliary ships support the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Of Sail
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface. The principal points of sail roughly correspond to 45° segments of a circle, starting with 0° directly into the wind. For many sailing craft 45° on either side of the wind is a ''no-go'' zone, where a sail is unable to mobilize power from the wind. Sailing on a course as close to the wind as possible—approximately 45°—is termed ''beating'', a point of sail when the sails are ''close-hauled''. At 90° off the wind, a craft is on a ''beam reach''. The point of sail between beating and a beam reach is called a ''close reach''. At 135° off the wind, a craft is on a ''broad reach''. At 180° off the wind (sailing in the same direction as the wind), a craft is ''running downwind''. A given point of sail (beating, close reach, beam reach, broad reach, and running downwind) is defined in reference to the true wind—the wind felt by a stationary observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeboard (nautical)
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relative to the ship's load line, regardless of deck arrangements, is the mandated and regulated meaning. In yachts, a low freeboard is often found on racing boats, for increased speed (by reducing weight and therefore drag). A higher freeboard will give more room in the cabin, but will increase weight and drag, compromising speed. A higher freeboard, such as used on ocean liners, also helps weather waves and so reduce the likelihood of being washed over by full water waves. A low-freeboard vessel is susceptible to taking in water in rough seas. Freighter ships and warships use high freeboard designs to increase internal volume, which also allows them to satisfy International Maritime Organization The International Maritime Organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navis Oneraria
Ancient Rome had a variety of ships that played crucial roles in its military, trade, and transportation activities. Rome was preceded in the use of the sea by other ancient, seafaring civilizations of the Mediterranean. The galley was a long, narrow, highly maneuverable ship powered by oarsmen, sometimes stacked in multiple levels such as biremes or triremes, and many of which also had sails. Initial efforts of the Romans to construct a war fleet were based on copies of Carthaginian warships. In the Punic wars in the mid-third century BC, the Romans were at first outclassed by Carthage at sea, but by 256 BC had drawn even and fought the wars to a stalemate. In 55 BC Julius Caesar used warships and transport ships to invade Britain. Numerous types of transport ships were used to carry foodstuffs or other trade goods around the Mediterranean, many of which did double duty and were pressed into service as warships or troop transports in time of war. Introduction Terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
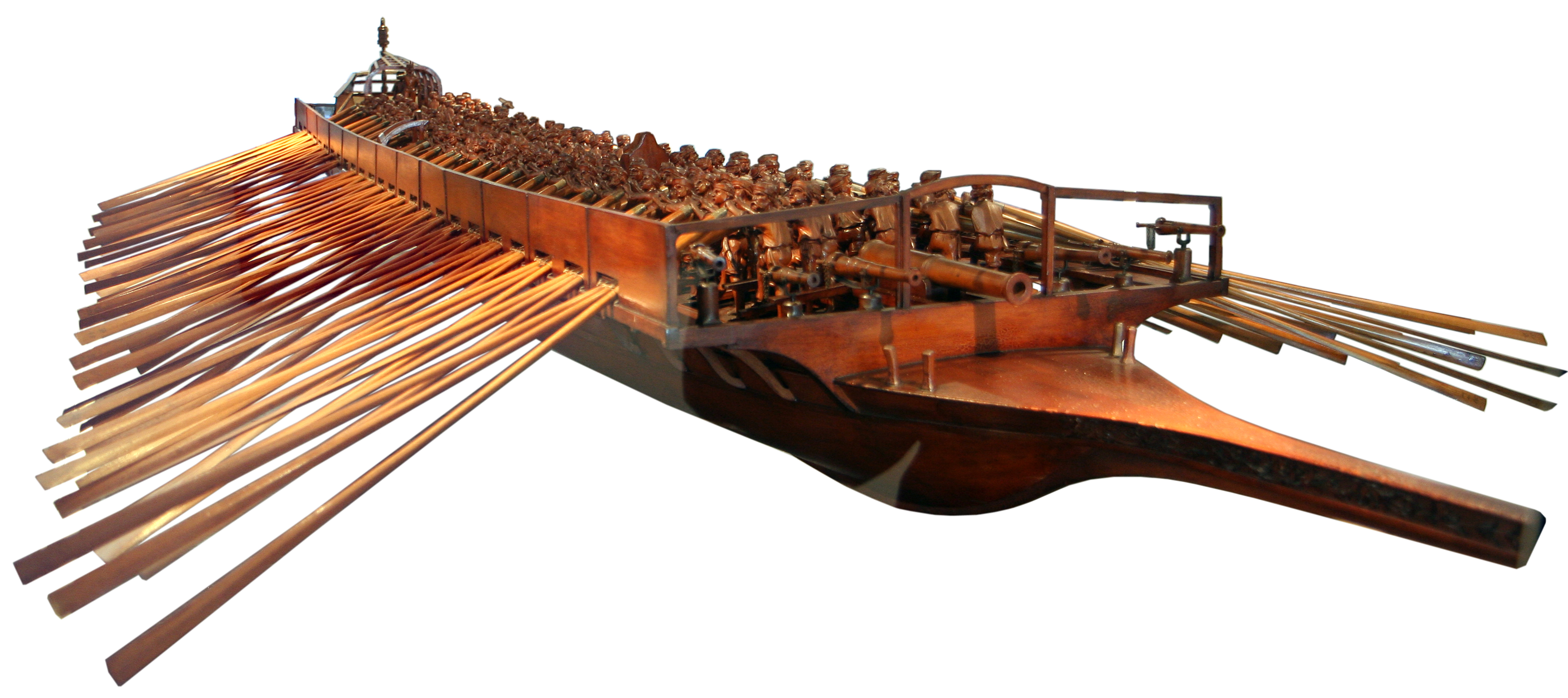
Trireme
A trireme ( ; ; cf. ) was an ancient navies and vessels, ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and ancient Rome, Romans. The trireme derives its name from its three rows of oars, manned with one man per oar. The early trireme was a development of the penteconter (ship), penteconter, an ancient warship with a single row of 25 oars on each side (i.e., a single-banked boat), and of the bireme (, ), a warship with two banks of oars, of Phoenician origin. The word ''dieres'' does not appear until the Roman period. According to Morrison and Williams, "It must be assumed the term pentekontor covered the two-level type". As a ship, it was fast and agile and was the dominant warship in the Mediterranean from the 7th to the 4th centuries BC, after which it was largely superseded by the larger quadriremes and quinqueremes. Triremes played a vital role in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |