|
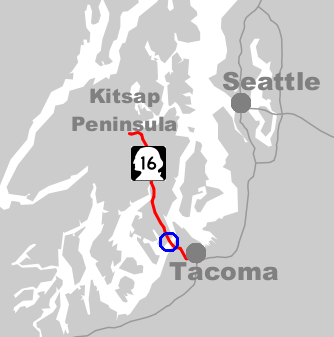
Tacoma Narrows Bridge
The Tacoma Narrows Bridge is a pair of twin bridges, twin suspension bridges that span the Tacoma Narrows strait of Puget Sound in Pierce County, Washington, Pierce County, Washington (state), Washington. The bridges connect the city of Tacoma, Washington, Tacoma with the Kitsap Peninsula and carry Washington State Route 16, State Route 16 (known as Primary State Highway 14 (Washington), Primary State Highway 14 until 1964) over the strait. Historically, the name "Tacoma Narrows Bridge" has applied to the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940), original bridge, nicknamed "Galloping Gertie", which opened in July 1940 but collapsed possibly because of aeroelastic flutter four months later, as well as to the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1950), successor of that bridge, which opened in 1950 and still stands today as the westbound lanes of the present-day two-bridge complex. The original Tacoma Narrows Bridge opened on July 1, 1940. The original bridge received its nickname "Galloping Gertie" for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940)
The 1940 Tacoma Narrows Bridge, the first bridge at this location, was a suspension bridge in the U.S. state of Washington that spanned the Tacoma Narrows strait of Puget Sound between Tacoma and the Kitsap Peninsula. It opened to traffic on July 1, 1940, and dramatically collapsed into Puget Sound on November 7 of the same year. The bridge's collapse has been described as "spectacular" and in subsequent decades "has attracted the attention of engineers, physicists, and mathematicians". Throughout its short existence, it was the world's third-longest suspension bridge by main span, behind the Golden Gate Bridge and the George Washington Bridge. Construction began in September 1938. From the time the deck was built, it began to move vertically in windy conditions, so construction workers nicknamed the bridge "Galloping Gertie". The motion continued after the bridge opened to the public, despite several damping measures. The bridge's main span finally collapsed in wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacoma Narrows
The Tacoma Narrows (or the Narrows), a strait, is part of Puget Sound in the U.S. state of Washington. A navigable maritime waterway between glacial landforms, the Narrows separates the Kitsap Peninsula from the city of Tacoma. The Narrows is spanned by the twin Tacoma Narrows Bridges ( State Route 16). An earlier bridge collapsed shortly after it opened. In 1841 Charles Wilkes, during the United States Exploring Expedition, named the strait simply ''Narrows''. Its name was formally set as ''The Narrows'' by Henry Kellett during the British Admiralty The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy. Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the ... chart reorganization of 1847. References Bodies of water of Pierce County, Washington Straits of Washington (state) Landforms of Puget Sound {{PierceCountyWA-ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deck (bridge)
A deck is the surface of a bridge. A structural element of its superstructure, it may be constructed of concrete, steel Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ..., grating, open grating, or wood. Sometimes the deck is covered by a track ballast, railroad bed and railroad track, track, asphalt concrete, or other form of pavement (material), pavement for ease of vehicle crossing. A concrete deck may be an integral part of the bridge structure (T-beam or double tee structure) or it may be supported with I-beams or steel girders. When a bridge deck is installed in a through truss, it is sometimes called a floor system. A suspended bridge deck will be suspended from the main structural elements on a suspension or arch bridge. On some bridges, such as a Tied-arch bridge, tied- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocker Spaniel
Cocker Spaniels are dogs belonging to two breeds of the spaniel dog type: the American Cocker Spaniel and the English Cocker Spaniel, both of which are commonly called simply Cocker Spaniel in their countries of origin. In the early 20th century, Cocker Spaniels also included small hunting spaniels. Cocker Spaniels were originally bred as hunting dogs in the UK, with the term "cocker" deriving from their use to hunt the Eurasian woodcock. When the breed was brought to the United States, it was bred to a different standard, which enabled it to specialize in hunting the American woodcock. Further physical changes were bred into the cocker in the United States during the early part of the 20th century. Spaniels were first mentioned in the 14th century by Gaston III, Count of Foix in his work the ''Livre de Chasse''. The "cocking" or "cocker spaniel" was a type of field or land spaniel in the 19th century. Prior to 1901, Cocker Spaniels were only separated from Field Spaniels and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Journal Of Physics
The ''American Journal of Physics'' is a monthly, peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Association of Physics Teachers and the American Institute of Physics. The editor-in-chief is Beth Parks of Colgate University."Current Frequency: Monthly, 2002; and Former Frequency varies, 1940-2001" Confirmation of Editor, ISSN, CODEN, and other relevant information. Aims and scope The focus of this journal is undergraduate and graduate level physics. The intended audience is college and university physics teachers and students. Coverage includes current research in physics, instructional laboratory equipment, laboratory demonstrations, teaching methodologies, lists of resources, and book reviews. In addition, historical, philosophical and cultural aspects of physics are also covered. According to the 2021 Journal Citation Reports from Clarivate, this journal has a 2020 impact factor of 1.022. History The former title of this journal was ''American Physics Teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximum amplitude response in the system. When this happens, the object or system absorbs energy from the external force and starts vibrating with a larger amplitude. Resonance can occur in various systems, such as mechanical, electrical, or acoustic systems, and it is often desirable in certain applications, such as musical instruments or radio receivers. However, resonance can also be detrimental, leading to excessive vibrations or even structural failure in some cases. All systems, including molecular systems and particles, tend to vibrate at a natural frequency depending upon their structure; when there is very little damping this frequency is approximately equal to, but slightly above, the resonant frequency. When an Oscillation, oscillat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroelasticity
Aeroelasticity is the branch of physics and engineering studying the interactions between the inertial, elastic, and aerodynamic forces occurring while an elastic body is exposed to a fluid flow. The study of aeroelasticity may be broadly classified into two fields: ''static aeroelasticity'' dealing with the static or steady state response of an elastic body to a fluid flow, and ''dynamic aeroelasticity'' dealing with the body's dynamic (typically vibrational) response. Aircraft are prone to aeroelastic effects because they need to be lightweight while enduring large aerodynamic loads. Aircraft are designed to avoid the following aeroelastic problems: # divergence where the aerodynamic forces increase the twist of a wing which further increases forces; # control reversal where control activation produces an opposite aerodynamic moment that reduces, or in extreme cases reverses, the control effectiveness; and # flutter which is uncontained vibration that can lead to the destr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Collapse Of The Tacoma Bridge
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon Moisseiff
Leon Solomon Moisseiff (November 10, 1872 – September 3, 1943) was a leading suspension bridge engineer in the United States in the 1920s and 1930s. He was awarded The Franklin Institute's Louis E. Levy Medal in 1933. His developments of the theory of suspension bridges are eclipsed by the dramatic failure of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940), Tacoma Narrows Suspension Bridge, his design, four months after its completion in 1940. The event was filmed and is shown to engineering students as a reminder of the possibility of failure and the importance of avoiding hubris. Biography Moisseiff was born in Riga, Latvia (at the time, Russian Empire), to a Jewish family. He started his education there and studied at the Baltic Polytechnic Institute for three years; he emigrated to the United States with his family at the age of 19, in 1891, because of political activities. In the US, he graduated from Columbia University with a degree in civil engineering in 1895. In his early 20s, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was an important American transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the Western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest between 1864 and 1970. It was approved and chartered by the 38th Congress of the United States in the national / federal capital of Washington, D.C., during the last years of the American Civil War (1861-1865), and received nearly of adjacent land grants, which it used to raise additional money in Europe (especially in President Henry Villard's home country of the new German Empire), for construction funding. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific Ocean, just south of the United States-Canada border when Ulysses S. Grant, drove in the final "golden spike" completing the line in western Montana Territory (future State of Montana in 1889), on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about of track and served a large area, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodachrome
Kodachrome is the brand name for a color reversal film introduced by Eastman Kodak in 1935. It was one of the first successful color materials and was used for both cinematography and still photography. For many years, Kodachrome was widely used for professional color photography, especially for images intended for publication in print media. Because of its complex processing requirements, the film was initially sold only with the cost of processing; independent photography stores were prohibited from developing Kodachrome. To develop the film, customers had to mail it to Kodak, which would then send the developed film back as part of the purchase price. In 1954, the U.S. Department of Justice found that this practice violated antitrust laws by being uncompetitive. Kodak then entered into a consent decree, requiring the company to offer Kodachrome film for sale without the development fee, as well as license Kodachrome development patents to independent photography stores. Kodak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toll Bridge
A toll bridge is a bridge where a monetary charge (or '' toll'') is required to pass over. Generally the private or public owner, builder and maintainer of the bridge uses the toll to recoup their investment, in much the same way as a toll road. History The practice of collecting tolls on bridges harks back to the days of ferry crossings where people paid a fee to be ferried across stretches of water. As boats became impractical to carry large loads, ferry operators looked for new sources of revenue. Having built a bridge, they hoped to recoup their investment by charging tolls for people, animals, vehicles, and goods to cross it. The original London Bridge across the river Thames opened as a toll bridge, but an accumulation of funds by the charitable trust that operated the bridge ( Bridge House Estates) saw that the charges were dropped. Using interest on its capital assets, the trust now owns and runs all seven central London bridges at no cost to taxpayers or users. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |