|
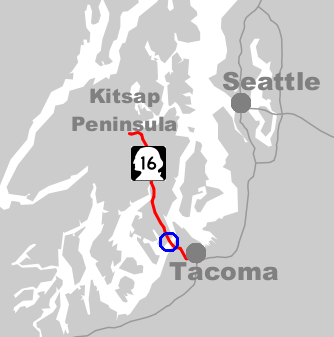
Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940)
The 1940 Tacoma Narrows Bridge, the first bridge at this location, was a suspension bridge in the U.S. state of Washington that spanned the Tacoma Narrows strait of Puget Sound between Tacoma and the Kitsap Peninsula. It opened to traffic on July 1, 1940, and dramatically collapsed into Puget Sound on November 7 of the same year. The bridge's collapse has been described as "spectacular" and in subsequent decades "has attracted the attention of engineers, physicists, and mathematicians". Throughout its short existence, it was the world's third-longest suspension bridge by main span, behind the Golden Gate Bridge and the George Washington Bridge. Construction began in September 1938. From the time the deck was built, it began to move vertically in windy conditions, so construction workers nicknamed the bridge "Galloping Gertie". The motion continued after the bridge opened to the public, despite several damping measures. The bridge's main span finally collapsed in wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon Moisseiff
Leon Solomon Moisseiff (November 10, 1872 – September 3, 1943) was a leading suspension bridge engineer in the United States in the 1920s and 1930s. He was awarded The Franklin Institute's Louis E. Levy Medal in 1933. His developments of the theory of suspension bridges are eclipsed by the dramatic failure of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (1940), Tacoma Narrows Suspension Bridge, his design, four months after its completion in 1940. The event was filmed and is shown to engineering students as a reminder of the possibility of failure and the importance of avoiding hubris. Biography Moisseiff was born in Riga, Latvia (at the time, Russian Empire), to a Jewish family. He started his education there and studied at the Baltic Polytechnic Institute for three years; he emigrated to the United States with his family at the age of 19, in 1891, because of political activities. In the US, he graduated from Columbia University with a degree in civil engineering in 1895. In his early 20s, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
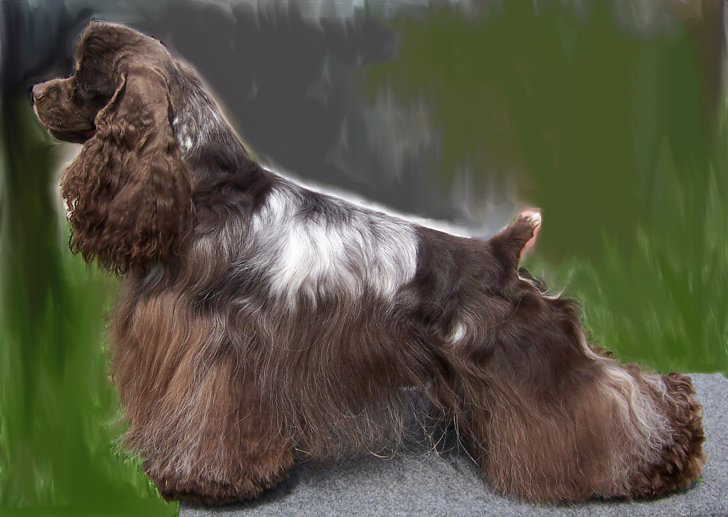
Cocker Spaniel
Cocker Spaniels are dogs belonging to two breeds of the spaniel dog type: the American Cocker Spaniel and the English Cocker Spaniel, both of which are commonly called simply Cocker Spaniel in their countries of origin. In the early 20th century, Cocker Spaniels also included small hunting spaniels. Cocker Spaniels were originally bred as hunting dogs in the UK, with the term "cocker" deriving from their use to hunt the Eurasian woodcock. When the breed was brought to the United States, it was bred to a different standard, which enabled it to specialize in hunting the American woodcock. Further physical changes were bred into the cocker in the United States during the early part of the 20th century. Spaniels were first mentioned in the 14th century by Gaston III, Count of Foix in his work the ''Livre de Chasse''. The "cocking" or "cocker spaniel" was a type of field or land spaniel in the 19th century. Prior to 1901, Cocker Spaniels were only separated from Field Spaniels and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
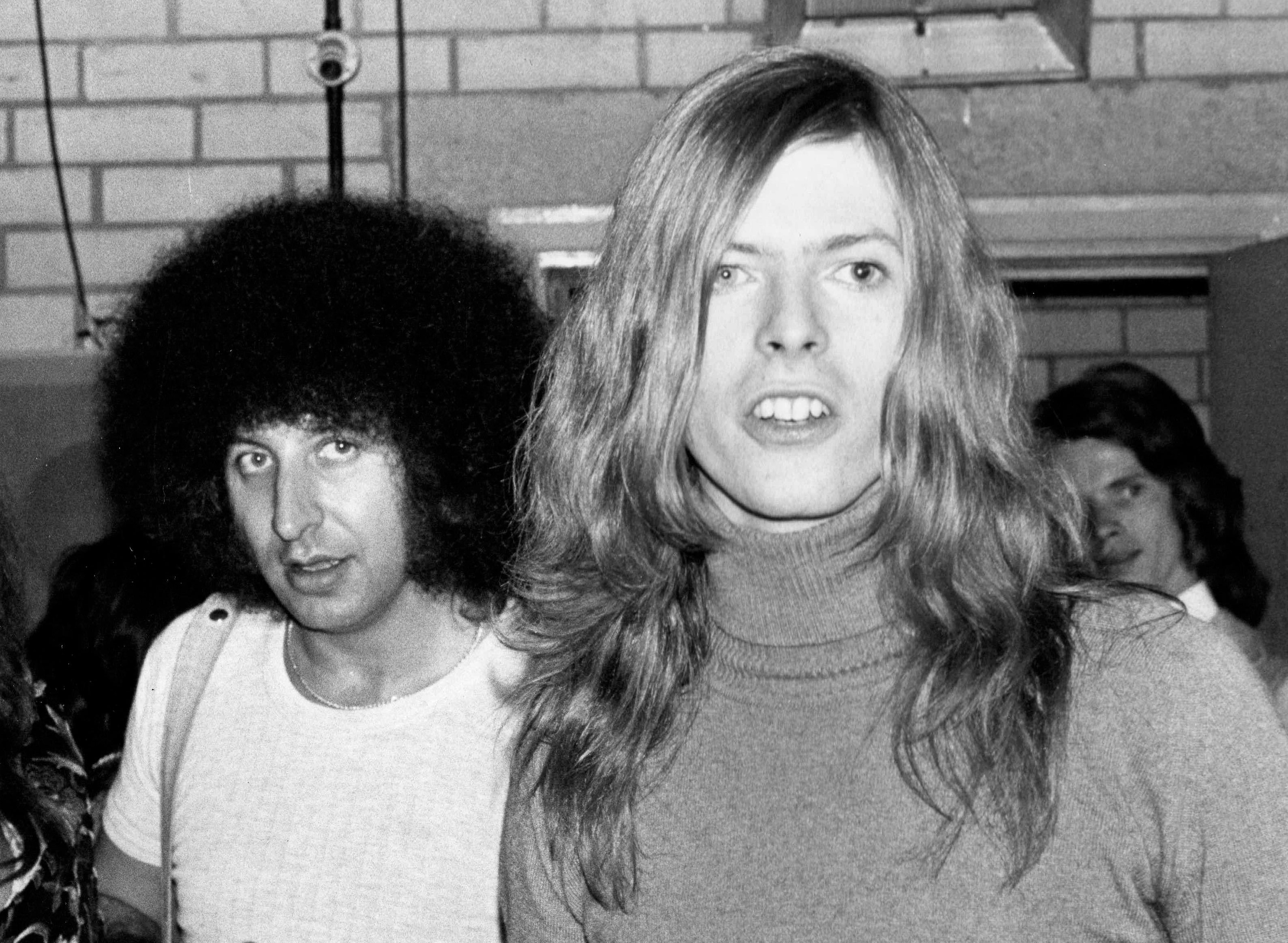
David B
David Robert Jones (8 January 194710 January 2016), known as David Bowie ( ), was an English singer, songwriter and actor. Regarded as one of the most influential musicians of the 20th century, Bowie was acclaimed by critics and musicians, particularly for his innovative work during the 1970s. His career was marked by reinvention and visual presentation, and his music and stagecraft have had a great impact on popular music. Bowie studied art, music and design before embarking on a professional career as a musician in 1963. He released a string of unsuccessful singles with local bands and David Bowie (1967 album), a self-titled solo album (1967) before achieving his first top-five entry on the UK singles chart with "Space Oddity" (1969). After a period of experimentation, he re-emerged in 1972 during the glam rock era with the alter ego Ziggy Stardust (character), Ziggy Stardust. The success of the single "Starman (song), Starman" and its album ''The Rise and Fall of Ziggy Star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Strauss (engineer)
Joseph Baermann Strauss (January 9, 1870 – May 16, 1938) was a German-American structural engineer who revolutionized the design of bascule bridges. He was the chief engineer of the Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco, California. Early life and education Strauss was born in Cincinnati, Ohio to an artistic family of German-Jewish ancestry. His mother was a pianist and his father, Raphael Strauss, was a writer and painter. He graduated from the University of Cincinnati in 1892 with a degree in civil engineering. He served as both class poet and class president, and was a brother of the Sigma Alpha Epsilon fraternity. Strauss had many hobbies, including poetry. After completion of the Golden Gate Bridge, he returned to his passion of poetry and wrote his most recognizable poem, "The Mighty Task is Done". He also wrote "The Redwoods" and his "Sequoia" can still be purchased by tourists visiting the California redwoods. He died in Los Angeles one year after the Golden Gate Bridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Scientist
''American Scientist'' (informally abbreviated ''AmSci'') is an American bimonthly science and technology magazine published since 1913 by Sigma Xi, The Scientific Research Honor Society. In the beginning of 2000s the headquarters was moved to Research Triangle Park, (Durham), North Carolina. Each issue includes feature articles written by scientists and engineers who review research in fields from molecular biology to computer engineering. Each issue also includes the work of cartoonist A cartoonist is a visual artist who specializes in both drawing and writing cartoons (individual images) or comics (sequential images). Cartoonists differ from comics writers or comics illustrators/artists in that they produce both the litera ...s, including those of Sidney Harris, Benita Epstein, and Mark Heath. Also included is the ''Scientists' Nightstand'' that reviews a vast range of science-related books and novels. ''American Scientist Online'' () was launched in May 2003. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamber Of Commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to advocate on behalf of the business community. Local businesses are members, and they elect a board of directors or executive council to set policy for the chamber. The board or council then hires a president, CEO, or executive director, plus staffing appropriate to size, to run the organization. A chamber of commerce may be a voluntary or a mandatory association of business firms belonging to different trades and industries. They serve as spokespeople and representatives of a business community. They differ from country to country. History The first chamber of commerce was founded in 1599 in Marseille, France, as the "Chambre de Commerce". The Royal Barcelona Board of Trade was established in 1758. The world's oldest English-speaking c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trestle Bridge
A trestle bridge is a bridge composed of a number of short spans supported by closely spaced frames usually carrying a railroad line. A trestle (sometimes tressel) is a rigid frame used as a support, historically a tripod used to support a stool or a pair of isosceles triangles joined at their apices by a plank or beam such as the support structure for a trestle table. Each supporting frame is a bent. A trestle differs from a viaduct in that viaducts have towers that support much longer spans and typically have a higher elevation. Timber and iron trestles (i.e. bridges) were extensively used in the 19th century, the former making up from 1 to 3 percent of the total length of the average railroad. In the 21st century, steel and sometimes concrete trestles are commonly used to bridge particularly deep valleys, while timber trestles remain common in certain areas. Many timber trestles were built in the 19th and early 20th centuries with the expectation that they would be te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was an important American transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the Western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest between 1864 and 1970. It was approved and chartered by the 38th Congress of the United States in the national / federal capital of Washington, D.C., during the last years of the American Civil War (1861-1865), and received nearly of adjacent land grants, which it used to raise additional money in Europe (especially in President Henry Villard's home country of the new German Empire), for construction funding. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific Ocean, just south of the United States-Canada border when Ulysses S. Grant, drove in the final "golden spike" completing the line in western Montana Territory (future State of Montana in 1889), on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about of track and served a large area, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics () is the study of the motion of atmosphere of Earth, air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics, and is an important domain of study in aeronautics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving Aircraft#Heavier-than-air – aerodynes, heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion (mechanics)
In the field of solid mechanics, torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied torque. Torsion could be defined as strain or angular deformation, and is measured by the angle a chosen section is rotated from its equilibrium position. The resulting stress (torsional shear stress) is expressed in either the Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa), an SI unit for newtons per square metre, or in pounds per square inch (psi) while torque is expressed in newton metres (N·m) or foot-pound force (ft·lbf). In sections perpendicular to the torque axis, the resultant shear stress in this section is perpendicular to the radius. In non-circular cross-sections, twisting is accompanied by a distortion called warping, in which transverse sections do not remain plane. For shafts of uniform cross-section unrestrained against warping, the torsion-related physical properties are expressed as: : T = \frac \tau= \frac G \varphi where: * ''T'' is the applied torque or moment of torsion in Nm. * \tau (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroelasticity
Aeroelasticity is the branch of physics and engineering studying the interactions between the inertial, elastic, and aerodynamic forces occurring while an elastic body is exposed to a fluid flow. The study of aeroelasticity may be broadly classified into two fields: ''static aeroelasticity'' dealing with the static or steady state response of an elastic body to a fluid flow, and ''dynamic aeroelasticity'' dealing with the body's dynamic (typically vibrational) response. Aircraft are prone to aeroelastic effects because they need to be lightweight while enduring large aerodynamic loads. Aircraft are designed to avoid the following aeroelastic problems: # divergence where the aerodynamic forces increase the twist of a wing which further increases forces; # control reversal where control activation produces an opposite aerodynamic moment that reduces, or in extreme cases reverses, the control effectiveness; and # flutter which is uncontained vibration that can lead to the destr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Resonance
Mechanical resonance is the tendency of a mechanical system to respond at greater amplitude when the frequency of its oscillations matches the system's natural frequency of vibration (its '' resonance frequency'' or ''resonant frequency'') closer than it does other frequencies. It may cause violent swaying motions and potentially catastrophic failure in improperly constructed structures including bridges, buildings and airplanes. This is a phenomenon known as resonance disaster. Avoiding resonance disasters is a major concern in every building, tower and bridge construction project. The Taipei 101 building for instance relies on a 660-ton pendulum—a tuned mass damper—to modify the response at resonance. The structure is also designed to resonate at a frequency which does not typically occur. Buildings in seismic zones are often constructed to take into account the oscillating frequencies of expected ground motion. Engineers designing objects that have engines must ensure t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |