|
Tabe Bas
Pirenzepine (Gastrozepin), an Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, M1 selective antagonist, is used in the treatment of peptic ulcers, as it reduces gastric acid secretion and reduces muscle spasm. It is in a class of drugs known as muscarinic receptor antagonists; acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system which initiates the rest-and-digest state (as opposed to fight-or-flight), resulting in an increase in gastric motility and digestion; whereas pirenzepine would inhibit these actions and cause decreased gastric motility leading to delayed gastric emptying and constipation. It has no effects on the brain and spinal cord as it cannot diffuse through the blood–brain barrier. Pirenzepine has been investigated for use in myopia control. It promotes the homodimerization or GPCR oligomer, oligomerisation of Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, M1 receptors. See also * AFDX-384 * Telenzepine References {{Tricyclics 4-Methylpiperazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
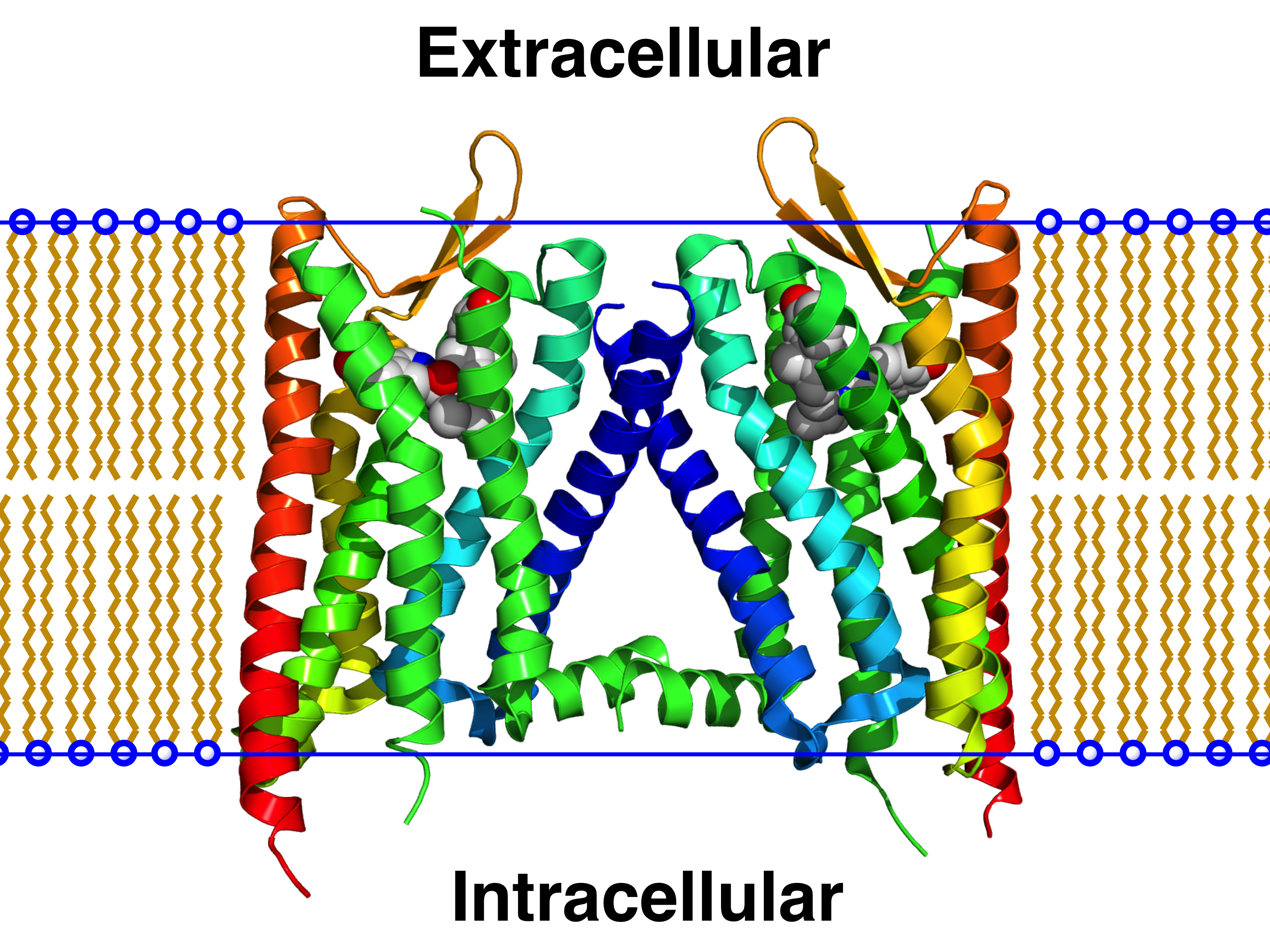
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1
The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1, is a muscarinic receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''CHRM1'' gene. It is localized to 11q13. This receptor is found mediating slow excitatory postsynaptic potential, EPSP at the ganglion in the postganglionic nerve, is common in exocrine glands and in the CNS. It is predominantly found bound to G proteins of class Gq alpha subunit, Gq that use upregulation of phospholipase C and, therefore, inositol trisphosphate and intracellular calcium as a signalling pathway. A receptor so bound would not be susceptible to Cholera toxin, CTX or Pertussis toxin, PTX. However, Gi (causing a downstream decrease in Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP) and Gs (causing an increase in cAMP) have also been shown to be involved in interactions in certain tissues, and so would be susceptible to PTX and CTX respectively. Effects * excitatory postsynaptic potential, EPSP in autonomic ganglia * Secr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AFDX-384
AFDX-384 (BIBN-161) is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, with selectivity for the M2 and M4 subtypes. It is used mainly for mapping the distribution of M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors in the brain, and studying their involvement in the development and treatment of dementia and schizophrenia Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f .... See also * Pirenzepine (M1 selective antagonist) References {{Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor modulators Dipropylamino compounds M2 receptor antagonists M4 receptor antagonists Piperidines Pyridobenzodiazepines Ureas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M4 Receptor Antagonists
M4 or M-4 most often refers to: * M4 carbine, an American carbine * M4 Sherman, an American World War II medium tank M4, M04, or M-4 may also refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''M4'' (EP), a 2006 EP by Faunts * ''M4'' (video game), a 1992 computer game developed for the Macintosh * ''M.IV'' ("Matrix IV"), the fictional Warner Brothers videogame project inside the 2021 film '' The Matrix Resurrections'' * Former name of band First to Eleven * M4, the robot assistant to the character Flint in the Star Trek episode Requiem for Methuselah Military Weapons * Benelli M4 Super 90, an Italian semi-automatic,gas-operated shotgun * M4 autocannon, an American 37 mm automatic gun * M4 Selectable Lightweight Attack Munition (SLAM), an American land mine * M4 SLBM, a French submarine-launched ballistic missile from 1985 * M4 Survival Rifle, an American rifle in aircraft survival gear * Spectre M4, an Italian submachine gun * M4 bayonet, an American World War II bayon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M1 Receptor Antagonists
M1, M01 or M-1 may refer to: Arts, entertainment & media * M-1 (rapper), one half of hip hop duo Dead Prez * Korg M1, a keyboard synthesizer * Leica M1, a 1959 35 mm camera model * Olympus OM-1, a 1972 manually operated 35mm single-lens reflex camera * M1 (TV channel), news channel of the Hungarian MTVA * M-1 (Lithuanian radio station) * M1 (Ukraine), a television channel * M1 (Russian TV channel) Economics and finance * M1 (money supply measure), in economics, a measure of the money supply * M1 Finance, an online financial services company Military equipment Vehicles US Armed Forces * M1 Abrams, a main battle tank * M1 armored car * M1 combat car, an early tank * M1 light tractor * M1 medium tractor * M1 heavy tractor Other * Bristol M.1, a 1916 British fighter aircraft * (M1), a WWI Royal Navy monitor * (1919), an early British submarine * , a Swedish Navy mine sweeper * , a Swedish Royal Navy mine layer Weapons US Armed Forces * 120 mm gun M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactams
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid through cyclization reactions. The term is a portmanteau of the words '' lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size. This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that hydrolysis of an α-lactam gives an α-amino acid and that of a β-Lactam gives a β-amino acid, and so on. Synthesis General synthetic methods are used for the organic synthesis of lactams. Beckmann rearrangement Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement. Schmidt reaction Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclohexanone with hydrazoic acid, forms ε - Caprolactum, which upon treatment with excess acid forms Cardiazole, a heart stimulant. Cyclization of amino acids Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetamides
Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CONH2. It is an amide derived from ammonia and acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent. The related compound ''N'',''N''-dimethylacetamide (DMA) is more widely used, but it is not prepared from acetamide. Acetamide can be considered an intermediate between acetone, which has two methyl (CH3) groups either side of the carbonyl (CO), and urea which has two amide (NH2) groups in those locations. Acetamide is also a naturally occurring mineral with the IMA symbol: Ace. Production Laboratory scale Acetamide can be produced in the laboratory from ammonium acetate by dehydration: : H4CH3CO2] → CH3C(O)NH2 + H2O Alternatively acetamide can be obtained in excellent yield via ammonolysis of acetylacetone under conditions commonly used in reductive amination. It can also be made from anhydrous acetic acid, acetonitrile and very well dried hydrogen chloride gas, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telenzepine
Telenzepine is a thienobenzodiazepine acting as selective M1 antimuscarinic. It is used in the treatment of peptic ulcers. Telenzepine is atropisomer Atropisomers are stereoisomers arising because of hindered rotation about a covalent bond, single bond, where Gibbs free energy, energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to all ...ic, in other words the molecule has a stereogenic C–N-axis. In neutral aqueous solution it displays a half-life for racemization of the order of 1000 years. The enantiomers have been resolved. The activity is related to the (+)-isomer which is about 500-fold more active than the (–)-isomer at muscarinic receptors in the rat cerebral cortex. See also * Pirenzepine References External links * 4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl compounds Carboxamides Lactams M1 receptor antagonists Thienobenzodiazepines {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPCR Oligomer
A GPCR oligomer is a protein complex that consists of a small number ( ''oligoi'' "a few", ''méros'' "part, piece, component") of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). It is held together by covalent bonds or by intermolecular forces. The subunits within this complex are called protomers, while unconnected receptors are called monomers. Receptor homomers consist of identical protomers, while heteromers consist of different protomers. Receptor homodimers – which consist of two identical GPCRs – are the simplest homomeric GPCR oligomers. Receptor heterodimers – which consist of two different GPCRs – are the simplest heteromeric GPCR oligomers. The existence of receptor oligomers is a general phenomenon, whose discovery has superseded the prevailing paradigmatic concept of the function of receptors as plain monomers, and has far-reaching implications for the understanding of neurobiological diseases as well as for the development of drugs. Discovery For a long time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcer disease is when the inner part of the stomach's gastric mucosa (lining of the stomach), the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus, gets damaged. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people with peptic ulcers have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include infection with ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. Other symptoms may include headaches and eye strain. Severe myopia is associated with an increased risk of macular degeneration, retinal detachment, cataracts, and glaucoma. Myopia results from the length of the eyeball growing too long or less commonly the lens being too strong. It is a type of refractive error. Diagnosis is by the use of cycloplegics during eye examination. Tentative evidence indicates that the risk of myopia can be decreased by having young children spend more time outside. This decrease in risk may be related to natural light exposure. Myopia can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or by refractive surgery. Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest method of correction. Contact lenses can provide a rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system, thus protecting the brain from harmful or unwanted substances in the blood. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the Capillary, capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive transport, passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and Molecular mass, large or Hydrophile, hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |