|
THC-VHS
THC valine hemisuccinate (THC-VHS, NB-1111, SBI-100) is a synthetic prodrug of tetrahydrocannabinol, developed at the University of Mississippi as a stabilised formulation for ophthalmic administration, for use in the treatment of glaucoma and other eye conditions requiring reduction in intraocular pressure. See also * THC hemisuccinate * THC-O-acetate * THC-O-phosphate * SP-111 * Cod-THC Cod-THC (Codeine Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol carbonate) is a synthetic codrug formed by linking tetrahydrocannabinol with codeine via a carbonate bridge. It is well absorbed orally and shows superior analgesic effects in animal studies compared to a ... References Benzochromenes Cannabinoids Prodrugs Carboxamides {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THC Hemisuccinate
THC hemisuccinate (Δ9-THC-O-hemisuccinate, Dronabinol hemisuccinate) is a synthetic derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol, developed in the 1990s. It is a water-soluble prodrug ester which is converted into THC inside the body, and was developed to overcome the poor bioavailability of THC when taken by non-inhaled routes of administration. In medical applications it has mainly been formulated as rectal suppositories. See also * THC methylcarbonate * THC-O-acetate * THC-O-phosphate * THC-VHS THC valine hemisuccinate (THC-VHS, NB-1111, SBI-100) is a synthetic prodrug of tetrahydrocannabinol, developed at the University of Mississippi as a stabilised formulation for ophthalmic administration, for use in the treatment of glaucoma and ... * SP-111 References Benzochromenes Cannabinoids {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of ''Cannabis'' and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a colorless oil. Medical uses THC, referred to as dronabinol in the pharmaceutical context, is approved in the United States as a capsule or solution to relieve chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia. THC is an active ingredient in nabiximols, a specific extract of ''Cannabis'' that was approved as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom in 2010 as a mouth spray for people with multiple sclerosis to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms. Nabiximols (as Sativex) is available as a prescription drug in Canada. In 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THC-O-acetate
THC-O-acetate (THC acetate ester, O-acetyl-THC, THC-O, AcO-THC) is the acetate ester of THC. The term ''THC-O-acetate'' and its variations are commonly used for two types of the substance, dependent on which cannabinoid it is synthesized from. The difference between Δ8-THC and Δ9-THC is the location of the double bond within the cyclohexene ring system. Physical data, chemistry, and properties THC acetate ester (THC-O or THCOA) can be synthesized from THC, or from THCA. The acetylation of THC does not change the properties of the compound to the same extent as with other acetate esters, as the parent compound (THC) is already highly lipophilic, but potency is nonetheless increased to some extent. While the acetate ester of Δ9-THC is the best studied, the acetate esters of other isomers, especially Δ8-THC but also Δ10-THC are also known, as are other esters such as THC-O-propionate, THC-O-phosphate, THC hemisuccinate, THC hemiglutarate, THC morpholinylbutyrate, THC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SP-111
THC morpholinylbutyrate (SP-111, Δ9-THC-O- -(morpholin-4-yl)butyrate'') is a synthetic derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol, developed in the 1970s. It is a prodrug which is converted into THC inside the body, and was one of the first derivatives of THC that is able to form water-soluble salts, giving it a significant advantage over THC for some applications. However, it is less potent than THC and the metabolic conversion to THC is relatively slow and variable, giving it unpredictable pharmacokinetics which has limited its research applications. See also * THC-O-acetate * THC-O-phosphate * THC hemisuccinate * THC methylcarbonate * THC-VHS THC valine hemisuccinate (THC-VHS, NB-1111, SBI-100) is a synthetic prodrug of tetrahydrocannabinol, developed at the University of Mississippi as a stabilised formulation for ophthalmic administration, for use in the treatment of glaucoma and ... * Nabitan * O-1057 References Benzochromenes Cannabinoids Prodrugs 4-Morpholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cod-THC
Cod-THC (Codeine Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol carbonate) is a synthetic codrug formed by linking tetrahydrocannabinol with codeine via a carbonate bridge. It is well absorbed orally and shows superior analgesic effects in animal studies compared to a simple mixture of the two drugs. See also * Benorilate * Codeine-6-glucuronide * Fenethylline Fenethylline (British Approved Name, BAN, United States Adopted Name, USAN) or fenetylline (International Nonproprietary Name, INN) is a codrug of amphetamine and theophylline and so a mutual prodrug of both. It is also spelled phenethylline; ... * THC-methylcarbonate * THC-O-acetate * THC-VHS References Benzochromenes Cannabinoids Carbonate esters Heterocyclic compounds with 5 rings Methoxy compounds Nitrogen heterocycles Codrugs {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodrug
A prodrug is a pharmacologically inactive medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (ADME). Prodrugs are often designed to improve bioavailability when a drug itself is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. A prodrug may be used to improve how selectively the drug interacts with cells or processes that are not its intended target. This reduces adverse or unintended effects of a drug, especially important in treatments like chemotherapy, which can have severe unintended and undesirable side effects. History Many herbal extracts historically used in medicine contain glycosides (sugar derivatives) of the active agent, which are hydrolyzed in the intestines to release the active and more bioavailable aglycone. For example, sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Mississippi
The University of Mississippi (Epithet, byname Ole Miss) is a Public university, public research university in University, near Oxford, Mississippi, United States, with a University of Mississippi Medical Center, medical center in Jackson, Mississippi, Jackson. It is Mississippi's oldest public university and is the state's largest by enrollment. The Mississippi Legislature chartered the university on February 24, 1844, and in 1848 admitted its first 80 students. During the American Civil War, Civil War, the university operated as a Confederate States of America, Confederate hospital and narrowly avoided destruction by Ulysses S. Grant's forces. In 1962, during the civil rights movement, Ole Miss riot of 1962, a race riot occurred on campus when Racial segregation in the United States, segregationists tried to prevent the enrollment of African American student James Meredith. The university has since taken measures to improve its image. The university is closely associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmic Drug Administration
Ophthalmic drug administration is the administration of a drug to the eyes, most typically as an eye drop formulation. Topical formulations are used to combat a multitude of diseased states of the eye. These states may include bacterial infections, eye injury, glaucoma, and dry eye. However, there are many challenges associated with topical delivery of drugs to the cornea of the eye. Eye drop formulations Two of the largest challenges faced when using topicals to treat pathological states of the eye include Adherence (medicine), patient compliance and ineffective absorbance of drugs into the cornea due to short contact times, solution drainage, tears turnover, and dilution or lacrimation. In fact, researchers in this field of drug delivery agree that less than 7% of drugs delivered to the eye reach and penetrate the corneal barrier, therefore, increasing the frequency of dosing used for topicals. This is one of the fundamental problem associated with using topicals to deliver dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
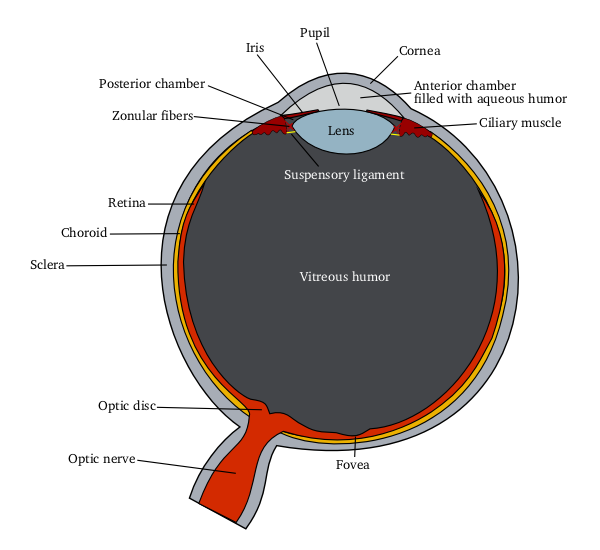
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time. A major risk factor for glaucoma is increased pressure within the eye, known as Intraocular pressure, intraocular pressure (IOP). It is associated with old age, a family history of glaucoma, and certain medical conditions or the use of some medications. The word ''glaucoma'' comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'gleaming, blue-green, gray'. Of the different types of glaucoma, the most common are called open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma. Inside the eye, a liquid called Aqueous humour, aqueous humor helps to maintain shape and provides nutrients. The aqueous humor normally drains through the trabecular meshwork. In open-angle glaucoma, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraocular Pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated to measure pressure in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Physiology Intraocular pressure is determined by the production and drainage of aqueous humour by the ciliary body and its drainage via the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral outflow. The reason for this is because the vitreous humour in the posterior segment has a relatively fixed volume and thus does not affect intraocular pressure regulation. An important quantitative relationship (Goldmann's equation) is as follows: :P_o = \frac + P_v Where: * P_o is the IOP in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) * F the rate of aqueous humour formation in microliters per minute (μL/min) * U the resorption of aqueous humour through the uveoscleral route (μL/min) * C is the facility of outflow in mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |