|
TDRS-B
TDRS-B was an American communications satellite, of first generation, which was to have formed part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was destroyed in 1986 when the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, disintegrated 73 seconds after launch. Launch TDRS-B was launched in the payload bay of ''Challenger'', attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS). It was to have been deployed from the Shuttle in low Earth orbit. The IUS would have then performed two burns to raise the satellite into a geosynchronous orbit. On the previous TDRS launch, TDRS-1, the IUS second-stage motor malfunctioned following the first-stage burn, resulting in a loss of control, and delivery of the satellite into an incorrect orbit. Launch failed TDRS-B was originally scheduled for launch on Canceled Space Shuttle missions#Canceled due to the late development of the Space Shuttle, STS-12 in March 1984; however, it was delayed and the flight cancelled following the IUS failure on TDRS-1. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canceled Space Shuttle Missions
During NASA's Space Shuttle program, several missions were canceled. Many were canceled as a result of the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, ''Challenger'' and the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster , ''Columbia'' disasters or due to delays in the development of the shuttle. Others were canceled because of changes in payload and mission requirements. Canceled due to the late development of the Space Shuttle In 1972, NASA's planners had projected 570 Space Shuttle missions between 1980 and 1991. Later, this estimate was lowered to 487 launches between 1980 and 1992. The details of the first 23 projected missions, listed in the third edition of ''Manned Spaceflight'' (Reginald Turnill, 1978) and the first edition of the ''STS Flight Assignment Baseline'', an internal NASA document published in October 1977, are: Later in the development process, NASA suggested using the first crewed Space Shuttle mission, STS-1, as a sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital test of the Space Shuttl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of TDRS Satellites
This is a list of Tracking and Data Relay Satellites. TDRS spacecraft are all in geostationary orbit and are operated by the United States NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and are used for communication between NASA facilities and spacecraft, including the Space Shuttle, Hubble Space Telescope, and International Space Station. As of 1 March 2019, 12 of the TDRS satellites launched were operational, two (TDRS-3, TDRS-5) had been placed in storage, two (TDRS-1 and TDRS-4) had been retired, and one (TDRS-B) had been lost in a Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, launch failure. Satellites References {{spaceflight lists and timelines Lists of satellites, TDRS Tracking and Data Relay Satellite TDRS satellites, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
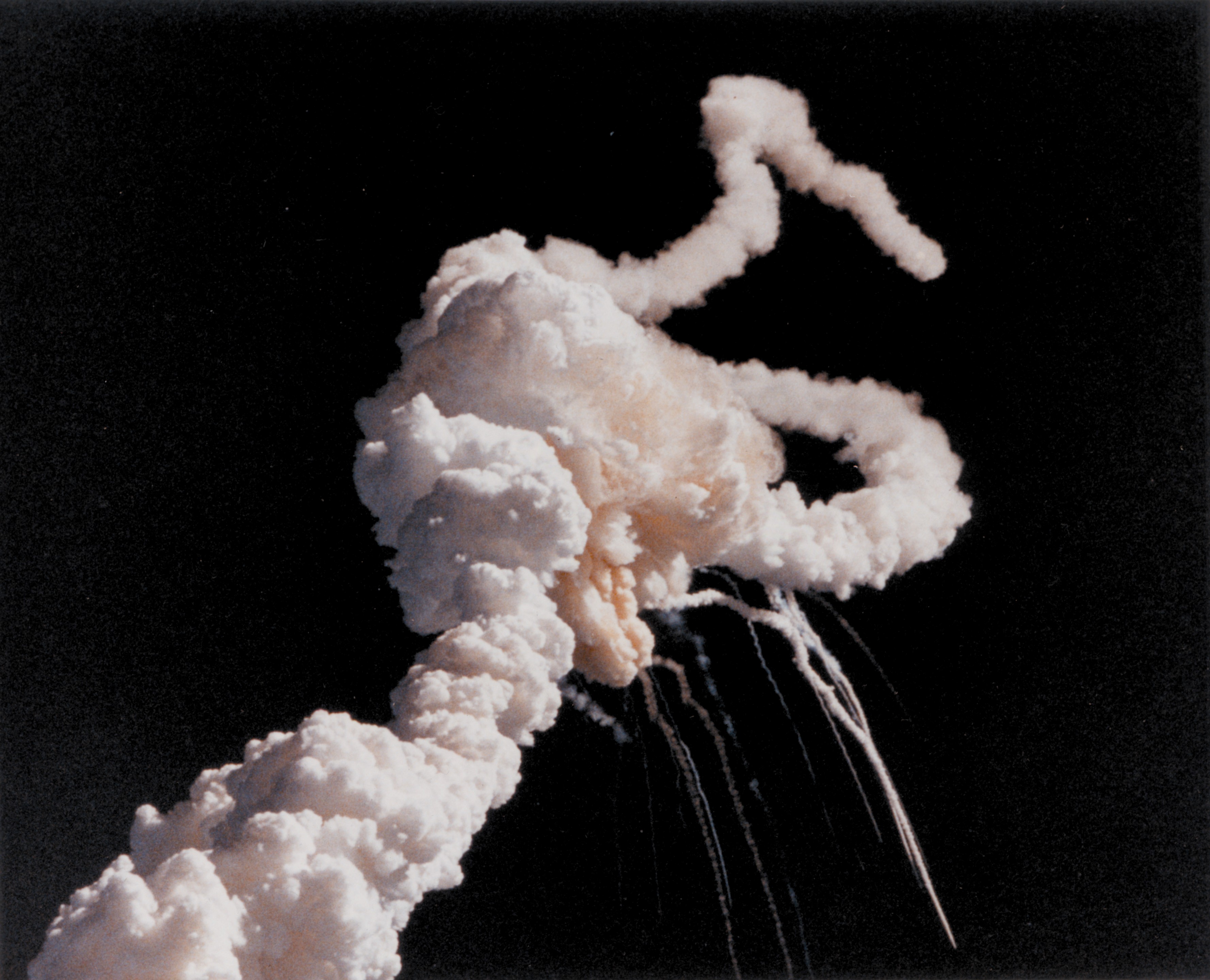
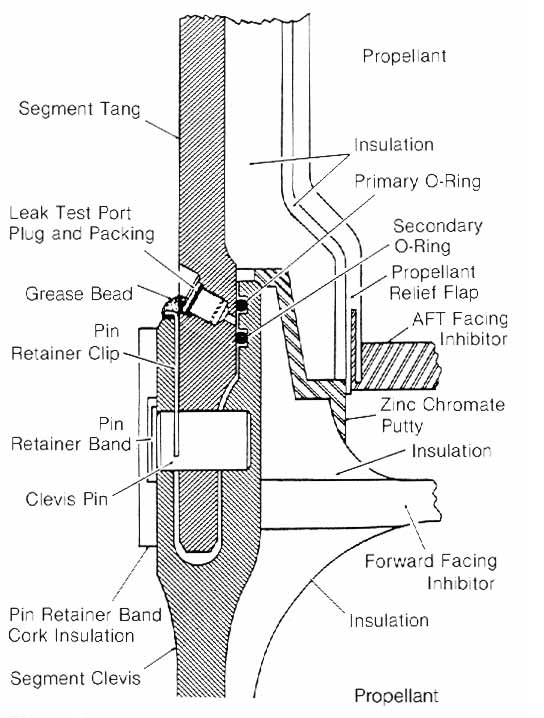
STS-51-L
STS-51-L was the disastrous 25th mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program and the final flight of Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. It was planned as the first Teacher in Space Project flight in addition to observing Halley's Comet for six days and performing a routine satellite deployment. The mission never achieved orbit; a structural failure during its ascent phase 73 seconds after launch from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39B on January 28, 1986, destroyed the orbiter and killed all seven crew members—Commander Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, Pilot Michael J. Smith, Mission Specialists Ellison S. Onizuka, Judith A. Resnik and Ronald E. McNair, and Payload Specialists Gregory B. Jarvis and S. Christa McAuliffe. Immediately after the failure, President Ronald Reagan convened the Rogers Commission to determine the cause of the explosion. The failure of an O-ring seal on the starboard Solid Rocket Booster (SRB) was determined to have caused the shuttle to break up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Challenger Disaster
On January 28, 1986, the Space Shuttle Challenger, Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, killing all seven crew members aboard. The spacecraft disintegrated above the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 16:39:13Coordinated Universal Time, UTC (11:39:13a.m. Eastern Time Zone, EST, local time at the launch site). It was the first fatal accident involving an List of space programs of the United States, American spacecraft while in flight. The mission, designated STS-51-L, was the 10th flight for the Space Shuttle orbiter, orbiter and the 25th flight of the Space Shuttle fleet. The crew was scheduled to deploy a commercial communications satellite and study Halley's Comet while they were in orbit, in addition to taking schoolteacher Christa McAuliffe into space under the Teacher in Space Project. The latter task resulted in a higher-than-usual media interest in and coverage of the mission; the launch and subsequent disaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challenger Explosion
On January 28, 1986, the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, killing all seven crew members aboard. The spacecraft disintegrated above the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 16:39:13 UTC (11:39:13a.m. EST, local time at the launch site). It was the first fatal accident involving an American spacecraft while in flight. The mission, designated STS-51-L, was the 10th flight for the orbiter and the 25th flight of the Space Shuttle fleet. The crew was scheduled to deploy a commercial communications satellite and study Halley's Comet while they were in orbit, in addition to taking schoolteacher Christa McAuliffe into space under the Teacher in Space Project. The latter task resulted in a higher-than-usual media interest in and coverage of the mission; the launch and subsequent disaster were seen live in many schools across the United States. The cause of the disaster was the failure of the primary and secondary O-ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-51-L Recovered Debris (TDRS) - GPN-2004-00007
STS-51-L was the disastrous 25th mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program and the final flight of Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. It was planned as the first Teacher in Space Project flight in addition to observing Halley's Comet for six days and performing a routine satellite deployment. The mission never achieved orbit; a structural failure during its ascent phase 73 seconds after launch from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39B on January 28, 1986, destroyed the orbiter and killed all seven crew members—Commander Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, Pilot Michael J. Smith, Mission Specialists Ellison S. Onizuka, Judith A. Resnik and Ronald E. McNair, and Payload Specialists Gregory B. Jarvis and S. Christa McAuliffe. Immediately after the failure, President Ronald Reagan convened the Rogers Commission to determine the cause of the explosion. The failure of an O-ring seal on the starboard Solid Rocket Booster (SRB) was determined to have caused the shuttle to break up in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TDRS-7
TDRS-7, known before launch as TDRS-G, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW as a replacement for TDRS-B, which had been lost in the ''Challenger'' accident, and was the last first generation TDRS satellite to be launched. History TDRS-7 is based on a custom satellite bus which was used for all seven first generation TDRS satellites. Whilst similar to its predecessors, it differed from them slightly in that twelve G/H band (C band (IEEE)) transponders which had been included on the previous satellites were omitted. It was the last communications satellite, other than amateur radio spacecraft, to be deployed by a Space Shuttle. Launch The TDRS-G satellite was deployed from during the STS-70 mission in 1995. ''Discovery'' was launched from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39B at 13:41:55 UTC on 13 July 1995. TDRS-G was deployed from ''Disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRW Inc
TRW Inc. was an American corporation involved in a variety of businesses, mainly aerospace, electronics, automotive, and credit reporting.http://www.fundinguniverse.com/company-histories/TRW-Inc-Company-History.html TRW Inc. It was a pioneer in multiple fields including electronic components, integrated circuits, computers, software and systems engineering. TRW built many spacecraft, including Pioneer 1, Pioneer 10, and several space-based observatories. It was #57 on the 1986 Fortune 500 list, and had 122,258 employees. The company was called Thompson Ramo Wooldridge Inc., after the 1958 merger of the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation and Thompson Products. This was later shortened to TRW. The company was founded in 1901 and lasted for just over a century until being acquired by Northrop Grumman in 2002. It spawned a variety of corporations, including Pacific Semiconductors, The Aerospace Corporation, Bunker-Ramo and Experian. Its automotive businesses were sold off by Northro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Upper Stage
The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), originally designated the Interim Upper Stage, was a Multistage rocket, two-stage, Solid-propellant rocket, solid-fueled space launch system developed by Boeing for the United States Air Force beginning in 1976 for raising payloads from low Earth orbit to higher orbits or interplanetary trajectories following launch aboard a Titan 34D or Titan IV rocket as its upper stage, or from the payload bay of the Space Shuttle as a space tug. Development During the development of the Space Shuttle, NASA, with support from the Air Force, wanted an upper stage that could be used on the Shuttle to deliver payloads from low earth orbit to higher energy orbits such as geostationary transfer orbit, GTO or geostationary orbit, GEO or to escape velocity for planetary probes. The candidates were the Centaur (rocket), Centaur, propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, the Transtage, propelled by hypergolic storable propellants Aerozine-50 and dinitrogen tetroxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39B
Launch Complex 39B (LC-39B) is the second of Launch Complex 39's three launch pads, located at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Florida. The pad, along with Launch Complex 39A, was first designed for the Saturn V launch vehicle, which at the time was the United States' most powerful rocket. Typically used to launch NASA's crewed spaceflight missions since the late 1960s, the pad is currently configured for use by the agency's Space Launch System rocket, a Shuttle-derived launch vehicle which is currently used in the Artemis program and subsequent Moon to Mars campaigns. The pad had also been leased by NASA to aerospace company Northrop Grumman, for use as a launch site for their Shuttle-derived OmegA launch vehicle, for National Security Space Launch flights and commercial launches, before the OmegA program was cancelled. History Apollo program In 1961, President Kennedy proposed to Congress the goal of landing a man on the Moon by the end of the decade. Congre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-70
STS-70 was the 21st flight of the Space Shuttle Space Shuttle Discovery, ''Discovery'', and the last of 7 shuttle missions to carry a Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS). This was the first shuttle mission controlled from the new mission control center room at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. STS-70 was also the first flight of the new Block 1 orbiter main engine, designed to improve both engine performance and safety. The mission was launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 13, 1995, only six days after the landing of sister ship ''Atlantis'', marking the fastest turnaround between flights in the history of the program. Crew Crew seat assignments Preparations and launch STS-70 had originally moved ahead of STS-71 because of a delay in the launch of the Russian Spektr laboratory module to the Russian space station Mir. However, on May 31, 1995, shuttle managers assessed damage to the External Tank of STS-70 caused by nesting northern flicker, flicker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TDRS-3
TDRS-3, known before launch as TDRS-C, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW, and is based on a custom satellite bus which was used for all seven first generation TDRS satellites. Launch The TDRS-C satellite was launched aboard during the STS-26 mission in 1988; the first Shuttle flight since the ''Challenger'' disaster which had resulted in the loss of the previous TDRS satellite, TDRS-B. ''Discovery'' launched from Launch Complex 39B at the Kennedy Space Center at 15:37:00 UTC on 29 September 1988. TDRS-C was deployed from ''Discovery'' around six hours after launch, and was raised to geostationary orbit by means of an Inertial Upper Stage. Deployment The two-stage solid-propellent Inertial Upper Stage made two burns. The first stage burn occurred shortly after deployment from ''Discovery'', and placed the satellite into a geosynchronous tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |