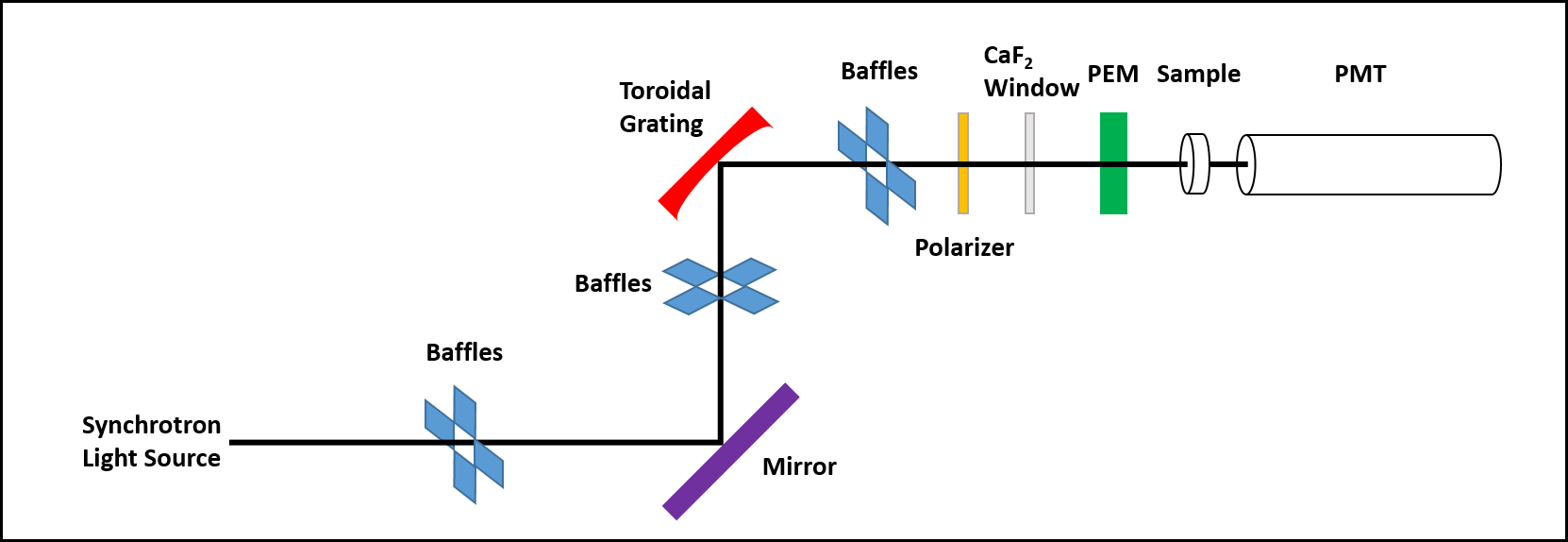|
Synchrotron Radiation Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
Synchrotron radiation circular dichroism spectroscopy, commonly referred to as SRCD and also known as VUV-circular dichroism or VUVCD spectroscopy, is a powerful extension to the technique of circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, often used to study structural properties of biological molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. The physical principles of SRCD are essentially identical to those of CD, in that the technique measures the difference in Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption (ΔA) of left (AL) and right (AR) Circular polarization, circularly polarized light (ΔA=AL-AR) by a sample in solution. To obtain a CD(SRCD) spectrum the sample must be innately optically active (Chirality, chiral), or, in some way be induced to have chiral properties, as only then will there be an observable difference in absorption of the left and right circularly polarized light. The major advantages of SRCD over CD arise from the ability to measure data over an extended wavelengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Dichroism
Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circular polarization, circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum of light, spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. Circular dichroism and optical rotation, circular birefringence are manifestations of optical activity. It is exhibited in the absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption bands of optical activity, optically active chirality (chemistry), chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, Ultraviolet, far-UV CD is used to investigate the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See '' polarization'' and ''plane of polarization'' for more information. The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonnie Ann Wallace
Bonnie Ann Wallace, FRSC (born 10 August 1951) is a British and American biophysicist and biochemist. She is a professor of molecular biophysics in the department of biological sciences, formerly the department of crystallography, at Birkbeck College, University of London, U.K. Early life and education Wallace was born in Greenwich, Connecticut in the United States, the only child of Arthur Victor Wallace and Maryjane Ann Wallace, who were both accountants. She attended Greenwich High School and had a strong interest in science from an early age. She commented on having a Christmas present of a chemistry set which was "quickly disposed of" when she experimented with burning sulphur in the basement of her home. At Greenwich High, she was encouraged to do more when, as top of her chemistry class, she was invited to join an extracurricular science programme. To answer the questions posed to the group, she would make suggestions in devising novel experiments beyond those prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptide chains and amino acid side chains, it was Dorothy Maud Wrinch who incorporated geometry into the prediction of protein structures. Wrinch demonstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik Linderstrøm-Lang at Stanford in 1952. Other types of biopolymers such as nucleic acids also possess characteristic secondary structures. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Band
In spectroscopy, an absorption band is a range of wavelengths, frequency, frequencies or energies in the electromagnetic spectrum that are characteristic of a particular transition from initial to final state in a substance. According to quantum mechanics, atoms and molecules can only hold certain defined quantities of energy, or exist in specific Quantum state, states. When such quantum, quanta of electromagnetic radiation are emitted or absorbed by an atom or molecule, energy of the radiation changes the state of the atom or molecule from an Ground state, initial state to a Excited state, final state. Overview When electromagnetic radiation is absorbed by an atom or molecule, the energy of the radiation changes the state of the atom or molecule from an Ground state, initial state to a Excited state, final state. The number of states in a specific energy range is discrete for gaseous or diluted systems, with discrete energy levels. Condensed matter physics, Condensed systems, lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Water
Heavy water (deuterium oxide, , ) is a form of water (molecule), water in which hydrogen atoms are all deuterium ( or D, also known as ''heavy hydrogen'') rather than the common hydrogen-1 isotope (, also called ''protium'') that makes up most of the hydrogen in normal water. The presence of the heavier isotope gives the water different nuclear properties, and the increase in mass gives it slightly different physical and chemical properties when compared to normal water. Deuterium is a heavy Isotopes of hydrogen, hydrogen isotope. Heavy water contains deuterium atoms and is used in nuclear reactors. Semiheavy water (HDO) is more common than pure heavy water, while heavy-oxygen water is denser but lacks unique properties. Tritiated water is radioactive due to tritium content. Heavy water has different physical properties from regular water, such as being 10.6% denser and having a higher melting point. Heavy water is less Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated at a given temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
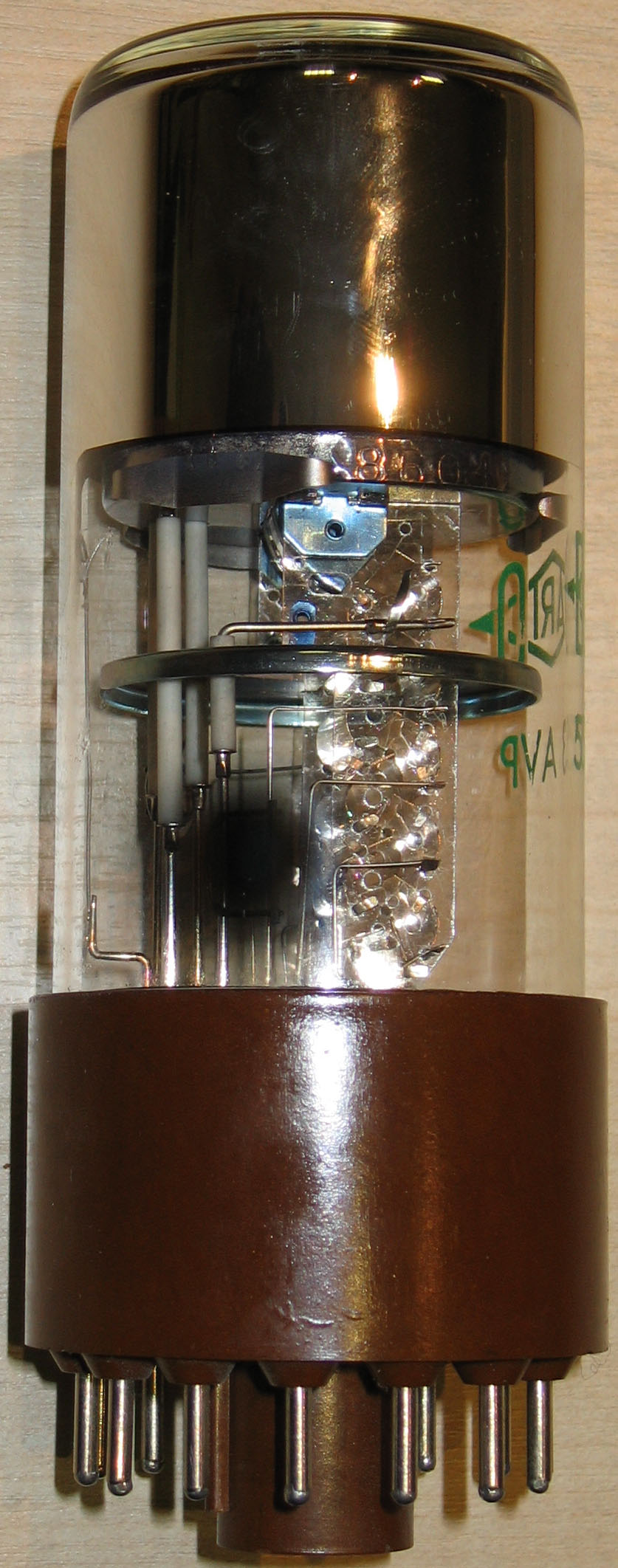
Photomultiplier Tube
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible light, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more specifically vacuum phototubes. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times or 108 (i.e., 160 decibel, dB),Decibels are power ratios. Power is proportional to I2 (current squared). Thus a current gain of 108 produces a power gain of 1016, or 160 decibel, dB in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is low. The combination of high Gain (electronics), gain, low Noise (electronics), noise, high frequency response or, equivalently, ultra-fast response, and large area of collection has maintained photomultipliers an essential place in Spectroscopy, low light level spectroscopy, confocal microscopy, Raman spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelastic Modulator
A photoelastic modulator (PEM) is an optical device used to modulate the polarization of a light source. The photoelastic effect is used to change the birefringence of the optical element in the photoelastic modulator. PEM was first invented by J. Badoz in the 1960s and originally called a "birefringence modulator." It was initially developed for physical measurements including optical rotary dispersion and Faraday rotation, polarimetry of astronomical objects, strain-induced birefringence, and ellipsometry. Later developers of the photoelastic modulator include J.C Kemp, S.N Jasperson and S.E Schnatterly. Description The basic design of a photoelastic modulator consists of a piezoelectric transducer and a half wave resonant bar; the bar being a transparent material (now most commonly fused silica). The transducer is tuned to the natural frequency of the bar. This resonance modulation results in highly sensitive polarization measurements. The fundamental vibration of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Fluoride
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white solid that is practically insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities. Chemical structure The compound crystallizes in a cubic motif called the fluorite structure. Ca2+ centres are eight-coordinate, being centred in a cube of eight F− centres. Each F− centre is coordinated to four Ca2+ centres in the shape of a tetrahedron. Although perfectly packed crystalline samples are colorless, the mineral is often deeply colored due to the presence of F-centers. The same crystal structure is found in numerous ionic compounds with formula AB2, such as CeO2, cubic ZrO2, UO2, ThO2, and PuO2. In the corresponding anti-structure, called the antifluorite structure, anions and cations are swapped, such as Be2C. Gas phase The gas phase is noteworthy for failing the predictions of VSEP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |