|
Surface Chemistry Of Paper
The surface chemistry of paper is responsible for many important paper properties, such as gloss, waterproofing, and printability. Many components are used in the paper-making process that affect the surface. Pigment and dispersion medium Coating components are subject to particle-particle, particle-solvent, and particle-polymer interactions. Van der Waals forces, electrostatic repulsions, and steric stabilization are the reasons for these interactions. Importantly, the characteristics of adhesion and cohesion between the components form the base coating structure. Calcium carbonate and kaolin are commonly used pigments. Pigments support a structure of fine porosity and form a light scattering surface. The surface charge of the pigment plays an important role in dispersion consistency. The surface charge of calcium carbonate is negative and not dependent on pH, however it can decompose under acidic conditions. Kaolin has negatively charged faces while the charge of its lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper-making
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a specialized craft and a medium for artistic expression. In papermaking, a dilute suspension consisting mostly of separate cellulose fibres in water is drained through a sieve-like screen, so that a mat of randomly interwoven fibres is laid down. Water is further removed from this sheet by pressing, sometimes aided by suction or vacuum, or heating. Once dry, a generally flat, uniform and strong sheet of paper is achieved. Before the invention and current widespread adoption of automated machinery, all paper was made by hand, formed or laid one sheet at a time by specialized laborers. Even today those who make paper by hand use tools and technologies quite similar to those existing hundreds of years ago, as originally developed in China and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylic Acid
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: propenoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually. History The word "acrylic" was coined in 1843, for a chemical derivative of acrolein, an acrid-smelling oil derived from glycerol. Production Acrylic acid is produced by oxidation of propylene, which is a byproduct of the production of ethylene and gasoline: : 2 CH2=CHCH3 + 3 O2 → 2 CH2=CHCO2H + 2 H2O Historical methods Because acrylic acid and its esters have long been valued commercially, many other methods have been developed. Most have been abandoned for economic or environmental reasons. An early method was the hydrocarboxylation of acetylene (" Reppe chemistry"): : This method req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Modification
Surface modification is the act of modifying the surface of a material by bringing physical, chemical or biological characteristics different from the ones originally found on the surface of a material. This modification is usually made to solid materials, but it is possible to find examples of the modification to the surface of specific liquids. The modification can be done by different methods with a view to altering a wide range of characteristics of the surface, such as: roughness,is available). hydrophilicity,is available). surface charge, surface energy, biocompatibility and reactivity. Surface engineering Surface engineering is the sub-discipline of materials science which deals with the surface of solid matter. It has applications to chemistry, mechanical engineering, and electrical engineering (particularly in relation to semiconductor manufacturing). Solids are composed of a bulk material covered by a surface. The surface which bounds the bulk material is calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
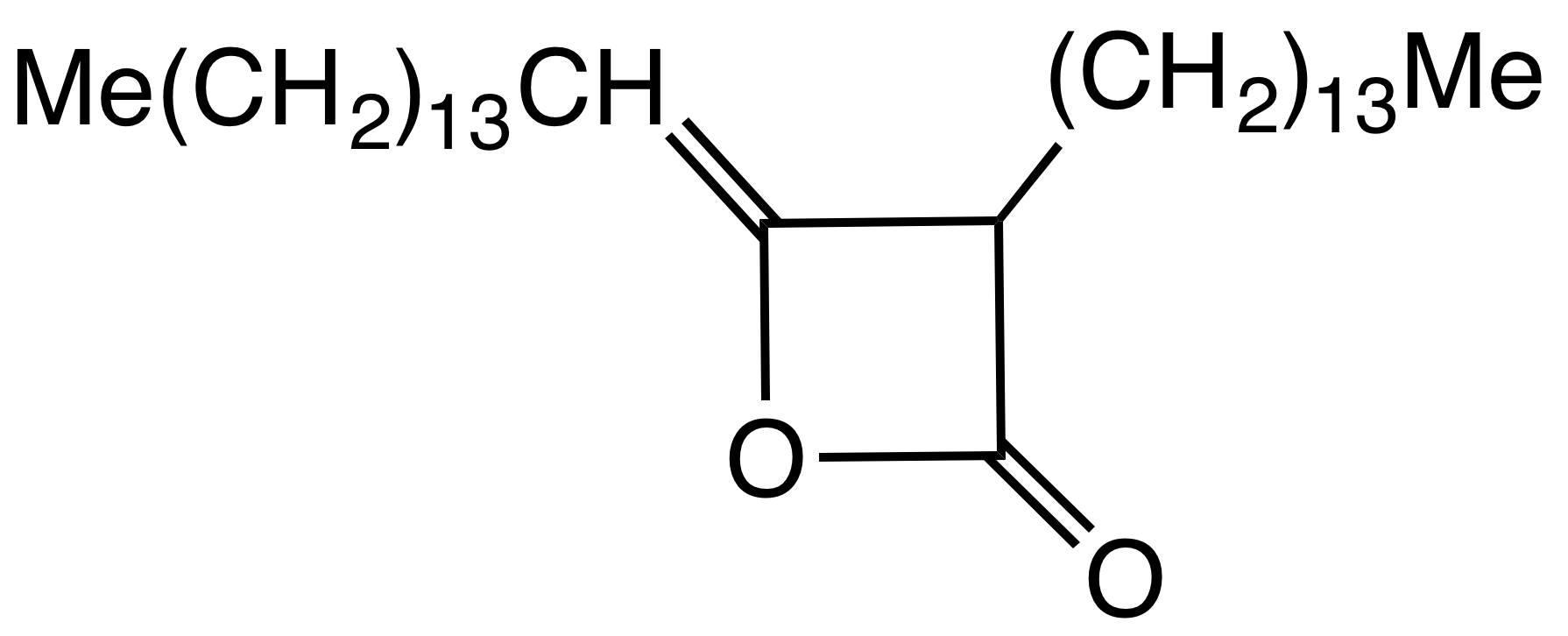
Alkyl Ketene Dimer
Alkyl ketene dimers (AKDs) are a family of organic compounds based on the 4-membered ring system of oxetan-2-one, which is also the central structural element of propiolactone and diketene. Attached to the oxetane ring of technically relevant alkyl ketene dimers there is a C12 – C16 alkyl group in the 3-position and a C13 – C17 alkylidene group in the 4-position. The main application of alkylated ketene dimers is in the sizing of paper and cardboard, as well as in the hydrophobation of cellulose fibers. The products thus modified are distinguished by higher mechanical strengths and less penetration of water, inks or printing inks. AKD's feature hydrophobic alkyl groups extending from a beta-propiolactone ring. A specific example is derived from the dimerization of the ketene of stearic acid. This ketene is generated by pyrolysis of stearoyl chloride. AKD's react with the hydroxyl groups on the cellulose via esterification reaction. The esterification is competitive with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkenyl Succinic Anhydride
Alkenyl succinic anhydrides (ASA) are modified five-membered succinic anhydrides bearing a branched iso- alkenyl chain (C14 to C22). They are colorless, and usually viscous liquids. They are widely used, especially in surface sizing of paper, paperboard, and cardboard, as well as in the hydrophobicization of cellulose fibers. Products treated with it show reduced penetration of aqueous media, such as inks or drinks (like milk or fruit juices). In terms of their mode of action, the anhydride is proposed to react with the hydroxyl groups on the cellulose, forming an ester. The alkenyl side-chain modifies the surface properties of the paper product. The application is similar to that for alkyl ketene dimers. In the United States alkenylsuccinic anhydrides are the preferred paper sizing agents, whereas in Europe, alkyl ketene dimers (AKDs) predominate. History The reaction of maleic anhydride (MAN) with aliphatic monounsaturated ''n''- and ''iso''-alkenes was described as early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. In contrast, hydrophobes are not attracted to water and may seem to be repelled by it. Hygroscopics ''are'' attracted to water, but are not dissolved by water. Molecules A hydrophilic molecule or portion of a molecule is one whose interactions with water and other polar substances are more thermodynamically favorable than their interactions with oil or other hydrophobic solvents. They are typically charge-polarized and capable of hydrogen bonding. This makes these molecules soluble not only in water but also in other polar solvents. Hydrophilic molecules (and portions of molecules) can be contrasted with hydrophobic molecules (and portions of molecules). In some cases, both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties occur in a single molecule. An example of these a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Angle1
Contact may refer to: Interaction Physical interaction * Contact (geology), a common geological feature * Contact lens or contact, a lens placed on the eye * Contact sport, a sport in which players make contact with other players or objects * Contact juggling * Contact mechanics, the study of solid objects that deform when touching each other * Contact process (mathematics), a model of an interacting particle system * Electrical contacts * ''Sparśa'', a concept in Buddhism that in Sanskrit/Indian language is translated as "contact", "touching", "sensation", "sense impression", etc. Social interaction * Contact (amateur radio) * Contact (law), a concept related to visitation rights * Contact (social), a person who can offer help in achieving goals * Contact Conference, an annual scientific conference * Extraterrestrial contact, see Search for extraterrestrial intelligence * First contact (anthropology), an initial meeting of two cultures * Language contact, the interaction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds. Dextrins can be produced from starch using enzymes like amylases, as during digestion in the human body and during malting and mashing, or by applying dry heat under acidic conditions ( pyrolysis or roasting). This procedure was first discovered in 1811 by Edme-Jean Baptiste Bouillon-Lagrange. The latter process is used industrially, and also occurs on the surface of bread during the baking process, contributing to flavor, color and crispness. Dextrins produced by heat are also known as pyrodextrins. Starch hydrolyses during roasting under acidic conditions, and short-chained starch parts partially rebranch with α-(1,6) bonds to the degraded starch molecule. See also Maillard reaction. Dextrins are white, yellow, or brown powder that are partially or fully water- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modified Starch
Modified starch, also called starch derivatives, are prepared by physically, enzymatically, or chemically treating native starch to change its properties. Modified starches are used in practically all starch applications, such as in food products as a thickening agent, stabilizer or emulsifier; in pharmaceuticals as a disintegrant; or as binder in coated paper. They are also used in many other applications. Starches are modified to enhance their performance in different applications. Starches may be modified to increase their stability against excessive heat, acid, shear, time, cooling, or freezing; to change their texture; to decrease or increase their viscosity; to lengthen or shorten gelatinization time; or to increase their visco-stability. Modification methods Acid-treated starch (INS 1401), also called thin boiling starch, is prepared by treating starch or starch granules with inorganic acids, e.g. hydrochloric acid breaking down the starch molecule and thus redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose
Hydroxyethyl cellulose is a gelling and thickening agent derived from cellulose. It is widely used in cosmetics, cleaning solutions, and other household products. Hydroxyethyl cellulose and methyl cellulose are frequently used with hydrophobic drugs in capsule formulations, to improve the drugs' dissolution in the gastrointestinal fluids. This process is known as hydrophilization. Hydroxyethyl cellulose is also used extensively in the oil & gas industry as a drilling mud additive under the name HEC as well in industrial applications, paint & coatings, ceramics, adhesives, emulsion polymerization, inks, construction, welding rods, pencils and joint fillers. Hydroxyethyl cellulose can be one of the main ingredients in water-based personal lubricants. It is also a key ingredient in the formation of big bubbles as it possesses the ability to dissolve in water but also provide structural strength to the soap bubble. Among other similar chemicals, it is often used as slime (and gun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)