|
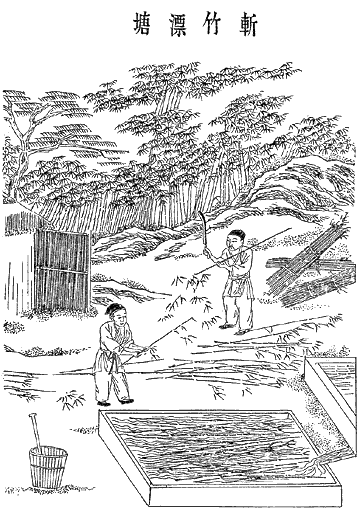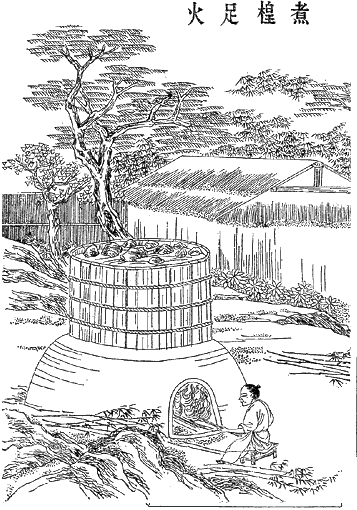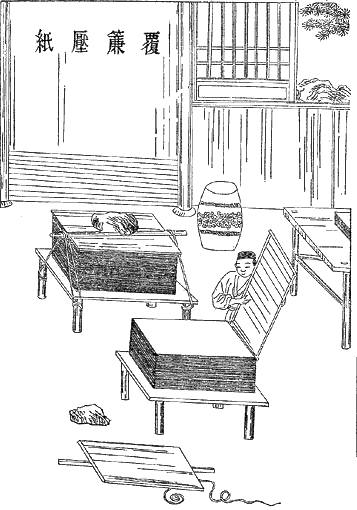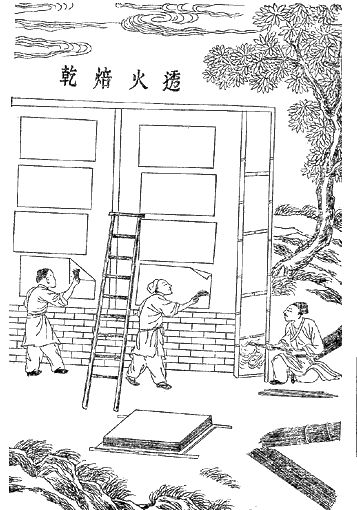
Paper-making
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a specialized craft and a medium for artistic expression. In papermaking, a dilute suspension consisting mostly of separate cellulose fibres in water is drained through a sieve-like screen, so that a mat of randomly interwoven fibres is laid down. Water is further removed from this sheet by pressing, sometimes aided by suction or vacuum, or heating. Once dry, a generally flat, uniform and strong sheet of paper is achieved. Before the invention and current widespread adoption of automated machinery, all paper was made by hand, formed or laid one sheet at a time by specialized laborers. Even today those who make paper by hand use tools and technologies quite similar to those existing hundreds of years ago, as originally developed in China and other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cai Lun
Cai Lun ( zh, s=蔡伦; courtesy name: Jingzhong ( zh, labels=no, t=敬仲, s=敬仲); – 121 CE), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Ts'ai Lun, was a Eunuchs in China, Chinese eunuch court official of the Eastern Han dynasty. He occupies a pivotal place in the history of paper due to his addition of Pulp (paper), pulp via Bark (botany), tree bark and hemp ends which resulted in the large-scale manufacture and worldwide spread of paper. Although traditionally regarded as the inventor of paper, earlier forms of paper have existed since the 3rd century BCE, so Cai's contributions are limited to innovation, rather than invention. Born in (in what is now Leiyang), Cai arrived at the imperial court in Old City of Luoyang, Luoyang by 75 CE, where he served as a Chamberlain (office), chamberlain for Emperor Ming of Han, Emperor Ming, and then as , an imperial messenger for Emperor Zhang of Han, Emperor Zhang. To assist Empress Dou (Zhang), Lady Dou in securing her adop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocco border, the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to Morocco–Western Sahara border, the south. Morocco also claims the Spain, Spanish Enclave and exclave, exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Plazas de soberanía, Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It has a population of approximately 37 million. Islam is both the official and predominant religion, while Arabic and Berber are the official languages. Additionally, French and the Moroccan dialect of Arabic are widely spoken. The culture of Morocco is a mix of Arab culture, Arab, Berbers, Berber, Culture of Africa, African and Culture of Europe, European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of largest cities in the Arab world, the Arab world, and List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East, the Middle East. The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is List of largest cities, one of the largest in the world by population with over 22.1 million people. The area that would become Cairo was part of ancient Egypt, as the Giza pyramid complex and the ancient cities of Memphis, Egypt, Memphis and Heliopolis (ancient Egypt), Heliopolis are near-by. Located near the Nile Delta, the predecessor settlement was Fustat following the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 641 next to an existing ancient Roman empire, Roman fortress, Babylon Fortress, Babylon. Subsequently, Cairo was founded by the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid dynasty in 969. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Known colloquially in Syria as () and dubbed, poetically, the "City of Jasmine" ( ), Damascus is a major cultural center of the Levant and the Arab world. Situated in southwestern Syria, Damascus is the center of a large metropolitan area. Nestled among the eastern foothills of the Anti-Lebanon mountain range inland from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean on a plateau above sea level, Damascus experiences an arid climate because of the rain shadow effect. The Barada, Barada River flows through Damascus. Damascus is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. First settled in the 3rd millennium BC, it was chosen as the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate from 661 to 750. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the Arab world, most populous cities in the Middle East and Arab world and forms 22% of the Demographics of Iraq, country's population. Spanning an area of approximately , Baghdad is the capital of its Baghdad Governorate, governorate and serves as Iraq's political, economic, and cultural hub. Founded in 762 AD by Al-Mansur, Baghdad was the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate and became its most notable development project. The city evolved into a cultural and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multi-ethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning". For much of the Abbasid era, duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central Asia. Samarkand is the capital of the Samarkand Region and a district-level city, that includes the urban-type settlements Kimyogarlar, Farxod, Farhod and Xishrav, Khishrav. With 551,700 inhabitants (2021), it is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, third-largest city in Uzbekistan. There is evidence of human activity in the area of the city dating from the late Paleolithic Era. Though there is no direct evidence of when Samarkand was founded, several theories propose that it was founded between the 8th and 7th centuries BC. Prospering from its location on the Silk Road between East Asia, China, Persia and Europe, at times Samarkand was one of the largest cities in Central Asia,Guidebook of history of Samarkand", and was an important city of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim World
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In a modern geopolitical sense, these terms refer to countries in which Islam is widespread, although there are no agreed criteria for inclusion. The term Muslim-majority countries is an alternative often used for the latter sense. The history of the Muslim world spans about 1,400 years and includes a variety of socio-political developments, as well as advances in the arts, science, medicine, philosophy, law, economics and technology during the Islamic Golden Age. Muslims look for guidance to the Quran and believe in the prophetic mission of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, but disagreements on other matters have led to the appearance of different religious schools of thought and sects within Islam. The Islamic conquests, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period#Ten Kingdoms, Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song frequently came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao dynasty, Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China following attacks by the Jin dynasty, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The History of the Song dynasty, dynasty's history is divided into two periods: during the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now East China. The #Southern Song, 1127–1279, Southern Song (; 1127–1279) comprise the period following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tea Bag
A tea bag (or teabag) is a small, porous, sealed bag or Packet (container), packet typically containing tea leaves (''Camellia sinensis'') or the leaves of other herbs, which is immersed in water to steeping, steep and make an infusion. Originally used only for making tea, they are now made for other herbal tea, tisanes (herbal "teas") as well. Tea bags are commonly made of Filter paper#Tea bags, filter paper or food grade plastic, food-grade plastic, or occasionally of silk cotton or silk. The tea bag performs the same function as a tea infuser. Tea bags can be used multiple times until there is no extraction left. Some tea bags have an attached piece of string with a paper label at the top that assists in removing the bag, while also displaying the brand or variety of tea. There are also special tea filters that can be used to pour loose tea into and brew it in a bag in a cup. History Tea bag patents date from 1903, when Roberta Lawson and Mary McLaren, of Milwaukee, Wiscon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toilet Paper
Toilet paper (sometimes called toilet/bath/bathroom tissue, or toilet roll) is a tissue paper product primarily used to clean the human anus, anus and surrounding region of Human feces, feces (after defecation), and to clean the external genitalia and perineum, perineal area of urine (after urination). It is commonly supplied as a long strip of perforated paper wrapped around a cylindrical paperboard core, for Toilet paper holder, storage in a dispenser within arm's reach of a toilet. The bundle, or ''roll of toilet paper'', is specifically known as a toilet roll, loo roll, or bog roll (in British English, Britain). There are other uses for toilet paper, as it is a readily available household product. It can be used for blowing the nose or wiping the eyes (or other uses of facial tissue). It can be used to wipe off sweat or absorb it. Some people may use the paper to absorb the bloody discharge that comes out of the vagina during menstruation. Toilet paper can be used in cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |