|
Superior Hypophyseal Artery
The superior hypophyseal artery is an artery supplying the pars tuberalis, the infundibulum of the pituitary gland, and the median eminence The median eminence, part of the inferior boundary of the hypothalamus in the brain, is attached to the infundibulum. The median eminence is a small swelling on the tuber cinereum, posterior to and atop the pituitary stalk; it lies in the area r .... It is a branch of the cerebral part of the internal carotid artery. References Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". However, in clinical settings, the classification system of the internal carotid artery usually follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier—C1 cervical, C2 petrous, C3 lacerum, C4 cavernous, C5 clinoid, C6 ophthalmic, and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
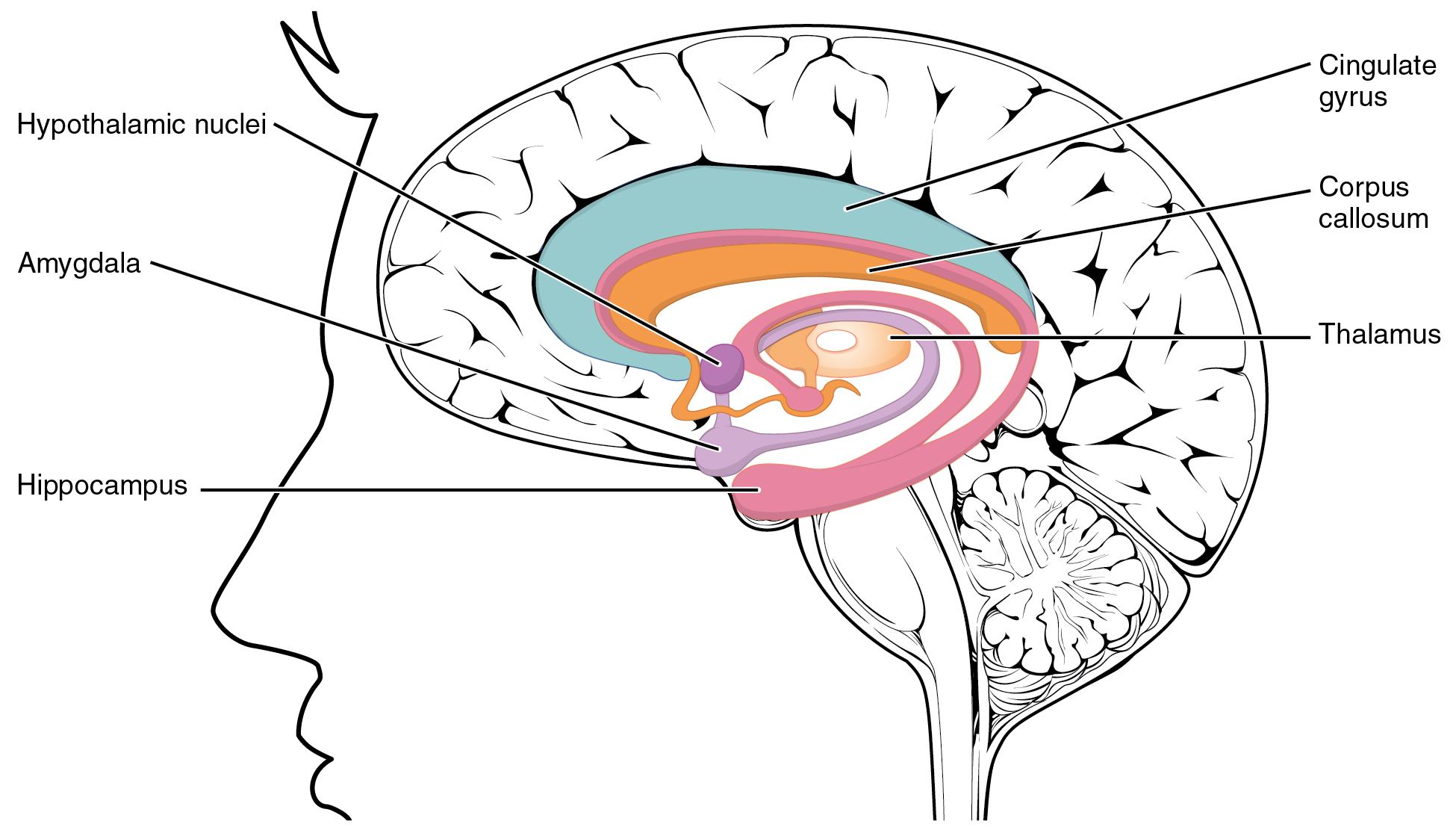
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary glan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pars Tuberalis
The pars tuberalis is part of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, and wraps the pituitary stalk in a highly vascularized sheath. Histology Principal cells of the pars tuberalis are low columnar in form, with the cytoplasm containing numerous lipid droplets, glycogen granules, and occasional colloid droplets. A sparse population of functional gonadotrophs are present (indicated by immunoreactivity for ACTH, FSH, and LH).Ross, Michael. Histology: A Text and Atlas. 5th ed., 2006. pp 695 References It is an extension of the pars distalis up and around infundibulum. External links * * Slide at pitt.edu {{Authority control Endocrine system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary glan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Eminence
The median eminence, part of the inferior boundary of the hypothalamus in the brain, is attached to the infundibulum. The median eminence is a small swelling on the tuber cinereum, posterior to and atop the pituitary stalk; it lies in the area roughly bounded on its posterolateral region by the cerebral peduncles, and on its anterolateral region by the optic chiasm. As one of the seven areas of the brain devoid of a blood–brain barrier, the median eminence is a circumventricular organ having permeable capillaries. Its main function is as a gateway for release of hypothalamic hormones, although it does share contiguous perivascular spaces with the adjacent hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, indicating a potential sensory role. __TOC__ Physiology The median eminence is a part of the hypothalamus from which regulatory hormones are released. It is integral to the hypophyseal portal system, which connects the hypothalamus with the pituitary gland. The pars nervosa (part of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |