|
Supercritical Water Reactor
The supercritical water reactor (SCWR) is a concept Generation IV reactor, designed as a light water reactor (LWR) that operates at supercritical pressure (i.e. greater than 22.1 MPa). The term ''critical'' in this context refers to the critical point of water, and must not be confused with the concept of criticality of the nuclear reactor. The water heated in the reactor core becomes a supercritical fluid above the critical temperature of 374 °C, transitioning from a fluid more resembling liquid water to a fluid more resembling saturated steam (which can be used in a steam turbine), without going through the distinct phase transition of boiling. In contrast, the well-established pressurized water reactors (PWR) have a primary cooling loop of liquid water at a subcritical pressure, transporting heat from the reactor core to a secondary cooling loop, where the steam for driving the turbines is produced in a boiler (called the steam generator). Boiling water react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercritical-Water-Cooled Reactor
The supercritical water reactor (SCWR) is a concept Generation IV reactor, designed as a light water reactor (LWR) that operates at supercritical pressure (i.e. greater than 22.1 MPa). The term ''critical'' in this context refers to the critical point of water, and must not be confused with the concept of criticality of the nuclear reactor. The water heated in the reactor core becomes a supercritical fluid above the critical temperature of 374 °C, transitioning from a fluid more resembling liquid water to a fluid more resembling saturated steam (which can be used in a steam turbine), without going through the distinct phase transition of boiling. In contrast, the well-established pressurized water reactors (PWR) have a primary cooling loop of liquid water at a subcritical pressure, transporting heat from the reactor core to a secondary cooling loop, where the steam for driving the turbines is produced in a boiler (called the steam generator). Boiling water rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beloyarsk Nuclear Power Station
The Beloyarsk Nuclear Power Station (NPS; russian: Белоярская атомная электростанция им. И. В. Курчатова []) was the third of the Soviet Union, Soviet Union's nuclear plants. It is situated by Zarechny, Sverdlovsk Oblast, Zarechny in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia. Zarechny township was created to service the station, which is named after the Beloyarsky District. The closest city is Yekaterinburg. Early reactors Two earlier reactors were constructed at Beloyarsk: an AMB-100 reactor (operational 1964–1983) and an AMB-200 reactor (operational 1967–1989). Both were supercritical water reactors; the first unit used 67 tons of uranium enriched to 1.8%, while the second unit used 50 tons of uranium enriched to 3.0%. The first unit had an indirect steam cycle, while the second had a direct one. Although they were comparable in power to the Shippingport Atomic Power Station, the Soviet planners regarded the Beloyarsk reactors as prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strength Of Materials
The field of strength of materials, also called mechanics of materials, typically refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members, such as beams, columns, and shafts. The methods employed to predict the response of a structure under loading and its susceptibility to various failure modes takes into account the properties of the materials such as its yield strength, ultimate strength, Young's modulus, and Poisson's ratio. In addition, the mechanical element's macroscopic properties (geometric properties) such as its length, width, thickness, boundary constraints and abrupt changes in geometry such as holes are considered. The theory began with the consideration of the behavior of one and two dimensional members of structures, whose states of stress can be approximated as two dimensional, and was then generalized to three dimensions to develop a more complete theory of the elastic and plastic behavior of materials. An important founding p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embrittlement
Embrittlement is a significant decrease of ductility of a material, which makes the material brittle. Embrittlement is used to describe any phenomena where the environment compromises a stressed material's mechanical performance, such as temperature or environmental composition. This is oftentimes undesirable as brittle fracture occurs quicker and can much more easily propagate than ductile fracture, leading to complete failure of the equipment. Various materials have different mechanisms of embrittlement, therefore it can manifest in a variety of ways, from slow crack growth to a reduction of tensile ductility and toughness. Mechanisms Embrittlement is a series complex mechanism that is not completely understood. The mechanisms can be driven by temperature, stresses, grain boundaries, or material composition. However, by studying the embrittlement process, preventative measures can be put in place to mitigate the effects. There are several ways to study the mechanisms. During me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiolysis
Radiolysis is the dissociation of molecules by ionizing radiation. It is the cleavage of one or several chemical bonds resulting from exposure to high-energy flux. The radiation in this context is associated with ionizing radiation; radiolysis is therefore distinguished from, for example, photolysis of the Cl2 molecule into two Cl-radicals, where (ultraviolet or visible spectrum) light is used. For example, water dissociates under alpha radiation into a hydrogen radical and a hydroxyl radical, unlike ionization of water which produces a hydrogen ion and a hydroxide ion. The chemistry of concentrated solutions under ionizing radiation is extremely complex. Radiolysis can locally modify redox conditions, and therefore the speciation and the solubility of the compounds. Water decomposition Of all the radiation-based chemical reactions that have been studied, the most important is the decomposition of water. When exposed to radiation, water undergoes a breakdown sequence into h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladding (nuclear Fuel)
Cladding is an outer layer of material covering another. It may refer to the following: *Cladding (boiler), the layer of insulation and outer wrapping around a boiler shell *Cladding (construction), materials applied to the exterior of buildings **Wall cladding, exterior material applied to the walls of a building ** Copper cladding, applying copper to the exterior of buildings **Rainscreen cladding, an exterior wall detail to create a capillary break and to allow drainage and evaporation of water *Cladding (fiber optics), fiber optics property to contain light in the core of the fiber by total internal reflection *Cladding (metalworking) Cladding is the bonding together of dissimilar metals. It is different from fusion welding or gluing as a method to fasten the metals together. Cladding is often achieved by extruding two metals through a die as well as pressing or rolling sh ..., a bonding together of dissimilar metals * Cladding (nuclear fuel), the outer layer of the fue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Radiation
Neutron radiation is a form of ionizing radiation that presents as free neutrons. Typical phenomena are nuclear fission or nuclear fusion causing the release of free neutrons, which then react with nuclei of other atoms to form new isotopes—which, in turn, may trigger further neutron radiation. Free neutrons are unstable, decaying into a proton, an electron, plus an electron antineutrino. Free neutrons have a mean lifetime of 887 seconds (14 minutes, 47 seconds). Neutron radiation is distinct from alpha, beta and gamma radiation. Sources Neutrons may be emitted from nuclear fusion or nuclear fission, or from other nuclear reactions such as radioactive decay or particle interactions with cosmic rays or within particle accelerators. Large neutron sources are rare, and usually limited to large-sized devices such as nuclear reactors or particle accelerators, including the Spallation Neutron Source. Neutron radiation was discovered from observing an alpha particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Rods
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing many neutrons without themselves decaying. These elements have different neutron capture cross sections for neutrons of various energies. Boiling water reactors (BWR), pressurized water reactors (PWR), and heavy-water reactors (HWR) operate with thermal neutrons, while breeder reactors operate with fast neutrons. Each reactor design can use different control rod materials based on the energy spectrum of its neutrons. Control rods have been used in nuclear aircraft engines like Project Pluto as a method of control. Operating principle Control rods are inserted into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted in order to control the rate of the nuclear chain reaction and, thereby, the thermal power output of the reactor, the rate of st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
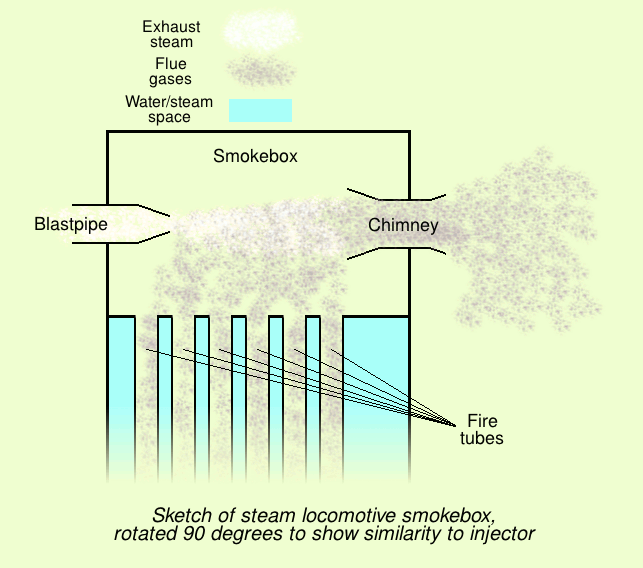
Jet Pump
An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow. A steam injector is a typical application of the principle used to deliver cold water to a boiler against its own pressure, using its own live or exhaust steam, replacing any mechanical pump. When first developed, its operation was intriguing because it seemed paradoxical, almost like perpetual motion, but it was later explained using thermodynamics. Other types of injector may use other pressurised motive fluids such as air. Depending on the application, an injector can also take the form of an ''eductor-jet pump'', a '' water eductor'' or an ''aspirator''. An '' ejector'' operates on similar principles to create a vacuum feed connection for braking systems etc. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressurized Water Reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan and Canada). In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms. The heated, high pressure water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to lower pressure water of a secondary system where steam is generated. The steam then drives turbines, which spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor (BWR), pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All light-water reactors use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator. Most use anywhere from two to four vertically mounted steam generators; VVER reactors use horizontal steam generators. PWRs were originally designed to serve as nuclear marine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely more susceptible than fast neutrons to propagate a nuclear chain reaction of uranium-235 or other fissile isotope by colliding with their atomic nucleus. Water (sometimes called "light water" in this context) is the most commonly used moderator (roughly 75% of the world's reactors). Solid graphite (20% of reactors) and heavy water (5% of reactors) are the main alternatives. Beryllium has also been used in some experimental types, and hydrocarbons have been suggested as another possibility. Moderation Neutrons are normally bound into an atomic nucleus, and do not exist free for long in nature. The unbound neutron has a half-life of 10 minutes and 11 seconds. The release of neutrons from the nucleus requires exceeding the binding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Reactor
A fast-neutron reactor (FNR) or fast-spectrum reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons (carrying energies above 1 MeV or greater, on average), as opposed to slow thermal neutrons used in thermal-neutron reactors. Such a fast reactor needs no neutron moderator, but requires fuel that is relatively rich in fissile material when compared to that required for a thermal-neutron reactor. Around 20 land based fast reactors have been built, accumulating over 400 reactor years of operation globally. The largest of this was the Superphénix Sodium cooled fast reactor in France that was designed to deliver 1,242 MWe. Fast reactors have been intensely studied since the 1950s, as they provide certain decisive advantages over the existing fleet of water cooled and water moderated reactors. These are: * More neutrons are produced when a fission occurs, resulting from the absorption of a fast neutron, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |