|
SuperMemo
SuperMemo (from "Super Memory") is a learning method and software package developed by SuperMemo World and SuperMemo R&D with Piotr Woźniak in Poland from 1985 to the present. It is based on research into long-term memory, and is a practical application of the spaced repetition learning method that has been proposed for efficient instruction by a number of psychologists as early as in the 1930s. The method is available as a computer program for Windows, Windows CE, Windows Mobile (Pocket PC), Palm OS (PalmPilot), etc. Course software by the same company (''SuperMemo World'') can also be used in a web browser or even without a computer. The desktop version of SuperMemo started as a flashcard software (SuperMemo 1.0 (1987)). Since SuperMemo 10 (2000), it began to support incremental reading. Software implementation The SuperMemo program stores a database of questions and answers constructed by the user. When reviewing information saved in the database, the program uses the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anki (software)
Anki (, ; ) is a free and open-source flashcard program. It uses techniques from cognitive science such as active recall testing and spaced repetition to aid the user in memorization. The name comes from the Japanese word for "memorization" (). The SM-2 algorithm, created for SuperMemo in the late 1980s, has historically formed the basis of the spaced repetition methods employed in the program. Anki's implementation of the algorithm has been modified to allow priorities on cards and to show flashcards in order of their urgency. Anki 23.10+ also has a native implementation of the Free Spaced Repetition Scheduler (FSRS) algorithm, which allows for more optimal spacing of card repetitions. Anki is content-agnostic, and the cards are presented using HTML and may include text, images, sounds, videos, and LaTeX equations. The decks of cards, along with the user's statistics, are stored in the open SQLite format. Features Notes Cards are generated from information stored as "no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
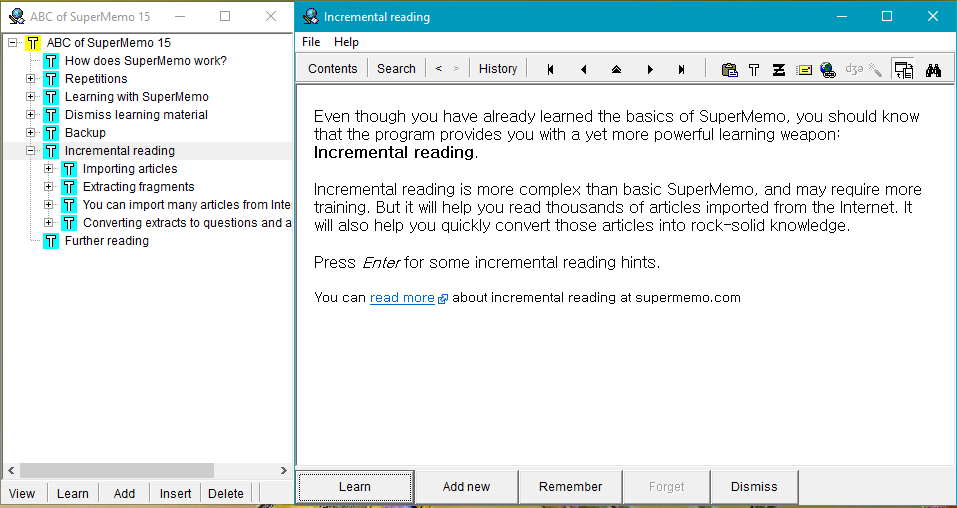
Incremental Reading
Incremental reading is a software-assisted method for learning and retaining information from reading, which involves the creation of flashcards out of electronic articles. "Incremental reading" means "reading in portions". Instead of a linear reading of articles one at a time, the method works by keeping a large list of electronic articles or books (often dozens or hundreds) and reading parts of several articles in each session. The user prioritizes articles in the reading list. During reading, key points of articles are broken up into flashcards, which are then learned and reviewed over an extended period with the help of a spaced repetition algorithm. This use of flashcards at later stages of the process is based on the spacing effect (the phenomenon whereby learning is greater when studying is spread out over time) and the testing effect (the finding that long-term memory is increased when some of the learning periods are devoted to retrieving the to-be-remembered informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piotr Woźniak (researcher)
Piotr A. Woźniak (; born 1962) is a Polish researcher best known for his work on SuperMemo, a learning system based on spaced repetition. Life Woźniak was born in March 1962 in Milanówek, Poland. He began to develop his spaced-repetition software after struggling to retain course material as a student at the Poznań University of Technology in the 1980s. He received a doctorate from the Wrocław University of Economics in 1995. His doctoral dissertation was entitled ''Economics of Learning: New Aspects in Designing Modern Computer Aided Self-Instruction Systems''. He prefers anonymity as it allows him to focus on his learning without distraction. Interests and ideas In addition to the theory of spaced repetition, Woźniak's research interests include incremental reading and the optimization of sleep. He has written extensively about the failure of schooling, believing that learning needs to be driven by the natural "learn drive". He supports the idea of a single internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemosyne (software)
Mnemosyne (named for the Greek goddess of memory, Mnemosyne) is a line of spaced repetition software developed since 2003. Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that has been shown to increase the rate of memorization. Features * Spacing algorithm based on an early version of the SuperMemo algorithm, SM-2, with some modifications that deal with early and late repetitions. * Supports pictures, sound, video, HTML, Flash and LaTeX * Portable (can be installed on a USB stick) * Categorization of cards * Learning progress statistics * Stores learning data (represented as decks of cards that each have a question and an answer side) in ".mem" database files, which are interoperable with a number of other spaced repetition applications * Plugins and JavaScript support * Review cards on Android devices. * Synchronization between other machines Overview Each day, the software displays each card that is scheduled for repetition. The user then grades their recollection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flashcard
A flashcard or flash card is a card bearing information on both sides, usually intended to practice and/or aid memorization. It can be virtual (part of a flashcard software) or physical. Typically, each flashcard bears a question or definition on one side and an answer or target term on the other. As such, flashcards are often used to memorize vocabulary, historical dates, formulae, or any subject matter that can be learned via a question-and-answer format. Flashcards are an application of the testing effect, the finding that long-term memory is increased when some part of an individual's learning period is devoted to retrieving information through testing with proper feedback. Study habits affect the rate at which a flashcard user learns, and proper spacing of flashcards has been proven to accelerate learning. Format Two-sided cards Physical flashcards are two-sided. They have a number of uses and can be simple or elaborate depending on the user's needs and preferences. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Flashcard Software
This article contains a list of notable flashcard software. Flashcards are widely used as a learning drill to aid Memory, memorization by way of spaced repetition. Software Platform support References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Org-mode
Mode (also: ''org-mode''; ) is a mode for document editing, formatting, and organizing within the free software text editor GNU Emacs and its derivatives, designed for notes, planning, and authoring. The name is used to encompass plain text files ("org files") that include simple marks to indicate levels of a hierarchy (such as the outline of an essay, a topic list with subtopics, nested computer code, etc.), and an editor with functions that can read the markup and manipulate hierarchy elements (expand/hide elements, move blocks of elements, check off to-do list items, etc.). Org Mode was created by Carsten Dominik in 2003, originally to organize his own life and work, and since the first release numerous other users and developers have contributed to this free software package. Emacs has included Org Mode as a major mode by default since 2006. Bastien Guerry is the maintainer since 2010, in cooperation with an active development community. Since its success in Emacs, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Links
An internal link is a type of hyperlink on a web page to another page or resource, such as an image or document, on the same website or domain. It is the opposite of an external link, a link that directs a user to content that is outside its domain. Hyperlinks are considered either "external" or "internal" depending on their target or destination. Generally, a link to a page outside the same domain or website is considered external, whereas one that points at another section of the same web page or to another page of the same website or domain is considered internal. Both internal and external links allow users of the website to navigate to another web page or resource. These definitions become clouded, however, when the same organization operates multiple domains functioning as a single web experience, e.g. when a secure commerce website is used for purchasing things displayed on a non-secure website. In these cases, links that are "external" by the above definition can conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (GNU) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that the source code—the preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers can also display content stored locally on the user's device. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches and consoles. As of 2024, the most used browsers worldwide are Google Chrome (~66% market share), Safari (~16%), Edge (~6%), Firefox (~3%), Samsung Internet (~2%), and Opera (~2%). As of 2023, an estimated 5.4 billion people had used a browser. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content and display it on the user's device. This process begins when the user inputs a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as ''https://en.wikipedia.org/'', into the browser's address bar. Virtually all URLs on the Web start with either ''http:'' or ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PalmPilot
The PalmPilot Personal and PalmPilot Professional are the second generation of Palm PDA devices produced by Palm Inc (then a subsidiary of U.S. Robotics, later 3Com). These devices were launched on March 10, 1997. Accessories and pricing Palm also sold the 10201U modem at 14.4 kbit/s, introduced at a price of $129 (this modem is also compatible with the Palm III and Palm IIIx devices). An upgrade kit was also available, which allowed users of the earlier Pilot 1000/5000 devices to upgrade the OS, ROM, and RAM to match the PalmPilot Professional. Initially suggested retail prices upon launch were $399 for the PalmPilot Professional (1 MB), $299 for the PalmPilot Personal (512 KB), and $199 for the Upgrade Kit. Upgrade kits were also available to existing registered Pilot users for $99 for a limited time after the launch. These kits included IR capability, a new plastic memory door to accommodate the IR diodes, a memory card with 1 MB, the new ROM for P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |