|
Structural Break Test
In econometrics and statistics, a structural break is an unexpected change over time in the parameters of regression models, which can lead to huge forecasting errors and unreliability of the model in general. This issue was popularised by David Hendry, who argued that lack of stability of coefficients frequently caused forecast failure, and therefore we must routinely test for structural stability. Structural stability − i.e., the time-invariance of regression coefficients − is a central issue in all applications of linear regression models. Structural break tests A single break in mean with a known breakpoint For linear regression models, the Chow test is often used to test for a single break in mean at a known time period for . This test assesses whether the coefficients in a regression model are the same for periods and . Other forms of structural breaks Other challenges occur where there are: :Case 1: a known number of breaks in mean with unknown break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
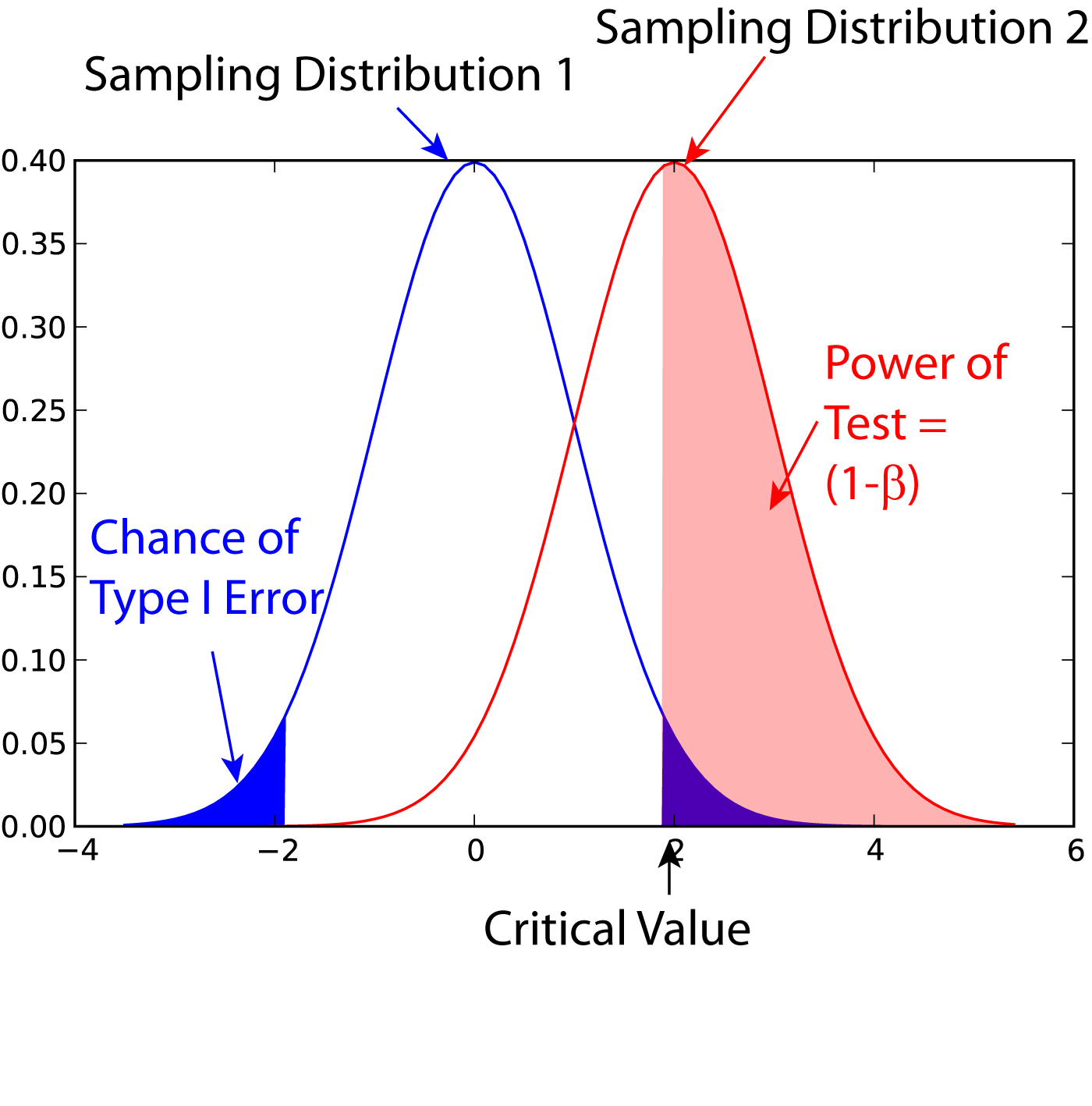 |
Statistical Power
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Structural Change
In economics, structural change is a shift or change in the basic ways a market or economy functions or operates. Such change can be caused by such factors as economic development, global shifts in capital and labor, changes in resource availability due to war or natural disaster or discovery or depletion of natural resources, or a change in political system. For example, a subsistence economy may be transformed into a manufacturing economy, or a regulated mixed economy may be liberalized. A current driver of structural change in the world economy is globalization. Structural change is possible because of the dynamic nature of the economic system. Patterns and changes in sectoral employment drive demand shifts through the income elasticity. Shifting demand for both locally sourced goods and for imported products is a fundamental part of development. The structural changes that move countries through the development process are often viewed in terms of shifts from primary, to seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Stata
Stata (, , alternatively , occasionally stylized as STATA) is a general-purpose statistical software package developed by StataCorp for data manipulation, visualization, statistics, and automated reporting. It is used by researchers in many fields, including biomedicine, epidemiology, sociology and science. Stata was initially developed by Computing Resource Center in California and the first version was released in 1985. In 1993, the company moved to College Station, TX and was renamed Stata Corporation, now known as StataCorp. A major release in 2003 included a new graphics system and dialog boxes for all commands. Since then, a new version has been released once every two years. The current version is Stata 17, released in April 2021. Technical overview and terminology User interface From its creation, Stata has always employed an integrated command-line interface. Starting with version 8.0, Stata has included a graphical user interface based on Qt framework which uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
GAUSS
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; german: Gauß ; la, Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to many fields in mathematics and science. Sometimes referred to as the ''Princeps mathematicorum'' () and "the greatest mathematician since antiquity", Gauss had an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science, and he is ranked among history's most influential mathematicians. Also available at Retrieved 23 February 2014. Comprehensive biographical article. Biography Early years Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss was born on 30 April 1777 in Brunswick (Braunschweig), in the Duchy of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (now part of Lower Saxony, Germany), to poor, working-class parents. His mother was illiterate and never recorded the date of his birth, remembering only that he had been born on a Wednesday, eight days before the Feast of the Ascension (which occurs 39 days after Easter). Gau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
R (programming Language)
R is a programming language for statistical computing and graphics supported by the R Core Team and the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Created by statisticians Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman, R is used among data miners, bioinformaticians and statisticians for data analysis and developing statistical software. Users have created packages to augment the functions of the R language. According to user surveys and studies of scholarly literature databases, R is one of the most commonly used programming languages used in data mining. R ranks 12th in the TIOBE index, a measure of programming language popularity, in which the language peaked in 8th place in August 2020. The official R software environment is an open-source free software environment within the GNU package, available under the GNU General Public License. It is written primarily in C, Fortran, and R itself (partially self-hosting). Precompiled executables are provided for various operating systems. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Statistical Packages
Statistical software are specialized computer programs for analysis in statistics and econometrics. Open-source * ADaMSoft – a generalized statistical software with data mining algorithms and methods for data management * ADMB – a software suite for non-linear statistical modeling based on C++ which uses automatic differentiation * Chronux – for neurobiological time series data * DAP – free replacement for SAS * Environment for DeveLoping KDD-Applications Supported by Index-Structures (ELKI) a software framework for developing data mining algorithms in Java * Epi Info – statistical software for epidemiology developed by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Apache 2 licensed * Fityk – nonlinear regression software (GUI and command line) * GNU Octave – programming language very similar to MATLAB with statistical features * gretl – gnu regression, econometrics and time-series library * intrinsic Noise Analyzer (iNA) – For analyzing int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Applied Economics (journal)
''Applied Economics'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by Routledge with focus on the application of economic analyses. It is currently published by Routledge and circulates 60 issues per year. It was established in 1969 by the founding Editor Maurice H. Peston. The current editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... is Mark P. Taylor. Its companion journal is '' Applied Economics Letters''. It incorporated ''Applied Financial Economics'' from 2015. External links * Economics journals English-language journals Publications established in 1969 Routledge academic journals Journals more frequent than weekly {{econ-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cointegration
Cointegration is a statistical property of a collection of time series variables. First, all of the series must be integrated of order ''d'' (see Order of integration). Next, if a linear combination of this collection is integrated of order less than d, then the collection is said to be co-integrated. Formally, if (''X'',''Y'',''Z'') are each integrated of order ''d'', and there exist coefficients ''a'',''b'',''c'' such that is integrated of order less than d, then ''X'', ''Y'', and ''Z'' are cointegrated. Cointegration has become an important property in contemporary time series analysis. Time series often have trends—either deterministic or stochastic. In an influential paper, Charles Nelson and Charles Plosser (1982) provided statistical evidence that many US macroeconomic time series (like GNP, wages, employment, etc.) have stochastic trends. Introduction If two or more series are individually integrated (in the time series sense) but some linear combination of them ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Independent And Identically Distributed Random Variables
In probability theory and statistics, a collection of random variables is independent and identically distributed if each random variable has the same probability distribution as the others and all are mutually independent. This property is usually abbreviated as ''i.i.d.'', ''iid'', or ''IID''. IID was first defined in statistics and finds application in different fields such as data mining and signal processing. Introduction In statistics, we commonly deal with random samples. A random sample can be thought of as a set of objects that are chosen randomly. Or, more formally, it’s “a sequence of independent, identically distributed (IID) random variables”. In other words, the terms ''random sample'' and ''IID'' are basically one and the same. In statistics, we usually say “random sample,” but in probability it’s more common to say “IID.” * Identically Distributed means that there are no overall trends–the distribution doesn’t fluctuate and all items in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Exact Test
In statistics, an exact (significance) test is a test such that if the null hypothesis is true, then all assumptions made during the derivation of the distribution of the test statistic are met. Using an exact test provides a significance test that maintains the type I error rate of the test (\alpha) at the desired significance level of the test. For example, an exact test at a significance level of \alpha = 5\%, when repeated over many samples where the null hypothesis is true, will reject at most 5\% of the time. This is in contrast to an ''approximate test'' in which the desired type I error rate is only approximately maintained (i.e.: the test might reject > 5% of the time), while this approximation may be made as close to \alpha as desired by making the sample size sufficiently large. Exact tests that are based on discrete test statistics may be conservative, indicating that the actual rejection rate lies below the nominal significance level \alpha. As an example, this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |