|
Striga (plant)
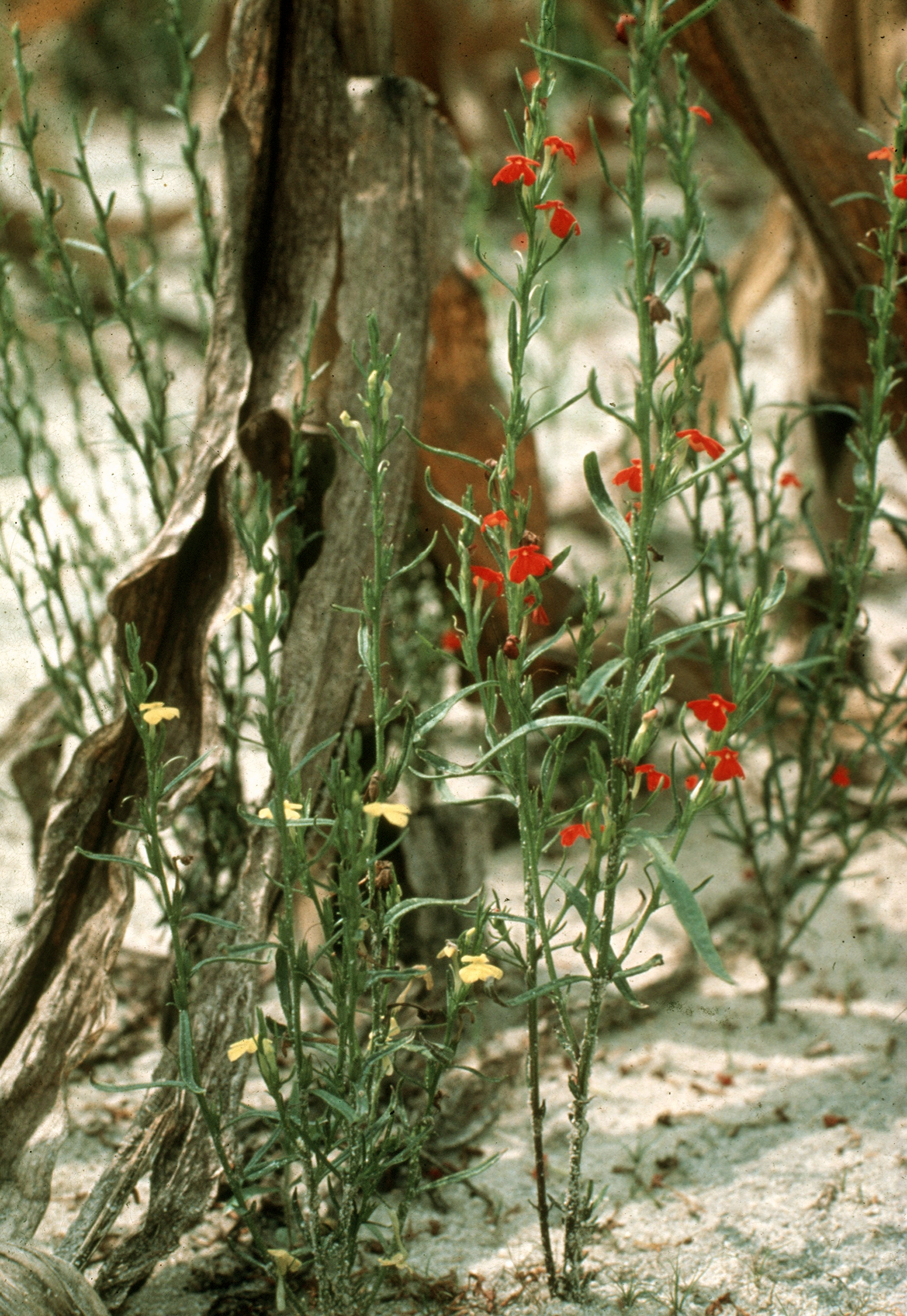
''Striga'', commonly known as witchweed, is a genus of parasitic plants that occur naturally in parts of Africa, Asia, and Australia. It is currently classified in the family Orobanchaceae, although older classifications place it in the Scrophulariaceae. Some species are serious pathogens of cereal crops, with the greatest effects being in savanna agriculture in Africa. It also causes considerable crop losses in other regions, including other tropical and subtropical crops in its native range and in the Americas. The generic name derives from Latin ''strī̆ga'', "witch". Witchweeds are characterized by bright-green stems and leaves and small, brightly colored and attractive flowers.Sand, Paul, Robert Eplee, and Randy Westbrooks. ''Witchweed Research and Control in the United States''. Champaign, IL: Weed Science Society of America, 1990. They are obligate hemiparasites of roots and require a living host for germination and initial development, though they can then survive on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striga Hermonthica
''Striga hermonthica'', commonly known as purple witchweed or giant witchweed, is a hemiparasitic plant that belongs to the family Orobanchaceae. It is devastating to major crops such as sorghum (''Sorghum bicolor'') and rice (''Oryza sativa''). In sub-Saharan Africa, apart from sorghum and rice, it also infests maize (''Zea mays''), pearl millet (''Pennisetum glaucum''), and sugar cane (''Saccharum officinarum''). ''Striga hermonthica'' has undergone horizontal gene transfer from ''Sorghum'' to its nuclear genome. The ''S. hermonthica'' gene, ''ShContig9483'', is most like a ''Sorghum bicolor'' gene, and additionally shows significant but lesser similarity to a gene from ''Oryza sativa''. It shows no similarity to any known eudicot gene. Host and symptoms Purple witchweed infects a variety of grasses and legumes in sub-saharan Africa, including rice, maize, millet, sugarcane, and cowpea. The symptoms mimic that of drought or nutrient-deficiency symptoms. Chlorosis, wilt, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoperiod
Photoperiod is the change of day length around the seasons. The rotation of the earth around its axis produces 24 hour changes in light (day) and dark (night) cycles on earth. The length of the light and dark in each phase varies across the seasons due to the tilt of the earth around its axis. The photoperiod defines the length of the light, for example a summer day the length of light could be 16 hours while the dark is 8 hours, whereas a winter day the length of day could be 8 hours, whereas the dark is 16 hours. Importantly, the seasons are different in the northern hemisphere than the southern hemisphere. Photoperiodism is the physiological reaction of organisms to the length of light or a dark period. It occurs in plants and animals. Plant photoperiodism can also be defined as the developmental responses of plants to the relative lengths of light and dark periods. They are classified under three groups according to the photoperiods: short-day plants, long-day plants, and day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overwintering
Overwintering is the process by which some organisms pass through or wait out the winter season, or pass through that period of the year when "winter" conditions (cold or sub-zero temperatures, ice, snow, limited food supplies) make normal activity or even survival difficult or near impossible. In some cases "winter" is characterized not necessarily by cold but by dry conditions; passing through such periods could likewise be called overwintering. Hibernation and migration are the two major ways in which overwintering is accomplished. Animals may also go into a state of reduced physiological activity known as torpor. Overwintering occurs in several classes of lifeform. Insects In entomology, overwintering is how an insect passes the winter season. Many insects overwinter as adults, pupae, or eggs. This can be done inside buildings, under tree bark, or beneath fallen leaves or other plant matter on the ground, among other places. All such overwintering sites shield the insect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sieve Tubes
Sieve elements or sieve tube elements are specialized cells that are important for the function of phloem, which is a highly organized tissue that transports organic compounds made during photosynthesis. Sieve elements are the major conducting cells in phloem. Conducting cells aid in transport of molecules especially for long-distance signaling. In plant anatomy, there are two main types of sieve elements. Companion cells and sieve cells originate from meristems, which are tissues that actively divide throughout a plant's lifetime. They are similar to the development of xylem, a water conducting tissue in plants whose main function is also transportation in the plant vascular system. Sieve elements' major function includes transporting sugars over long distance through plants by acting as a channel. Sieve elements elongate cells containing sieve areas on their walls. Pores on sieve areas allow for cytoplasmic connections to neighboring cells, which allows for the movement of photosy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortex (botany)
In botany, a cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a vascular plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The cortex is composed mostly of large thin-walled parenchyma cells of the ground tissue system and shows little to no structural differentiation. The outer cortical cells often acquire irregularly thickened cell walls, and are called collenchyma cells. Plants Stems and branches In the three dimensional structure of herbaceous stems, the epidermis, cortex and vascular cambium form concentric cylinders around the inner cylindrical core of pith. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts, giving them a green color. They can therefore produce simple carbohydrates through photosynthesis. In woody plants, the cortex is located between the periderm (bark) and the vascular tissue ( phloem, in particular). It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haustorium
In botany and mycology, a haustorium (plural haustoria) is a rootlike structure that grows into or around another structure to absorb water or nutrients. For example, in mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the structure penetrates the host's tissue and draws nutrients from it. In mycology, it refers to the appendage or portion of a parasitic fungus (the hyphal tip), which performs a similar function. Microscopic haustoria penetrate the host plant's cell wall and siphon nutrients from the space between the cell wall and plasma membrane but do not penetrate the membrane itself. Larger (usually botanical, not fungal) haustoria do this at the tissue level. The etymology of the name corresponds to the Latin word '' haustor'' meaning ''the one who draws, drains or drinks'', and refers to the action performed by the outgrowth. In fungi Fungi in all major divisions form haustoria. Haustoria take several forms. Generally, on penetration, the fungus increases the surface ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds benzene.html" ;"title="uch as benzene">uch as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds", resulting in "a fully Conjugated system, conjugated cyclic diketone, dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone" (thus the name of the class). Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (''ortho''-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone. The name is derived from that of quinic acid (with the suffix "-one" indicating a ketone), since it is one of the compounds obtained upon oxidation of quinic acid. Quinic acid, like quinine is obtained from cinchona bark, called quinaquina in the indigenous languages of Peruvian tribes. Properties Quinones are oxidized derivatives of aromatic compounds an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strigolactone
Strigolactones are a group of chemical compounds produced by roots of plants. Due to their mechanism of action, these molecules have been classified as plant hormones or phytohormones. So far, strigolactones have been identified to be responsible for three different physiological processes: First, they promote the germination of parasitic organisms that grow in the host plant's roots, such as Striga asiatica, ''Striga'' ''lutea'' and other plants of the genus ''Striga''. Second, strigolactones are fundamental for the recognition of the plant by symbiotic Fungus, fungi, especially arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, because they establish a mutualistic association with these plants, and provide phosphate and other soil nutrients. Third, strigolactones have been identified as branching inhibition hormones in plants; when present, these compounds prevent excess bud growing in stem terminals, stopping the branching mechanism in plants. Strigolactones comprise a diverse group, but they all h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haustoria
In botany and mycology, a haustorium (plural haustoria) is a rootlike structure that grows into or around another structure to absorb water or nutrients. For example, in mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the structure penetrates the host's tissue and draws nutrients from it. In mycology, it refers to the appendage or portion of a parasitic fungus (the hyphal tip), which performs a similar function. Microscopic haustoria penetrate the host plant's cell wall and siphon nutrients from the space between the cell wall and plasma membrane but do not penetrate the membrane itself. Larger (usually botanical, not fungal) haustoria do this at the tissue level. The etymology of the name corresponds to the Latin word '' haustor'' meaning ''the one who draws, drains or drinks'', and refers to the action performed by the outgrowth. In fungi Fungi in all major divisions form haustoria. Haustoria take several forms. Generally, on penetration, the fungus increases the surface ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exudate
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation. ''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin language, Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat'). Medicine An exudate is any fluid that filters from the circulatory system into lesions or areas of inflammation. It can be a pus-like or clear fluid. When an injury occurs, leaving skin exposed, it leaks out of the blood vessels and into nearby tissues. The fluid is composed of serum (blood), serum, fibrin, and White blood cell, leukocytes. Exudate may ooze from cuts or from areas of infection or inflammation. Types * Purulent or suppurative exudate consists of plasma with both active and dead neutrophils, fibrinogen, and necrotic parenchymal cells. This kind of exudate is consistent with more severe infections, and is commonly referred to as pus. * Fibrinous exudate is composed mainly of fibrinogen and fibrin. It is characteristic of Rheuma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striga Root Connections
''Striga'', commonly known as witchweed, is a genus of parasitic plants that occur naturally in parts of Africa, Asia, and Australia. It is currently classified in the family Orobanchaceae, although older classifications place it in the Scrophulariaceae. Some species are serious pathogens of cereal crops, with the greatest effects being in savanna agriculture in Africa. It also causes considerable crop losses in other regions, including other tropical and subtropical crops in its native range and in the Americas. The generic name derives from Latin ''strī̆ga'', "witch". Witchweeds are characterized by bright-green stems and leaves and small, brightly colored and attractive flowers.Sand, Paul, Robert Eplee, and Randy Westbrooks. ''Witchweed Research and Control in the United States''. Champaign, IL: Weed Science Society of America, 1990. They are obligate hemiparasites of roots and require a living host for germination and initial development, though they can then survive on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |