|
Stream (abstract Data Type)
In type theory and functional programming, a stream is a potentially infinite analog of a list (computing), list, given by the Algebraic data type, coinductive definition: data Stream α = Nil , Cons α (Stream α) Generating and computing with streams requires lazy evaluation, either implicitly in a lazily evaluated language or by creating and forcing thunk (functional programming), thunks in an eager language. In total languages they must be defined as codata (computer science), codata and can be iterated over using (guarded) corecursion. Java (programming language), Java provides the interface under the namespace. JavaScript provides the , and interfaces. Python (programming language), Python have the and classes in the module. .NET provides the abstract class which is implemented by classes such as and . In Rust (programming language), Rust a struct can implement the trait. There is also the struct wraps an in-memory buffer. See also * Coinduction Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Theory
In mathematics and theoretical computer science, a type theory is the formal presentation of a specific type system. Type theory is the academic study of type systems. Some type theories serve as alternatives to set theory as a foundation of mathematics. Two influential type theories that have been proposed as foundations are: * Typed λ-calculus of Alonzo Church * Intuitionistic type theory of Per Martin-Löf Most computerized proof-writing systems use a type theory for their foundation. A common one is Thierry Coquand's Calculus of Inductive Constructions. History Type theory was created to avoid paradoxes in naive set theory and formal logic, such as Russell's paradox which demonstrates that, without proper axioms, it is possible to define the set of all sets that are not members of themselves; this set both contains itself and does not contain itself. Between 1902 and 1908, Bertrand Russell proposed various solutions to this problem. By 1908, Russell arrive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
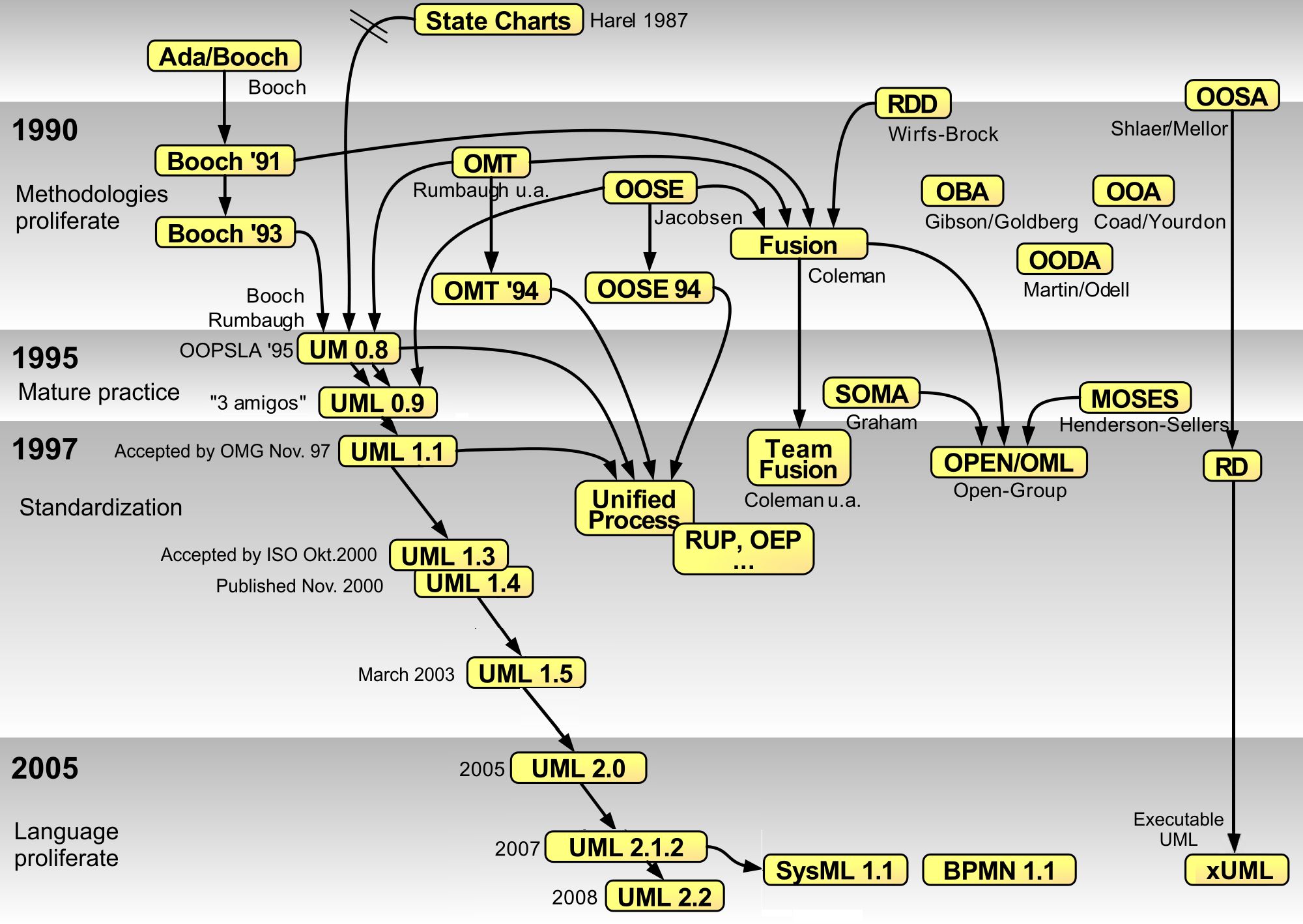
UML Dotnet Streams
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Theory
In mathematics and theoretical computer science, a type theory is the formal presentation of a specific type system. Type theory is the academic study of type systems. Some type theories serve as alternatives to set theory as a foundation of mathematics. Two influential type theories that have been proposed as foundations are: * Typed λ-calculus of Alonzo Church * Intuitionistic type theory of Per Martin-Löf Most computerized proof-writing systems use a type theory for their foundation. A common one is Thierry Coquand's Calculus of Inductive Constructions. History Type theory was created to avoid paradoxes in naive set theory and formal logic, such as Russell's paradox which demonstrates that, without proper axioms, it is possible to define the set of all sets that are not members of themselves; this set both contains itself and does not contain itself. Between 1902 and 1908, Bertrand Russell proposed various solutions to this problem. By 1908, Russell arrive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coinduction
In computer science, coinduction is a technique for defining and proving properties of systems of concurrent interacting objects. Coinduction is the mathematical dual to structural induction. Coinductively defined data types are known as codata and are typically infinite data structures, such as streams. As a definition or specification, coinduction describes how an object may be "observed", "broken down" or "destructed" into simpler objects. As a proof technique, it may be used to show that an equation is satisfied by all possible implementations of such a specification. To generate and manipulate codata, one typically uses corecursive functions, in conjunction with lazy evaluation. Informally, rather than defining a function by pattern-matching on each of the inductive constructors, one defines each of the "destructors" or "observers" over the function result. In programming, co-logic programming (co-LP for brevity) "is a natural generalization of logic programming and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust (programming Language)
Rust is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose programming language emphasizing Computer performance, performance, type safety, and Concurrency (computer science), concurrency. It enforces memory safety, meaning that all Reference (computer science), references point to valid memory. It does so without a conventional Garbage collection (computer science), garbage collector; instead, memory safety errors and data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the object lifetime of references Compiler, at compile time. Rust does not enforce a programming paradigm, but was influenced by ideas from functional programming, including Immutable object, immutability, higher-order functions, algebraic data types, and pattern matching. It also supports object-oriented programming via structs, Enumerated type, enums, traits, and methods. It is popular for systems programming. Software developer Graydon Hoare created Rust as a personal project while working at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior. Web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine that executes the client code. These engines are also utilized in some servers and a variety of apps. The most popular runtime system for non-browser usage is Node.js. JavaScript is a high-level, often just-in-time–compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard. It has dynamic typing, prototype-based object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is multi-paradigm, supporting event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles. It has application programming interfaces (APIs) for working with text, dates, regular expressions, standard data structures, and the Document Object Model (DOM). The ECMAScript standard does not include any input/output (I/O), such as netwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a High-level programming language, high-level, General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, Memory safety, memory-safe, object-oriented programming, object-oriented programming language. It is intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' (Write once, run anywhere, WORA), meaning that compiler, compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to Java bytecode, bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax (programming languages), syntax of Java is similar to C (programming language), C and C++, but has fewer low-level programming language, low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as Reflective programming, reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. Java gained popularity sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corecursion
In computer science, corecursion is a type of operation that is Dual (category theory), dual to recursion (computer science), recursion. Whereas recursion works analysis, analytically, starting on data further from a base case and breaking it down into smaller data and repeating until one reaches a base case, corecursion works synthetically, starting from a base case and building it up, iteratively producing data further removed from a base case. Put simply, corecursive algorithms use the data that they themselves produce, bit by bit, as they become available, and needed, to produce further bits of data. A similar but distinct concept is ''Generative recursion#Structural versus generative recursion, generative recursion'', which may lack a definite "direction" inherent in corecursion and recursion. Where recursion allows programs to operate on arbitrarily complex data, so long as they can be reduced to simple data (base cases), corecursion allows programs to produce arbitrarily co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are Tree (data structure), trees of Expression (computer science), expressions that map Value (computer science), values to other values, rather than a sequence of Imperative programming, imperative Statement (computer science), statements which update the State (computer science), running state of the program. In functional programming, functions are treated as first-class citizens, meaning that they can be bound to names (including local Identifier (computer languages), identifiers), passed as Parameter (computer programming), arguments, and Return value, returned from other functions, just as any other data type can. This allows programs to be written in a Declarative programming, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codata (computer Science)
In computer science, coinduction is a technique for defining and proving properties of systems of concurrent interacting objects. Coinduction is the mathematical dual to structural induction. Coinductively defined data types are known as codata and are typically infinite data structures, such as streams. As a definition or specification, coinduction describes how an object may be "observed", "broken down" or "destructed" into simpler objects. As a proof technique, it may be used to show that an equation is satisfied by all possible implementations of such a specification. To generate and manipulate codata, one typically uses corecursive functions, in conjunction with lazy evaluation. Informally, rather than defining a function by pattern-matching on each of the inductive constructors, one defines each of the "destructors" or "observers" over the function result. In programming, co-logic programming (co-LP for brevity) "is a natural generalization of logic programming and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Language
Total functional programming (also known as strong functional programming, to be contrasted with ordinary, or ''weak'' functional programming) is a programming paradigm that restricts the range of programs to those that are provably terminating. Restrictions Termination is guaranteed by the following restrictions: # A restricted form of recursion, which operates only upon 'reduced' forms of its arguments, such as Walther recursion, substructural recursion, or "strongly normalizing" as proven by abstract interpretation of code. # Every function must be a total (as opposed to partial) function. That is, it must have a definition for everything inside its domain. #* There are several possible ways to extend commonly used partial functions such as division to be total: choosing an arbitrary result for inputs on which the function is normally undefined (such as \forall x \in \mathbb. x \div 0 = 0 for division); adding another argument to specify the result for those inputs; or exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |