|
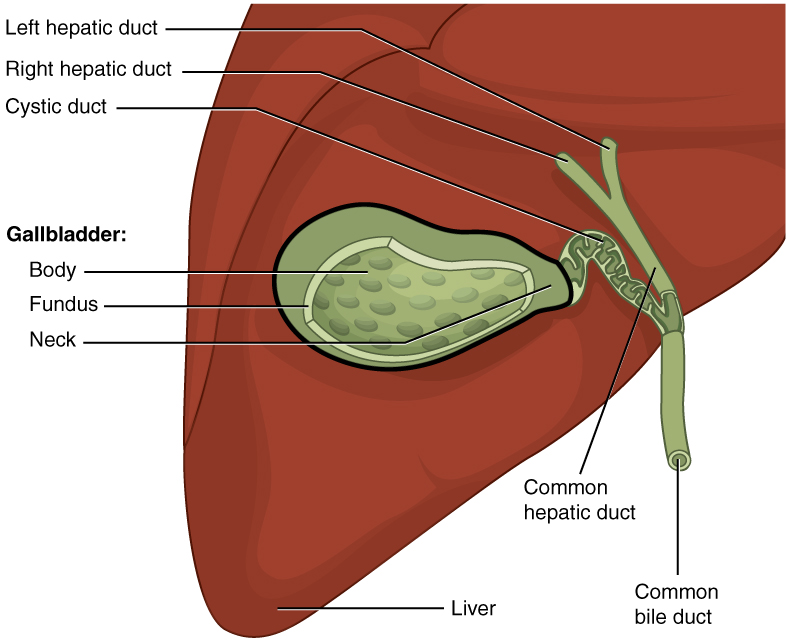
Strawberry Gallbladder
In surgical pathology, strawberry gallbladder, more formally cholesterolosis of the gallbladder and gallbladder cholesterolosis, is a change in the gallbladder wall due to excess cholesterol. The name ''strawberry gallbladder'' comes from the typically stippled appearance of the mucosal surface on gross examination, which resembles a strawberry. The term was coined by surgical pathologist William C. MacCarty of the Mayo Clinic in 1910. Cholesterolosis results from abnormal deposits of cholesterol esters in macrophages within the lamina propria (foam cells) and in mucosal epithelium. The gallbladder may be affected in a patchy localized form or in a diffuse form. The diffuse form macroscopically appears as a bright red mucosa with yellow mottling (due to lipid), hence the term ''strawberry'' gallbladder. It is not tied to cholelithiasis (gallstones) or cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). Additional images Image:Gallbladder cholesterolosis micro.jpg, Micrograph of cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic () is a Nonprofit organization, private American Academic health science centre, academic Medical centers in the United States, medical center focused on integrated health care, healthcare, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science, education, and research. It maintains three major campuses in Rochester, Minnesota; Jacksonville, Florida; and Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona. Mayo Clinic employs over 7,300 physicians and scientists, along with another 66,000 administrative and allied health staff. The practice specializes in treating difficult cases through Health care#Tertiary care, tertiary care and Medical tourism#United States, destination medicine. It is home to the top-15 ranked Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine in addition to many of the highest regarded residency education programs in the United States. It spends over $660 million a year on research and has more than 3,000 full-time research personnel. William Worrall Mayo settled his family i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rokitansky-Aschoff Sinuses
Adenomyomatosis is a benign condition characterized by hyperplastic changes of unknown cause involving the wall of the gallbladder. Pathophysiology Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses are pseudodiverticula or pockets in the wall of the gallbladder. They may be microscopic or macroscopic. Histologically, they are outpouchings of gallbladder mucosa into the gallbladder muscle layer and subserosal tissue as a result of hyperplasia and herniation of epithelial cells through the fibromuscular layer of the gallbladder wall. Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses are not of themselves considered abnormal but they can be associated with cholecystitis. They form as a result of increased pressure in the gallbladder and recurrent damage to the wall of the gallbladder. Associations Black pigment gallstones can form in Rokitansky–Aschoff sinuses of the gallbladder after the fourth to fifth decades of life in absence of the typical risk factors for bilirubin supersaturation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either Laparoscopy, laparoscopically, or via an Minimally invasive procedures#Open surgery, open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include Biliary injury, bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, vasculobiliary injury, retained gallstones, liver abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include Right upper quadrant (abdomen), right upper abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks (biliary colic) precede acute cholecystitis. The pain lasts longer in cholecystitis than in a typical gallbladder attack. Without appropriate treatment, recurrent episodes of cholecystitis are common. Complications of acute cholecystitis include gallstone pancreatitis, common bile duct stones, or cholangitis, inflammation of the common bile duct. More than 90% of the time acute cholecystitis is caused from blockage of the cystic duct by a gallstone. Risk factors for gallstones include combined oral contraceptive pill, birth control pills, pregnancy, a family history of gallstones, obesity, diabetes, cirrhosis, liver disease, or rapid weight loss. Occasionally, acute cholecystitis occurs as a result of vasculitis or chemotherapy, or during recovery from major tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts. Most people with gallstones (about 80%) are asymptomatic. However, when a gallstone obstructs the bile duct and causes acute cholestasis, a reflexive smooth muscle spasm often occurs, resulting in an intense cramp-like visceral pain in the right upper part of the abdomen known as a biliary colic (or "gallbladder attack"). This happens in 1–4% of those with gallstones each year. Complications from gallstones may include inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), obstructive jaundice, and infection in bile ducts ( cholangitis). Symptoms of these complications may include pain that lasts longer than five hours, fever, yellowish skin, vomiting, da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William C
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foam Cell
Foam cells, also called lipid-laden macrophages, are a type of cell that contain cholesterol. These can form a plaque that can lead to atherosclerosis and trigger myocardial infarction and stroke. Foam cells are fat-laden cells with a M2 macrophage-like phenotype. They contain low density lipoproteins (LDL) and can be rapidly detected by examining a fatty plaque under a microscope after it is removed from the body. They are named because the lipoproteins give the cell a foamy appearance. Despite the connection with cardiovascular diseases they might not be inherently dangerous. Some foam cells are derived from smooth muscle cells and present a limited macrophage-like phenotype. Formation Foam cell formation is triggered by a number of factors including the uncontrolled uptake of modified low density lipoproteins (LDL), the upregulation of cholesterol esterification and the impairment of mechanisms associated with cholesterol release. Foam cells are a significant component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown Hybrid (biology), hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit is appreciated for its aroma, bright red colour, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is eaten either fresh or in prepared foods such as fruit preserves, jam, ice cream, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavourings and aromas are widely used in commercial products. Botanically, the strawberry is not a berry (botany), berry, but an aggregate fruit, aggregate accessory fruit, accessory fruit. Each apparent 'seed' on the outside of the strawberry is actually an achene, a botanical fruit with a seed inside it. The garden strawberry was first bred in Brittany, France, in the 1750s via a cross of ''Virginia strawberry, F. virginiana'' from eastern North America and ''Fragaria chiloensis, F. chiloensis'', which was brought from Chile by Amédé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Examination
Gross processing, "grossing" or "gross pathology" is the process by which pathology specimens undergo examination with the bare eye to obtain diagnosis, diagnostic information, as well as cutting and tissue sampling in order to prepare material for subsequent histopathology, microscopic ''examination.'' Responsibility Gross examination of surgical pathology, surgical specimens is typically performed by a pathology, pathologist, or by a pathologists' assistant working within a pathology practice. Individuals trained in these fields are often able to gather diagnostically critical information in this stage of processing, including the stage and margin status of surgically removed tumors. Steps The initial step in any examination of a clinical specimen is confirmation of the identity of the patient and the anatomy, anatomical site from which the specimen was obtained. Sufficient clinical data should be communicated by the clinical team to the pathology team in order to guide the app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |