|
Stratospheric Observatory For Infrared Astronomy
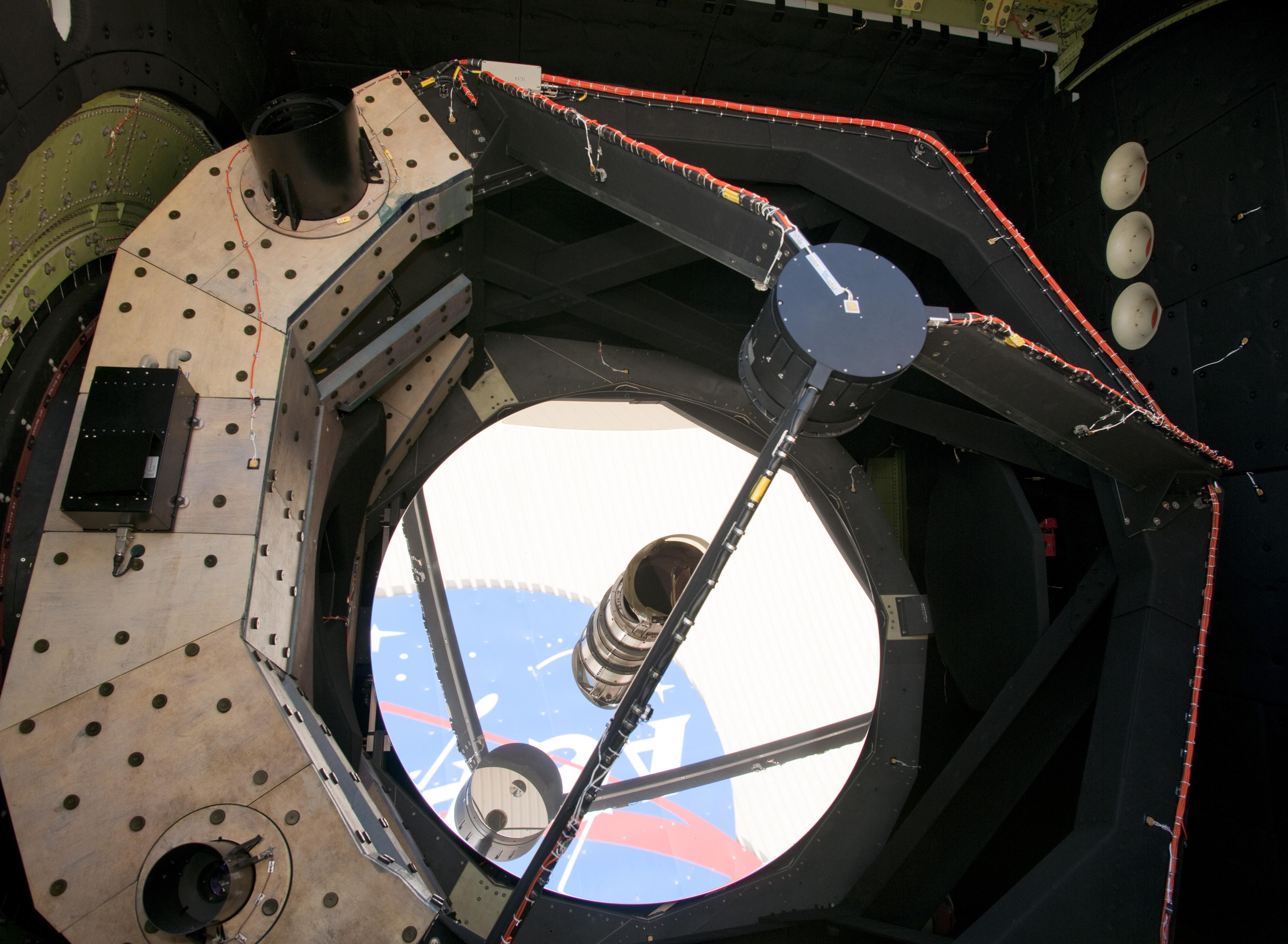
The Stratospheric Observatory For Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) was an 80/20 joint project of NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) to construct and maintain an airborne observatory. NASA awarded the contract for the development of the aircraft, operation of the observatory and management of the American part of the project to the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) in 1996. The DSI (German SOFIA Institute; ) managed the German parts of the project which were primarily science-and telescope-related. SOFIA's telescope saw first light on May 26, 2010. SOFIA was the successor to the Kuiper Airborne Observatory. During 10-hour, overnight flights, it observed celestial magnetic fields, star-forming regions, comets, nebulae, and the Galactic Center. Science flights have now concluded, after the landing of the 921st and last flight in the early morning of September 29, 2022. The Boeing 747SP used to carry the telescope has been preserved and put on display at the Pima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Astronomical Instrumentation
The ''Journal of Astronomical Instrumentation'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers astronomical instruments and its various components being proposed, developed, under construction, and in use. The journal focuses on astronomical instrumentation topics in all wavebands (radio wave to gamma ray) and includes the disciplines of heliophysics, space weather, lunar and planetary science, exoplanet exploration, and astroparticle observation (cosmic rays, cosmic neutrinos, etc.). It was established in 2012 and is published by World Scientific. The journal occasionally publishes thematic issues on specific topics or projects. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * Astrophysics Data System * EBSCO databases * Emerging Sources Citation Index * InfoTrac databases * INSPIRE-HEP * Scopus Scopus is a scientific abstract and citation database, launched by the academic publisher Elsevier as a competitor to older Web of Science in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasmyth Telescope
The Nasmyth telescope, also called Nasmyth–Cassegrain or Cassegrain–Nasmyth, is a reflecting telescope developed by the Scottish inventor James Nasmyth in 1845. It is a modified form of a Cassegrain telescope, with light reflected sideways to an eyepiece. Scheme As in the Cassegrain telescope, the light falls on a concave primary mirror, then is reflected towards a convex secondary mirror. A comparatively small tertiary flat mirror reflects the light to one of the sides of the telescope. (The central hole in the primary mirror may still host a Cassegrain focus if the tertiary can be moved out of the way.) This flat mirror is placed on the altitude axis, so that the beam exits through a hole in the middle of the altitude bearing. This means the eyepiece or instrument does not need to move up and down with the telescope as the tertiary mirror's angle with the main telescope axis is adjustable as a function of the telescope's pointing and the star's elevation above the horizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichroism
In optics, a dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths (colours) (not to be confused with Dispersion (optics), dispersion), or one in which light rays having different Polarization (waves), polarizations are absorbed by different amounts. In beam splitters The original meaning of ''dichroic'', from the Greek language, Greek ''dikhroos'', two-coloured, refers to any optical device which can split a beam of light into two beams with differing wavelengths. Such devices include mirrors and dichroic filter, filters, usually treated with optical coatings, which are designed to reflect light over a certain range of wavelengths and transmit light which is outside that range. An example is the dichroic prism, used in some camcorders, which uses several coatings to split light into red, green and blue components for recording on separate charge-coupled device, CCD arrays, however it is now more common to have a Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-number
An f-number is a measure of the light-gathering ability of an optical system such as a camera lens. It is calculated by dividing the system's focal length by the diameter of the entrance pupil ("clear aperture").Smith, Warren ''Modern Optical Engineering'', 4th Ed., 2007 McGraw-Hill Professional, p. 183. The f-number is also known as the focal ratio, f-ratio, or f-stop, and it is key in determining the depth of field, diffraction, and Exposure (photography), exposure of a photograph. The f-number is dimensionless number, dimensionless and is usually expressed using a lower-case Ƒ, hooked f with the format ''N'', where ''N'' is the f-number. The f-number is also known as the inverse relative aperture, because it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the relative aperture, defined as the aperture diameter divided by focal length. The relative aperture indicates how much light can pass through the lens at a given focal length. A lower f-number means a larger relative apertur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Reflector
{{disambiguation ...
Hyperbolic may refer to: * of or pertaining to a hyperbola, a type of smooth curve lying in a plane in mathematics ** Hyperbolic geometry, a non-Euclidean geometry ** Hyperbolic functions, analogues of ordinary trigonometric functions, defined using the hyperbola * of or pertaining to hyperbole, the use of exaggeration as a rhetorical device or figure of speech * ''Hyperbolic'' (album), by Pnau, 2024 See also * Exaggeration * Hyperboloid In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
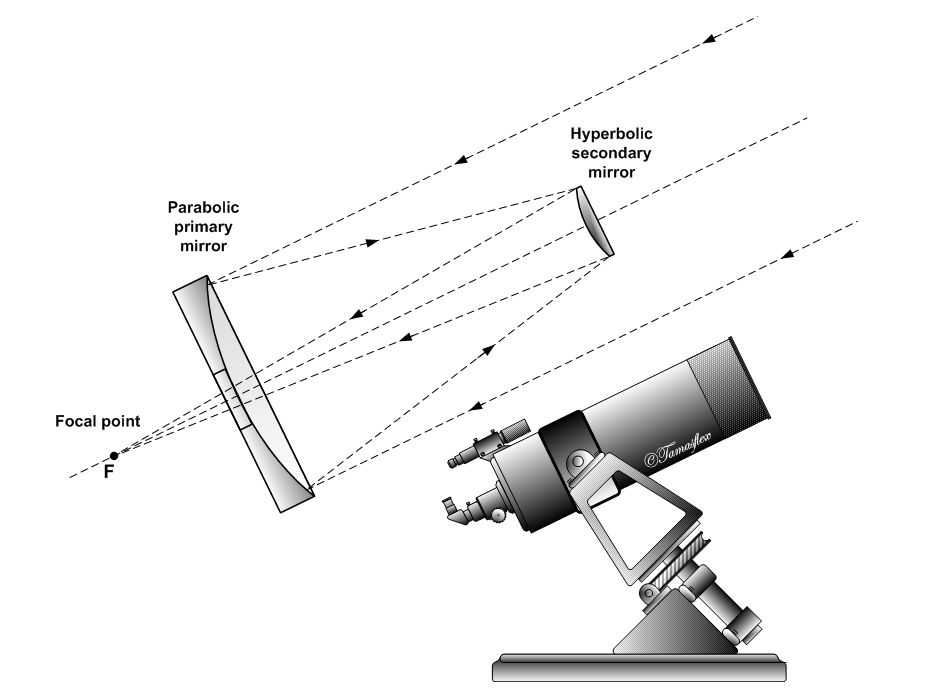
Parabolic Reflector
A parabolic (or paraboloid or paraboloidal) reflector (or dish or mirror) is a Mirror, reflective surface used to collect or project energy such as light, sound, or radio waves. Its shape is part of a circular paraboloid, that is, the surface generated by a parabola revolving around its axis. The parabolic reflector transforms an incoming plane wave travelling along the axis into a spherical wave converging toward the focus. Conversely, a spherical wave generated by a point source placed in the focus (optics), focus is reflected into a plane wave propagating as a collimated beam along the axis. Parabolic reflectors are used to collect energy from a distant source (for example sound waves or incoming star light). Since the principles of Specular reflection, reflection are reversible, parabolic reflectors can also be used to collimate radiation from an isotropic source into a parallel beam (optics), beam. In optics, parabolic mirrors are used to gather light in reflecting telescop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and Antenna (radio), radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the Focus (optics), focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a Telephoto lens, telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflector Telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptric telescope. From the time of Newton to the 1800s, the mirror itself was made of metalusually speculum metal. This type included Newton's first designs and the largest telesco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOFIA 2
Sofia is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain, in the western part of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar (river), Iskar river and has many mineral springs, such as the Sofia Central Mineral Baths. It has a humid continental climate. Known as Serdica in Classical antiquity, antiquity, Sofia has been an area of human habitation since at least 7000 BC. The recorded history of the city begins with the attestation of the conquest of Serdica by the Roman Republic in 29 BC from the Celtic settlement of Southeast Europe, Celtic tribe Serdi. During the decline of the Roman Empire, the city was raided by Huns, Visigoths, Pannonian Avars, Avars, and Slavs. In 809, Serdica was incorporated into the First Bulgarian Empire by Khan (title), Khan Krum and became known as Sredets. In 1018, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines ended Bulgarian rule until 1194, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ames Research Center
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laboratory. That agency was dissolved and its assets and personnel transferred to the newly created NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on October 1, 1958. NASA Ames is named in honor of Joseph Sweetman Ames, a physicist and one of the founding members of NACA. At last estimate NASA Ames had over US$3 billion in capital equipment, 2,300 research personnel and a US$750 million annual budget. Ames was founded to conduct wind-tunnel research on the aerodynamics of propeller-driven aircraft; however, its role has expanded to encompass spaceflight and information technology. Ames plays a role in many NASA missions. It provides leadership in astrobiology; small satellites; robotic lunar exploration; the search for habitable plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmdale Regional Airport
Palmdale Regional Airport is an airport in Palmdale, California, United States. The city of Palmdale took over the airport at the end of 2013, managing it via the Palmdale Airport Authority. The airport currently does not have any scheduled passenger airline service. Overview and facilities PMD and USAF Plant 42, Plant 42 are separate facilities that share a common runway at the site. The facility is located in the Antelope Valley, approximately 60 miles from downtown Los Angeles. The airport covers 5,832 acres (2,360 hectare, ha) at an elevation of 2,543 feet (775 m) above mean sea level. It has three runways with concrete surfaces: 4/22 is 12,001 by 150 feet (3,658 x 46 m); 7/25 is 12,002 by 200 feet (3,658 x 61 m); 72/252 is 6,000 by 75 feet (1,829 x 23 m). 7/25 was built to withstand an 8.3 Richter Scale earthquake, making it one of the world's strongest runways. Another smaller runway, 72/252, is used as an assault strip. In January 2024, Los Angeles County Supervisor K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |