|
Stratarches
(, : (archaic) or (modern)) means 'ruler of the army' in Greek, and is a title associated with successful generals. In modern Greek usage, it corresponds to the rank of Field Marshal. Byzantine Empire The term originated in the Byzantine Empire, where, in the 9th to 11th centuries, the were a class of senior officials in charge of military finances and administration, including the (commander of the foreign imperial guards), the ''droungarios'' of the Fleet, the who supervised the army's horse-breeding farms, the ( Count of the Stable) and the of the . By the late 11th century, this technical meaning was forgotten, and the term , along with variants such as ('grand ') and ('all-'), came to be used as an honorific epithet for important generals. In this use it is for instance used to describe the famed literary hero Digenis Akritas, or famous past commanders, such as Belisarius. Modern Greece In modern Greek history, the title (modern phonetic transliteration: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army (in countries without the rank of Generalissimo), and as such, few persons are ever appointed to it. It is considered as a five-star rank (OF-10) in modern-day armed forces in many countries. Promotion to the rank of field marshal in many countries historically required extraordinary military achievement by a general (a wartime victory). However, the rank has also been used as a Division (military), divisional command rank and as a brigade command rank. Examples of the different uses of the rank include Afghanistan, Austria-Hungary, India, Pakistan, Prussia/Germany and Sri Lanka for an extraordinary achievement; Spain and Mexico for a divisional command (); and France, Portugal and Brazil for a brigade command (, ). Origins The origin of the term dates to the early Middle Ages, originally meaning the keeper of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandros Papagos
Alexandros Papagos (; 9 December 1883 – 4 October 1955) was a Greek military officer who led the Hellenic Army in World War II and the later stages of the subsequent Greek Civil War. The only Greek army career officer to rise to the rank of Field Marshal, Papagos became the first Chief of the Hellenic National Defence General Staff from 1950 until his resignation the following year. He then entered politics, founding the nationalist Greek Rally party and becoming the country's Prime Minister after his victory in the 1952 elections. His premiership was shaped by the Cold War and the aftermath of the Greek Civil War, and was defined by several key events, including Greece becoming a member of NATO; U.S. military bases being allowed on Greek territory and the formation of a powerful and vehemently anti-communist security apparatus. Papagos' tenure also saw the start of the Greek economic miracle, and rising tensions with Britain and Turkey during the Cyprus Emergency over the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategos
''Strategos'' (), also known by its Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized form ''strategus'', is a Greek language, Greek term to mean 'military General officer, general'. In the Hellenistic world and in the Byzantine Empire, the term was also used to describe a military governor. In the modern Hellenic Army, it is the highest officer rank. Etymology ''Strategos'' is a compound of two Greek words: ''stratos'' and ''agos''. ''Stratos'' (στρατός) means 'army', literally 'that which is spread out', coming from the proto-Indo-European root *stere-, 'to spread'. ''Agos'' (ἀγός) means 'leader', from ''agein'' (ἄγειν), 'to lead', from the pelasgic root *ag-, 'to drive, draw out or forth, move'. Classical Greece Athens In its most famous attestation, in Classical Athens, the office of ''strategos'' existed already in the 6th century BC, but it was only with the reforms of Cleisthenes in 501 BC that it assumed its most recognizable form: Cleisthenes instituted a boa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoros Kolokotronis
Theodoros Kolokotronis (; 3 April 1770 – ) was a Greek general and the pre-eminent leader of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1829) against the Ottoman Empire. The son of a klepht leader who fought the Ottomans during the Orlov revolt, Kolokotronis also operated as a klepht and an armatolos early in his life. While serving in the British army during the Napoleonic Wars, he became influenced by the revolutionary ideas of the era. On the outbreak of the Greek War of Independence, he organized a band of Moreot klephts and captured Tripolitsa in late 1821. Kolokotronis achieved his greatest success at the 1822 Battle of Dervenakia, where he routed the Ottoman forces under the command of Mahmud Dramali Pasha. From 1823 to 1825, he took part in the Greek civil wars and, following the defeat of his faction, he was briefly imprisoned in Hydra. In 1825, Kolokotronis was released and appointed commander-in-chief of the Greek forces in Peloponnese. He defended Greece agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
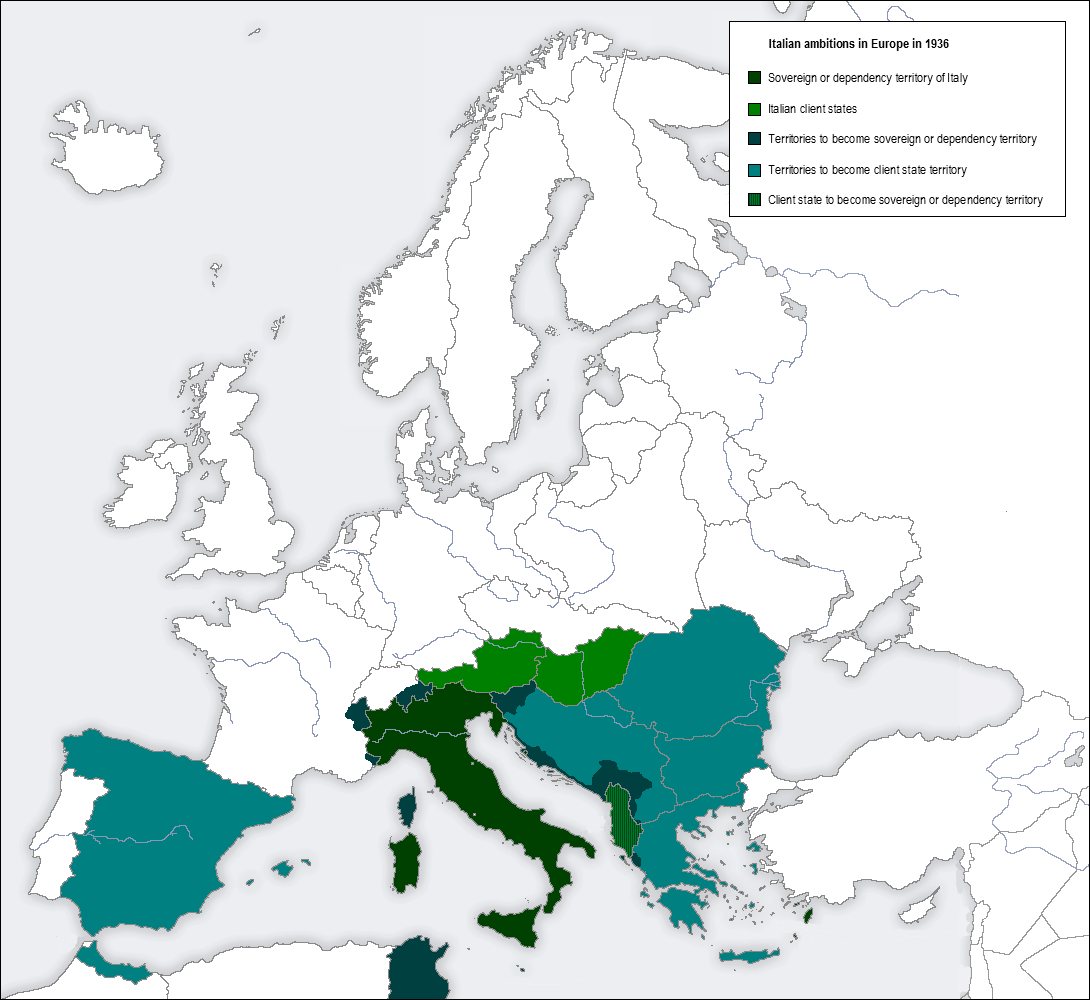
Greco-Italian War
The Greco-Italian War (), also called the Italo-Greek War, Italian campaign in Greece, Italian invasion of Greece, and War of '40 in Greece, took place between Italy and Greece from 28 October 1940 to 23 April 1941. This conflict began the Balkans campaign of World War II between the Axis powers and the Allies, and eventually turned into the Battle of Greece with British and German involvement. On 10 June 1940, Italy declared war on France and the United Kingdom. By September 1940, the Italians had invaded France, British Somaliland and Egypt. This was followed by a hostile press campaign in Italy against Greece, accused of being a British ally. A number of provocations culminated in the sinking of the Greek light cruiser ''Elli'' by the Italians on 15 August. On 28 October, Mussolini issued an ultimatum to Greece demanding the cession of Greek territory, which the Prime Minister of Greece, Ioannis Metaxas, rejected. Italy's invasion of Greece, launched with the divisions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Monarchy
Monarchy of Greece () or Greek monarchy () is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign (''Basileus'') reigns as the head of state of Greece. Monarchy in Greece lasted from 1832 to 1924 and from 1935 to 1973. History The monarchy of Greece was created by the London Conference of 1832 at which the First Hellenic Republic was abolished. The Greek crown was originally offered to Prince Leopold of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha but he declined, later being elected the king of the Belgians. In 1832, Prince Otto of Bavaria of the House of Wittelsbach was styled "His Majesty Otto I, King of Greece", over which he reigned for 30 years until he was deposed in 1862. After Otto's deposition as king, the crown was offered to many others, including the novelist and former British colonial secretary Edward Bulwer-Lytton. A head of state referendum was held in 1862 to name a new king. The vast majority of Greek people wanted Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine II Of Greece
Constantine II (, ; 2 June 1940 – 10 January 2023) was the last King of Greece, reigning from 6 March 1964 until the abolition of the Greek monarchy on 1 June 1973. Constantine was born in Athens as the only son of Crown Prince Paul and Crown Princess Frederica of Greece. Being of Danish descent, he was also born as a prince of Denmark. As his family was forced into exile during the Second World War, he spent the first years of his childhood in Egypt and South Africa. He returned to Greece with his family in 1946 during the Greek Civil War. After Constantine's uncle, George II, died in 1947, Paul became the new king and Constantine the crown prince. As a young man, Constantine was a competitive sailor and Olympian, winning a gold medal in the 1960 Rome Olympics in the Dragon class along with Odysseus Eskitzoglou and George Zaimis in the yacht ''Nireus''. From 1964, he served on the International Olympic Committee. Constantine acceded as king following his father's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Of Greece
Paul (; 14 December 1901 – 6 March 1964) was King of Greece from 1 April 1947 until his death on 6 March 1964. Paul was born in Athens as the third son of Constantine I of Greece, Crown Prince Constantine and Sophia of Prussia, Crown Princess Sophia of Greece. In 1912, the year before his father ascended the throne, Paul joined the Royal Hellenic Navy at eleven years old, becoming the youngest cadet at the time. After the National Schism during World War I, Constantine's abdication was forced and Paul and his family went into exile in Switzerland. Paul's brother, Alexander of Greece, Alexander, became the Greek sovereign in 1917 when Constantine and Paul were exiled, however, Alexander's death in 1920 led to Constantine's restoration. In 1922, Paul's other brother, George II of Greece, George, became the monarch. However, 1924 Greek republic referendum, a referendum in 1924 two years later saw the abolition of the Greek monarchy. Paul moved to Italy with his family and then to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George II Of Greece
George II (; 19 July [Old Style and New Style dates, Old Style: 7 July] 1890 – 1 April 1947) was King of Greece from 27 September 1922 until 25 March 1924, and again from 25 November 1935 until his death on 1 April 1947. The eldest son of King Constantine I of Greece and Princess Sophia of Prussia, George followed his father into exile in 1917 following the National Schism, while his younger brother Alexander of Greece, Alexander was installed as king. Constantine was restored to the throne in 1920 after Alexander's death, but was forced to abdicate two years later in the aftermath of the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922), Greco-Turkish War. George acceded to the Greek throne, but after a Leonardopoulos–Gargalidis coup d'état attempt, failed royalist coup in October 1923 he was exiled to Romania. Greece was proclaimed a republic in March 1924 and George was formally deposed and stripped of Greek nationality. He remained in exile until the Greek monarchy was restored in 1935, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, Montenegro and Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defeated it, in the process stripping the Ottomans of their European provinces, leaving only East Thrace, Eastern Thrace under Ottoman control. In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria fought against the other four combatants of the first war. It also faced an attack from Kingdom of Romania, Romania from the north. The Ottoman Empire lost the bulk of its territory in Europe. Although not involved as a combatant, Austria-Hungary became relatively weaker as a much enlarged Serbia pushed for union of the South Slavs, Slavic peoples. The war set the stage for the July Crisis, July crisis of 1914 and as a prelude to the First World War. By the early 20th century, Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I Of Greece
Constantine I (, Romanization, romanized: ''Konstantínos I''; – 11 January 1923) was King of Greece from 18 March 1913 to 11 June 1917 and again from 19 December 1920 to 27 September 1922. He was commander-in-chief of the Hellenic Army during the unsuccessful Greco-Turkish War (1897), Greco-Turkish War of 1897 and led the Greek forces during the successful Balkan Wars of 1912–1913, in which Greece expanded to include Thessaloniki, doubling in area and population. The eldest son of George I of Greece, he succeeded to the throne following his father's assassination in 1913. Constantine's disagreement with Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos over whether Greece should enter World War I led to the National Schism. Under Allied duress, the country was essentially split between the pro-Venizelos North and the royalist South, ushering in a protracted civil war. He forced Venizelos to resign twice, but in 1917 Constantine left Greece, after threats by the Allies of World War I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |