|
Strain Energy Release Rate
In fracture mechanics, the energy release rate, G, is the rate at which energy is transformed as a material undergoes fracture. Mathematically, the energy release rate is expressed as the decrease in total potential energy per increase in fracture surface area, and is thus expressed in terms of energy per unit area. Various energy balances can be constructed relating the energy released during fracture to the energy of the resulting new surface, as well as other dissipative processes such as plasticity and heat generation. The energy release rate is central to the field of fracture mechanics when solving problems and estimating material properties related to fracture and fatigue. Definition The energy release rate G is defined as the instantaneous loss of total potential energy \Pi per unit crack growth area s, : G \equiv -\frac , where the total potential energy is written in terms of the total strain energy \Omega, surface traction \mathbf, displacement \mathbf, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture Mechanics
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials. It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics to characterize the material's resistance to fracture. Theoretically, the stress ahead of a sharp crack tip becomes infinite and cannot be used to describe the state around a crack. Fracture mechanics is used to characterise the loads on a crack, typically using a single parameter to describe the complete loading state at the crack tip. A number of different parameters have been developed. When the plastic zone at the tip of the crack is small relative to the crack length the stress state at the crack tip is the result of elastic forces within the material and is termed linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) and can be characterised using the stress intensity factor K. Although the load on a crack can be arbitrary, in 1957 G. Irwin foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young's Modulus
Young's modulus (or the Young modulus) is a mechanical property of solid materials that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness when the force is applied lengthwise. It is the modulus of elasticity for tension or axial compression. Young's modulus is defined as the ratio of the stress (force per unit area) applied to the object and the resulting axial strain (displacement or deformation) in the linear elastic region of the material. Although Young's modulus is named after the 19th-century British scientist Thomas Young, the concept was developed in 1727 by Leonhard Euler. The first experiments that used the concept of Young's modulus in its modern form were performed by the Italian scientist Giordano Riccati in 1782, pre-dating Young's work by 25 years. The term modulus is derived from the Latin root term '' modus'', which means ''measure''. Definition Young's modulus, E, quantifies the relationship between tensile or compressive stress \sigma (force per unit ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate System
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane (geometry), plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point (geometry), point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the positive and negative numbers, signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called ''coordinate lines'', ''coordinate axes'' or just ''axes'' (plural of ''axis'') of the system. The point where the axes meet is called the ''Origin (mathematics), origin'' and has as coordinates. The axes direction (geometry), directions represent an orthogonal basis. The combination of origin and basis forms a coordinate frame called the Cartesian frame. Similarly, the position of any point in three-dimensional space can be specified by three ''Cartesian coordinates'', which are the signed distances from the point to three mutually perpendicular planes. More generally, Cartesian coordinates specify the point in an -dimensional Euclidean space for any di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain Energy Release Rate
In fracture mechanics, the energy release rate, G, is the rate at which energy is transformed as a material undergoes fracture. Mathematically, the energy release rate is expressed as the decrease in total potential energy per increase in fracture surface area, and is thus expressed in terms of energy per unit area. Various energy balances can be constructed relating the energy released during fracture to the energy of the resulting new surface, as well as other dissipative processes such as plasticity and heat generation. The energy release rate is central to the field of fracture mechanics when solving problems and estimating material properties related to fracture and fatigue. Definition The energy release rate G is defined as the instantaneous loss of total potential energy \Pi per unit crack growth area s, : G \equiv -\frac , where the total potential energy is written in terms of the total strain energy \Omega, surface traction \mathbf, displacement \mathbf, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodal Release Debounded (born 1999), Mexican singer and songwriter
{{Disambig ...
Nodal may refer to: * Nodal, the adjectival form of the noun :wikt:node * Nodal homolog, a protein encoded by the gene NODAL and responsible for left-right asymmetry * Nodal (software), a novel music composition program * Christian Nodal Christian Jesús González Nodal (born January 11, 1999) is a Mexican singer and songwriter. Born and raised in Sonora, he is mainly known for popularizing "mariacheño", a fusion genre between mariachi and Norteño (music), norteño music. Nod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain Energy Release Rate
In fracture mechanics, the energy release rate, G, is the rate at which energy is transformed as a material undergoes fracture. Mathematically, the energy release rate is expressed as the decrease in total potential energy per increase in fracture surface area, and is thus expressed in terms of energy per unit area. Various energy balances can be constructed relating the energy released during fracture to the energy of the resulting new surface, as well as other dissipative processes such as plasticity and heat generation. The energy release rate is central to the field of fracture mechanics when solving problems and estimating material properties related to fracture and fatigue. Definition The energy release rate G is defined as the instantaneous loss of total potential energy \Pi per unit crack growth area s, : G \equiv -\frac , where the total potential energy is written in terms of the total strain energy \Omega, surface traction \mathbf, displacement \mathbf, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element Method
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. Computers are usually used to perform the calculations required. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two- or three-space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). There are also studies about using FEM to solve high-dimensional problems. To solve a problem, FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DCB Specimen Path
DCB may stand for: * Dame Commander of the Order of the Bath * Development Credit Bank, a private-sector bank in India * David Campbell Bannerman (born 1960), a British politician * David Crowder Band, a Christian rock band * ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' * Dulwich College Beijing, a British international school in Beijing, China * Dope Circle Boyz, a Finnish hip-hop group In science and technology * Disconnecting circuit breaker, a high-voltage circuit breaker with disconnectors integrated into the breaking chamber * Data center bridging, in computer networking * Data Control Block, a data structure for accessing data sets on IBM mainframes * Double Cantilever Beam, a test specimen in fracture mechanics * Dichlorobenzene * Digital Control Bus, a proprietary MIDI-like interface by Roland Corporation * Direct Copper Bonding, also Direct Bonding Copper, a type of power electronic substrate * Direct Carrier Billing, a method of doing digital financial transactions * Dithioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Integral
In mathematics, a line integral is an integral where the function (mathematics), function to be integrated is evaluated along a curve. The terms ''path integral'', ''curve integral'', and ''curvilinear integral'' are also used; ''contour integral'' is used as well, although that is typically reserved for #Complex line integral, line integrals in the complex plane. The function to be integrated may be a scalar field or a vector field. The value of the line integral is the sum of values of the field at all points on the curve, weighted by some scalar function on the curve (commonly arc length or, for a vector field, the Dot product, scalar product of the vector field with a Differential (infinitesimal), differential vector in the curve). This weighting distinguishes the line integral from simpler integrals defined on interval (mathematics), intervals. Many simple formulae in physics, such as the definition of Work (physics), work as have natural continuous analogues in terms of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J-integral
The J-integral represents a way to calculate the strain energy release rate, or work (energy) per unit fracture surface area, in a material. The theoretical concept of J-integral was developed in 1967 by G. P. Cherepanov and independently in 1968 by James R. Rice,J. R. Rice, ''A Path Independent Integral and the Approximate Analysis of Strain Concentration by Notches and Cracks'', Journal of Applied Mechanics, 35, 1968, pp. 379–386. who showed that an energetic contour path integral (called ''J'') was independent of the path around a crack. Experimental methods were developed using the integral that allowed the measurement of critical fracture properties in sample sizes that are too small for Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM) to be valid.Lee, R. F., & Donovan, J. A. (1987). J-integral and crack opening displacement as crack initiation criteria in natural rubber in pure shear and tensile specimens. Rubber chemistry and technology, 60(4), 674–688/ref> These experiments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
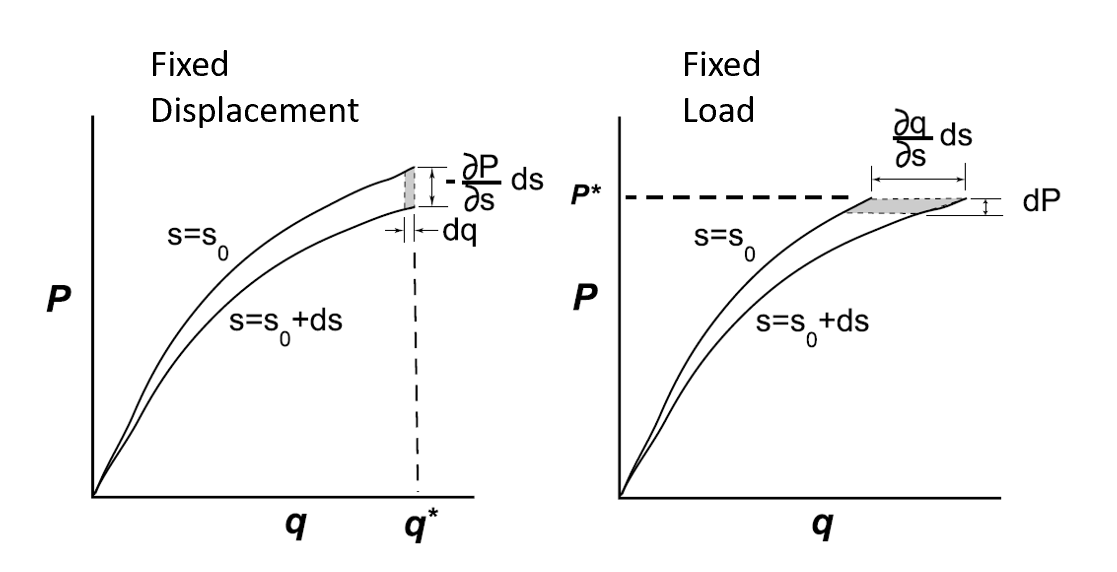
Graphical Illustration Of G Under Fixed Displacement And Fixed Load Conditions
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of the data, as in design and manufacture, in typesetting and the graphic arts, and in educational and recreational software. Images that are generated by a computer are called computer graphics. Examples are photographs, drawings, line art, mathematical graphs, line graphs, charts, diagrams, typography, numbers, symbols, geometric designs, maps, engineering drawings, or other images. Graphics often combine text, illustration, and color. Graphic design may consist of the deliberate selection, creation, or arrangement of typography alone, as in a brochure, flyer, poster, web site, or book without any other element. The objective can be clarity or effective communication, association with other cultural elements, or merely the creation of a distinctive style. Graphics can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DCB Specimen
DCB may stand for: * Dame Commander of the Order of the Bath * Development Credit Bank, a private-sector bank in India * David Campbell Bannerman (born 1960), a British politician * David Crowder Band, a Christian rock band * ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' * Dulwich College Beijing, a British international school in Beijing, China * Dope Circle Boyz, a Finnish hip-hop group In science and technology * Disconnecting circuit breaker, a high-voltage circuit breaker with disconnectors integrated into the breaking chamber * Data center bridging, in computer networking * Data Control Block, a data structure for accessing data sets on IBM mainframes * Double Cantilever Beam, a test specimen in fracture mechanics * Dichlorobenzene * Digital Control Bus, a proprietary MIDI-like interface by Roland Corporation * Direct Copper Bonding, also Direct Bonding Copper, a type of power electronic substrate * Direct Carrier Billing, a method of doing digital financial transactions * Dithioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |