|
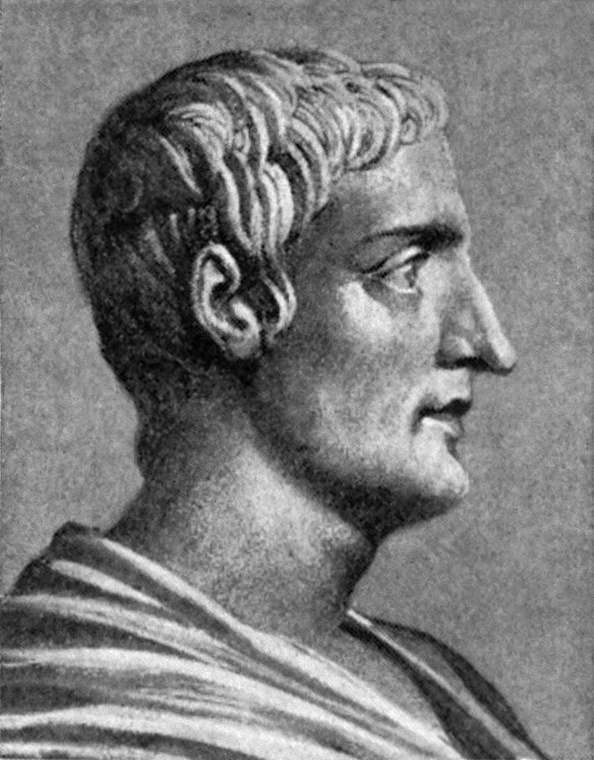
Stjepan Verković
Stefan or Stjepan Ilija Verković was a 19th-century Bosnian ethnographer and folklorist. Born to Bosnian Croat parents, he identified as ''South Slav'' and initially he supported the Serbian and later the Bulgarian national cause. Biography Verković was born in Ugljara, Ottoman Empire on March 5, 1821. He passed his education in the Franciscan school of Tolisa (1830–1833), and then studied philosophy and theology in Zagreb University, where he was influenced by the ideas of the Illyrian movement. In 1843, he contacted the Serbian government and in the following years he served secret missions in parts of today Croatia, Montenegro, Kosovo and Serbia, then under Austrian or Ottoman rule. During his tours through the Balkan lands he searched for medieval Slavonic manuscripts, antique coins and various antiques, recorded folk songs and customs. In 1848 he met in Belgrade Ilija Garašanin and adopted his pan-Serbian ideas. Subsequently, he refused a job in the Serbian state adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugljara
Ugljara is a village in the municipality of Orašje, Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th .... Demographics According to the 2013 census, its population was 1,205. References Populated places in Orašje {{PosavinaCanton-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey (East Thrace). Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia (region), Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'', from ancient Greek ''Thrake'' (Θρᾴκη), referred originally to the Thracians (ancient Greek ''Thrakes'' Θρᾷκες), an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' (ancient Greek Εὐρώπη), also at first referred to this region, before that term expanded to include its Europe, modern sense. It has been suggested that the name ''Thrace'' derives from the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Scientists From The Ottoman Empire
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was Abolitionism, abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnographers
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation, where the researcher participates in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these in their local contexts. It had its origin in social and cultural anthropology in the early twentieth century, but has, since then, spread to other social science disciplines, notably sociology. Ethnographers mainly use qualitative methods, though they may also include quantitative data. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folklorists
Folklore studies (also known as folkloristics, tradition studies or folk life studies in the UK) is the academic discipline devoted to the study of folklore. This term, along with its synonyms, gained currency in the 1950s to distinguish the academic study of traditional culture from the folklore artifacts themselves. It became established as a field across both Europe and North America, coordinating with ( German), ( Norwegian), and ( Swedish), among others. Overview A 1982 UNESCO document titled "Recommendation on the Safeguarding of Traditional Culture and Folklore" declared a global need to establish provisions protecting folklore from varying dangers identified in the document. UNESCO further published the Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage in 2003. The American Folklife Preservation Act (P.L. 94-201) passed in 1976 by the United States Congress in conjunction with the Bicentennial Celebration included a definition of folklore, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
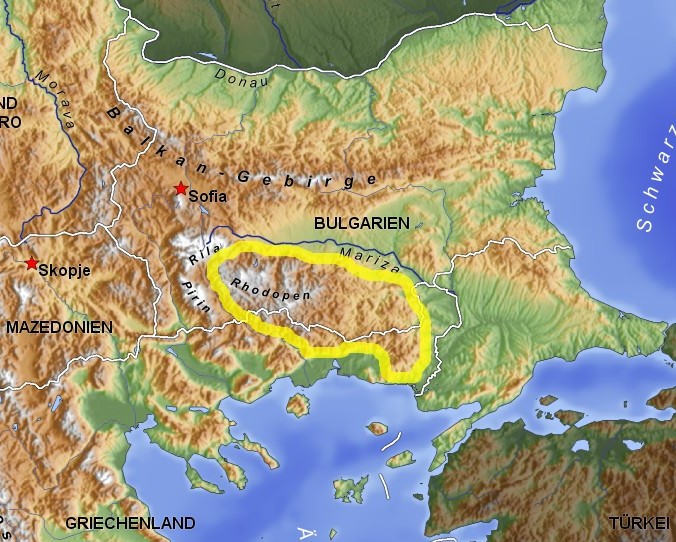
Rhodopes
The Rhodopes (; , ; , ''Rodopi''; ) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. Name and mythology The name of the Rhodope Mountains is of Thracian origin. Rhod-ope (Род-oпа) is interpreted as the first name of a river, meaning "rusty/reddish river", wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomaks
Pomaks (; Macedonian: Помаци ; ) are Bulgarian-speaking Muslims inhabiting Bulgaria, northwestern Turkey, and northeastern Greece. The strong ethno-confessional minority in Bulgaria is recognized officially as Bulgarian Muslims by the government. The term has also been used as a wider designation, including also the Slavic Muslim populations of North Macedonia and Albania. Most Pomaks today live in Turkey, where they have settled as muhacirs as a result of escaping previous ethnic cleansing in Bulgaria. Bulgaria recognizes their language as a Bulgarian dialect, whereas in Greece and Turkey they self-declare their language as the Pomak language. The community in Greece is commonly fluent in Greek, and in Turkey, Turkish, while the communities in these two countries, especially in Turkey, are increasingly adopting Turkish as their first language as a result of education and family links with the Turkish people. They are not officially recognized as one people with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plovdiv
Plovdiv (, ) is the List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, second-largest city in Bulgaria, 144 km (93 miles) southeast of the capital Sofia. It had a population of 490,983 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is a cultural hub in Bulgaria and was the European Capital of Culture in 1999 and 2019. The city is an important economic, transport, cultural, and educational centre. Plovdiv joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2016. Archeological symbols of Plovdiv Plovdiv is in a fertile region of south-central Bulgaria on the two banks of the Maritsa River. The city has historically developed on seven syenite hills, some of which are high. Because of these hills, Plovdiv is often referred to in Bulgaria as "The City of the Seven Hills". There is evidence of habitation in the area dating back to the 6th millennium BCE, when the first Neolithic settlements were established. The city was subsequently a Thracians, Thracian settlement, later being conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veda
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''. The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest Hindu texts, scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas (mantras and benedictions), the Brahmanas (commentaries on and explanation of rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices – Yajñas), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veda Slovena
''Veda Slovena'' (Веда Словена in Modern Bulgarian, originally written as Веда Словенахъ) is an ethnographic collection of folk songs and legends of the Muslim Bulgarians; the subtitle of the book indicated that they were collected from the regions of Thrace and Macedonia (see image right). The first volume of which was printed in 1874 in Belgrade and the second in 1881 in Saint Petersburg under the authorship of Bosnian Croat Stjepan Verković. The collection has unusual themes and content - it deals with pagan gods, supernatural beings, mythological heroes, ancient kings and lords - knowledge and cultural memories formed long before the Islamization of the Pomaks, but also before the Christianization of the Bulgarian people. The collection was assembled by Bulgarian teacher Ivan Gologanov for 12 years and is famous for containing numerous elements of ancient Slavic mythology notwithstanding the conversions first to Christianity and then to Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Songs Of The Macedonian Bulgarians
''Folk Songs of the Macedonian Bulgarians'' (, , ) is an ethnographic collection of folk songs collected by Stefan Verković, considered to be his most valuable contribution in the field of Bulgarian folklore. It was published in Serbian in 1860, in Belgrade.Народне песме македонски Бугара. Скупио Стефанъ И. Верковићъ. Кньига прва Женске песме. У Београду, Правителственомъ кньигопечатньомъ, 1860. Background The book contains 335 folk songs that are lyrical and were therefore called ''female'' by Verković. The songs were collected by him during his time as a Serbian ethological agent in then- Ottoman town of Serres (today in Greece). The collected material was from the eastern parts of the Macedonian region. The title, preface, notes and explanations of the songs are in Serbian, and at the end there is an explanation of some unknown words in Serbian. However, the son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian National Revival
The Bulgarian Revival (, ''Balgarsko vazrazhdane'' or simply: Възраждане, ''Vazrazhdane'', and ), sometimes called the Bulgarian National Revival, was a period of socio-economic development and national integration among Bulgarian people under Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rule. It is commonly accepted to have started with the historical book, ''Istoriya Slavyanobolgarskaya'', written in 1762 by Paisius of Hilendar, Paisius, a Bulgarian monk of the Hilandar monastery at Mount Athos, leading to the National awakening of Bulgaria and the Bulgarian National Awakening, modern Bulgarian nationalism, and lasting until the Liberation of Bulgaria in 1878 as a result of the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878. Characteristics The period is remarkable for its characteristic architecture which can still be observed in old Bulgarian towns such as Tryavna, Koprivshtitsa and Veliko Tarnovo, the rich literary heritage of authors like Ivan Vazov and Hristo Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |