Thrace on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

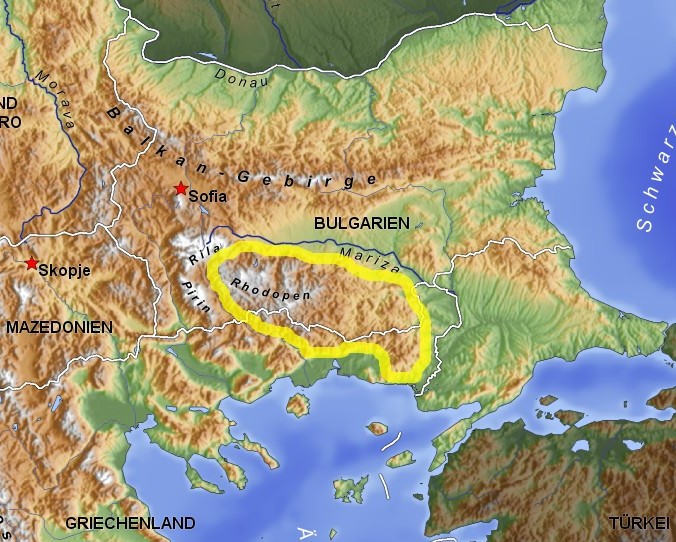
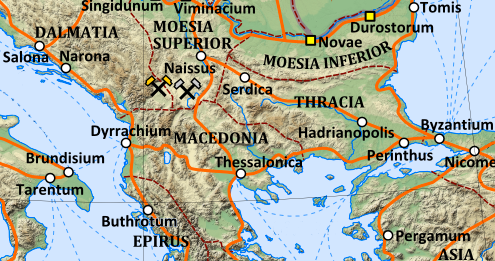

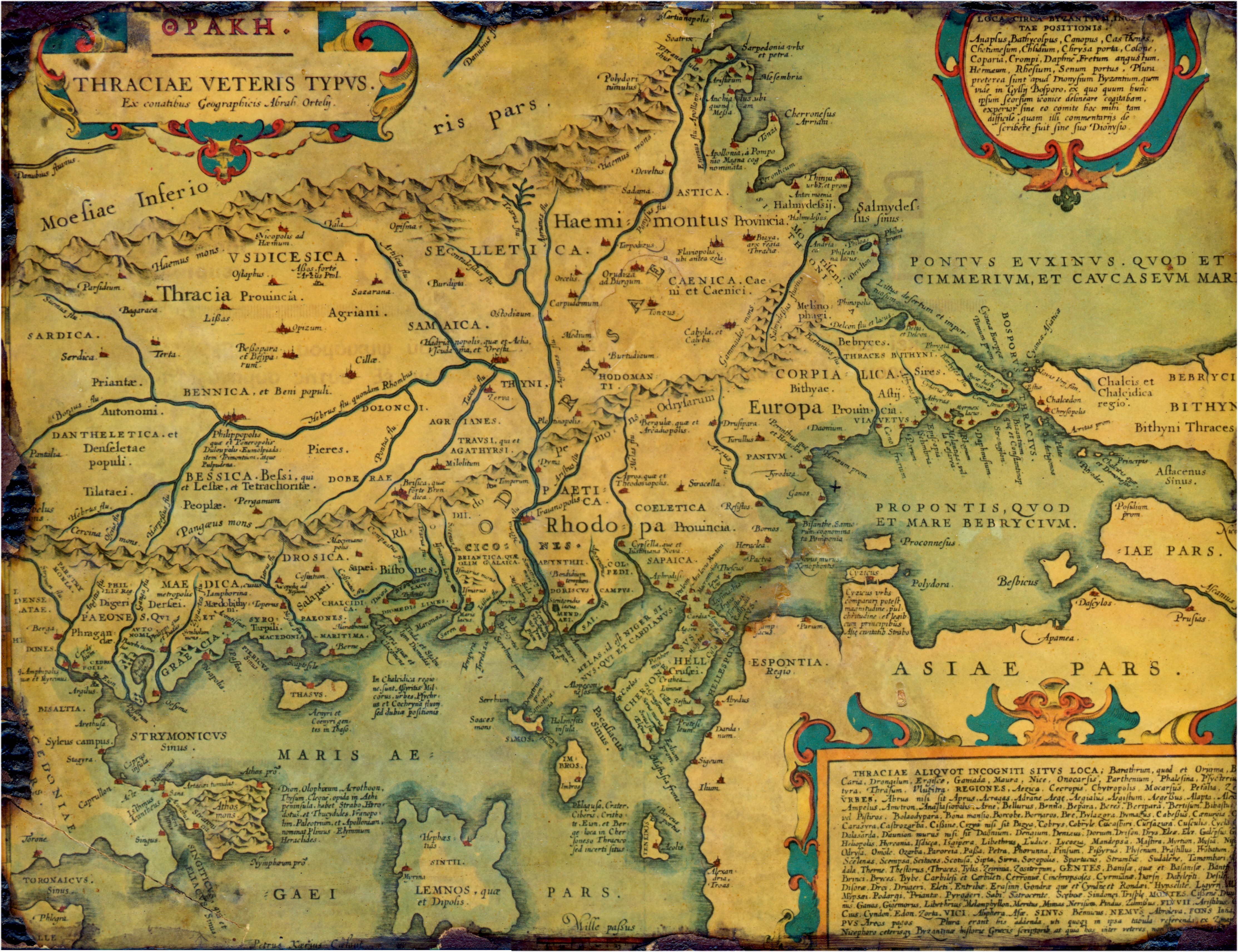

 Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in

 Indigenous
Indigenous
Trakiya Heights.
SCAR
Ethnological Museum of Thrace
comprehensive website on Thracian history and culture.
Bulgaria's most famous Thracian Treasure – The Panagyurishte Gold Treasure to return home after two years lapse
Bulgaria's Thracian Heritage.
including images of the comprehensive art collection of Thracian gold found on the territory of contemporary Bulgaria.
Information on Ancient Thrace
*The People of the God-Sun Ar and Areia (modern Thrace
The People of the God-Sun Ar and Areia (Modern Thrace)Possible Orphic Lyre rock engraving discovered in Bulgaria's Eastern Rhodope Mountains
{{coord, 42, N, 26, E, source:wikidata, display=title Thrace, Ancient Greek geography Historical regions in Greece History of Thrace Thracians Geography of Turkey Historical regions in Bulgaria Historical regions in Turkey




 Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains
The Balkan mountain range is located in the eastern part of the Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border between Bulgaria and Serbia. It then runs f ...
to the north, the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
to the south, and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria ( Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece ( Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey (East Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically in Southeast Europe. Turkish Thrace accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest c ...
). Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and to the west into Macedonia.
Etymology
The word ''Thrace'', fromancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
''Thrake'' (Θρᾴκη), referred originally to the Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
(ancient Greek ''Thrakes'' Θρᾷκες), an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' (ancient Greek Εὐρώπη), also at first referred to this region, before that term expanded to include its modern sense.
It has been suggested that the name ''Thrace'' derives from the name of the principal river of the region, the Hebros. The river's name may be derived from the Indo-European ''arg'' "white river" (the opposite of Vardar
The Vardar (; , , ) or Axios (, ) is the longest river in North Macedonia and a major river in Greece, where it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . The maximum depth of ...
, meaning "black river"). According to an alternative theory, Hebros means "goat" in Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
.
Sixth century geographer Stephanus of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephen of Byzantium (; , ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD) was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethnica'' (). Only meagre fragments of the dictionary survive, but the epit ...
claimed that, long before the ancient Greeks started referring to the region as ''Thrace'', it was known as Aria (Αρια) and Perki (Περκη).
In Turkish, Thrace is commonly referred to as '' Rumeli'', meaning "Land of the Romans", which was the name traditionally given by Turkic societies to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
and Orthodox Christians.
In Greek mythology, Thrace is named after the heroine and sorceress Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
, who was the daughter of Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus ( ; , also , , or ) was a Titans, Titan son of Uranus (mythology), Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys (mythology), Tethys, and the father of the River gods (Greek mythology), river gods ...
and Parthenope, and sister of Europa.
Geography
Borders
The historical boundaries of Thrace have varied. Theancient Greeks
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically re ...
employed the term "Thrace" to refer to all of the territory which lay north of Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
inhabited by the Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
, a region which "had no definite boundaries" and to which other regions (like Macedonia and even Scythia
Scythia (, ) or Scythica (, ) was a geographic region defined in the ancient Graeco-Roman world that encompassed the Pontic steppe. It was inhabited by Scythians, an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people.
Etymology
The names ...
) were added. In one ancient Greek source, the very Earth is divided into "Asia, Libya, Europa and Thracia". As the Greeks gained knowledge of world geography, "Thrace" came to designate the area bordered by the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
on the north, by the Euxine Sea (Black Sea) on the east, by northern Macedonia in the south, and by Illyria
In classical and late antiquity, Illyria (; , ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; , ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.
The Ancient Gree ...
to the west. This largely coincided with the Thracian Odrysian kingdom, whose borders varied over time. After the Macedonian conquest, this region's former border with Macedonia was shifted from the Struma River to the Mesta River. This usage lasted until the Roman conquest. Henceforth, (classical) Thrace referred only to the tract of land largely covering the same extent of space as the modern geographical region. In its early period, the Roman province of Thrace was of this extent, but after the administrative reforms of the late 3rd century, Thracia's much reduced territory became the six small provinces which constituted the Diocese of Thrace
The Diocese of Thrace (, ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the eastern Balkan Peninsula (comprising territories in modern south-eastern Romania, central and eastern Bulgaria, and Greek and Turkish Thrace) ...
. The medieval Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
theme of Thrace contained only what today is East Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically in Southeast Europe. Turkish Thrace accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest c ...
.
Cities
The largest cities of Thrace are:Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, Plovdiv
Plovdiv (, ) is the List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, second-largest city in Bulgaria, 144 km (93 miles) southeast of the capital Sofia. It had a population of 490,983 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is a cultural hub ...
, Çorlu, Tekirdağ, Burgas
Burgas (, ), sometimes transliterated as Bourgas, is the second largest city on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the region of Northern Thrace and the List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, fourth-largest city in Bulgaria after Sofia, Plovdiv, an ...
, Edirne
Edirne (; ), historically known as Orestias, Adrianople, is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the Edirne Province, province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second c ...
, Stara Zagora
Stara Zagora (, ) is a city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of Stara Zagora Province. It is located in the Upper Thracian Plain, near the cities of Kazanlak, Plovdiv, and Sliven. Its population is 121,582 making it the sixth largest c ...
, Sliven, Yambol, Haskovo, Komotini, Alexandroupoli
Alexandroupolis (, ) or Alexandroupoli (, ) is a city in Greece and the capital of the Evros (regional unit), Evros regional unit. It is the largest city in Greek Thrace and the region of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, with a population of 71,75 ...
, Xanthi, and Kırklareli.
Demographics and religion
Most of the Bulgarian andGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
population are Orthodox Christians, while most of the Turkish inhabitants of Thrace are Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s.
Ancient Greek mythology
Ancient Greek mythology provides the Thracians with a mythical ancestor Thrax, the son of the war-godAres
Ares (; , ''Árēs'' ) is the List of Greek deities, Greek god of war god, war and courage. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. The Greeks were ambivalent towards him. He embodies the physical valor necessary for ...
, who was said to reside in Thrace. The Thracians appear in Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
's ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'' as Trojan allies, led by Acamas and Peiros. Later in the ''Iliad'', Rhesus, another Thracian king, makes an appearance. Cisseus, father-in-law to the Trojan elder Antenor, is also given as a Thracian king.
Homeric Thrace was vaguely defined, and stretched from the River Axios in the west to the Hellespont
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey t ...
and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
in the east. The Catalogue of Ships
The Catalogue of Ships (, ''neōn katálogos'') is an epic catalogue in Book 2 of Homer's ''Iliad'' (2.494–759), which lists the contingents of the Achaean army that sailed to Troy. The catalogue gives the names of the leaders of each conting ...
mentions three separate contingents from Thrace: Thracians led by Acamas and Peiros, from Aenus; Cicones led by Euphemus
In Greek mythology, Euphemus (, ''Eὔphēmos'', "reputable") was counted among the Calydonian hunters and the Argonauts, and was connected with the legend of the foundation of Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene.
Family
Euphemus was a son of Poseidon, ...
, from southern Thrace, near Ismaros; and from the city of Sestus, on the Thracian (northern) side of the Hellespont, which formed part of the contingent led by Asius. Ancient Thrace was home to numerous other tribes, such as the Edones
The Edoni (also ''Edones'', ''Edonians'', ''Edonides'') () were a Thracian tribe who dwelt mostly between the Nestus and the Strymon rivers in southern Thrace, but also once dwelt west of the Strymon at least as far as the Axios. They inhabite ...
, Bisaltae, Cicones, and Bistones in addition to the tribe that Homer specifically calls the "Thracians".
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
is replete with Thracian kings, including Diomedes
Diomedes (Jones, Daniel; Roach, Peter, James Hartman and Jane Setter, eds. ''Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary''. 17th edition. Cambridge UP, 2006.) or Diomede (; ) is a hero in Greek mythology, known for his participation in the Trojan ...
, Tereus, Lycurgus, Phineus, Tegyrius, Eumolpus, Polymnestor, Poltys, and Oeagrus (father of Orpheus
In Greek mythology, Orpheus (; , classical pronunciation: ) was a Thracians, Thracian bard, legendary musician and prophet. He was also a renowned Ancient Greek poetry, poet and, according to legend, travelled with Jason and the Argonauts in se ...
).
Thrace is mentioned in Ovid
Publius Ovidius Naso (; 20 March 43 BC – AD 17/18), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a younger contemporary of Virgil and Horace, with whom he i ...
's ''Metamorphoses
The ''Metamorphoses'' (, , ) is a Latin Narrative poetry, narrative poem from 8 Common Era, CE by the Ancient Rome, Roman poet Ovid. It is considered his ''Masterpiece, magnum opus''. The poem chronicles the history of the world from its Cre ...
'', in the episode of Philomela, Procne
Procne (; , ''Próknē'' ) or Progne is a minor figure in Greek mythology. She was an Athens, Athenian princess as the elder daughter of a king of Athens named Pandion I, Pandion. Procne was married to the king of Thrace, Tereus, who instead lu ...
, and Tereus: Tereus, the King of Thrace, lusts after his sister-in-law, Philomela. He kidnaps her, holds her captive, rapes her, and cuts out her tongue. Philomela manages to get free, however. She and her sister, Procne, plot to get revenge, by killing her son Itys (by Tereus) and serving him to his father for dinner. At the end of the myth, all three turn into birds – Procne into a swallow
The swallows, martins, and saw-wings, or Hirundinidae are a family of passerine songbirds found around the world on all continents, including occasionally in Antarctica. Highly adapted to aerial feeding, they have a distinctive appearance. The ...
, Philomela into a nightingale
The common nightingale, rufous nightingale or simply nightingale (''Luscinia megarhynchos''), is a small passerine bird which is best known for its powerful and beautiful song. It was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, ...
, and Tereus into a hoopoe.
The city of Dicaea in Thrace was named after the son of Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
, Dicaeus.
History
Ancient and Roman history

 Indigenous
Indigenous Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
were divided into numerous tribes. The first to take greater control of Thrace, in part or whole, were the Achaemenian
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
in the late 6th century BC. The region was incorporated into their empire as the Satrapy of Skudra, after the Scythian campaign of Darius the Great. Thracian soldiers were used in Persian armies and are depicted in carvings of the Persepolis
Persepolis (; ; ) was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and ...
and Naqsh-e Rostam
Naqsh-e Rostam (; , ) is an ancient archeological site and necropolis located about 13 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars province, Iran. A collection of ancient Iranian rock reliefs are cut into the face of the mountain and the mount ...
. Persians' presence in Thracia lasted for more than a century, ending with the conquests in the 4th century BC by Alexander the Great of Macedon, who divided the vast realm between his generals. Notably, Thracian troops are known to have accompanied Alexander when he crossed the Hellespont
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey t ...
which abuts Thrace, during the invasion of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
itself.
The Thracians recorded no collective name for themselves; terms such as ''Thrace'' and ''Thracians'' were assigned by the Greeks.
Divided into separate tribes, the Thracians did not form any lasting political organizations until the founding of the Odrysian state in the 4th century BC. Like Illyrians
The Illyrians (, ; ) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking people who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan populations, alon ...
, the locally ruled Thracian tribes of the mountainous regions maintained a warrior tradition, while the tribes based in the plains were purportedly more peaceable. Recently discovered funeral mounds in Bulgaria suggest that Thracian kings did rule regions of Thrace with distinct Thracian national identity.
During this period, a subculture of celibate
Celibacy (from Latin ''caelibatus'') is the state of voluntarily being unmarried, sexually abstinent, or both. It is often in association with the role of a religious official or devotee. In its narrow sense, the term ''celibacy'' is applied on ...
ascetics called the Ctistae
The Ctistae or Ktistai () were an Asceticism, ascetic group or class among the ancient Mysians.
The Mysians avoided consuming any living thing, and therefore lived on such foodstuffs as milk and honey. For this reason, they were referred to as "go ...
lived in Thrace, where they served as philosophers, priests, and prophets.
Sections of Thrace particularly in the south started to become hellenized before the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
as Athenian and Ionian colonies were set up in Thrace before the war. Spartan and other Doric colonists followed them after the war. The special interest of Athens to Thrace is underlined by the numerous finds of Athenian silverware in Thracian tombs. In 168 BC, after the Third Macedonian war
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman fe ...
and the subjugation of Macedonia to the Romans, Thrace also lost its independence and became a tributary to Rome. Towards the end of the 1st century BC Thrace lost its status as a client kingdom as the Romans began to directly appoint their kings. This situation lasted until 46 AD, when the Romans finally turned Thrace into a Roman province (Romana provincia Thracia).
During the Roman domination, within the geographical borders of ancient Thrace, there were two separate Roman provinces, namely Thrace ("provincia Thracia") and Lower Moesia ("Moesia inferior"). Later, in the times of Diocletian, the two provinces were joined and formed the so-called "Dioecesis Thracia". The establishment of Roman colonies and mostly several Greek cities, as was Nicopolis, Topeiros, Traianoupolis, Plotinoupolis, and Hadrianoupolis resulted from the Roman Empire's urbanization. The Roman provincial policy in Thrace favored mainly not the Romanization but the Hellenization of the country, which had started as early as the Archaic period through the Greek colonisation and was completed by the end of Roman antiquity. As regards the competition between the Greek and Latin language, the very high rate of Greek inscriptions in Thrace extending south of Haemus Mountains proves the complete language Hellenization of this region. The boundaries between the Greek and Latin speaking Thrace are placed just above the northern foothills of Haemus Mountains.
During the imperial period many Thracians – particularly members of the local aristocracy of the cities – had been granted the right of the Roman citizen
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cu ...
ship (civitas Romana) with all its privileges. Epigraphic evidence show a large increase in such naturalizations in the times of Trajan and Hadrian, while in 212 AD the emperor Caracalla granted, with his well-known decree (constitutio Antoniniana
The (Latin for "Constitution r Edictof Antoninus"), also called the Edict of Caracalla or the Antonine Constitution, was an edict issued in AD 212 by the Roman emperor Caracalla. It declared that all free men in the Roman Empire were to be ...
), the Roman citizenship to all the free inhabitants of the Roman Empire.
During the same period (in the 1st–2nd century AD), a remarkable presence of Thracians is testified by the inscriptions outside the borders (extra fines) both in the Greek territory and in all the Roman provinces, especially in the provinces of Eastern Roman Empire.
Medieval history
By the mid-5th century, as theWestern Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
began to crumble, Thracia fell from the authority of Rome and into the hands of Germanic tribal rulers. With the fall of the Western Roman Empire, Thracia turned into a battleground territory for the better part of the next 1,000 years. The surviving eastern portion of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in the Balkans, later known as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, retained control over Thrace until the 7th century when the northern half of the entire region was incorporated into the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northe ...
and the remainder was reorganized in the Thracian theme. The Empire regained the lost regions in the late 10th century until the Bulgarians regained control of the northern half at the end of the 12th century. Throughout the 13th century and the first half of the 14th century, the region was changing in the hands of the Bulgarian and the Byzantine Empire (excluding Constantinople). In 1265, the area suffered a Mongol raid from the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
, led by Nogai Khan, and between 1305 and 1307 the area was raided by the Catalan company.
Ottoman period
In 1352, the Ottoman Turks conducted their first incursion into the region subduing it completely within a matter of two decades and ruled it for five centuries in general peace. In 1821, several parts of Thrace, such as Lavara,Maroneia
Maroneia () is a village and a former municipality in Rhodope regional unit, East Macedonia and Thrace, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Maroneia-Sapes, of which it is a municipal unit. The munic ...
, Sozopolis, Aenos, Callipolis, and Samothraki rebelled during the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
.
Modern history
With theCongress of Berlin
At the Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878), the major European powers revised the territorial and political terms imposed by the Russian Empire on the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of San Stefano (March 1878), which had ended the Rus ...
in 1878, Northern Thrace was incorporated into the semi-autonomous Ottoman province of Eastern Rumelia, which united with Bulgaria in 1885. The rest of Thrace was divided among Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
at the beginning of the 20th century, following the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, M ...
, World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the Greco-Turkish War. In Summer 1934, up to 10,000 Jews were maltreated, bereaved, and then forced to quit the region (see 1934 Thrace pogroms). From Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
and Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
between 1934 and 1938 a large wave of Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
immigrants called ''Göçmenler'' went to East Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically in Southeast Europe. Turkish Thrace accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest c ...
.
Today, ''Thracian'' is a geographical term used in Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, and Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
.
Notable Thracians
*Orpheus
In Greek mythology, Orpheus (; , classical pronunciation: ) was a Thracians, Thracian bard, legendary musician and prophet. He was also a renowned Ancient Greek poetry, poet and, according to legend, travelled with Jason and the Argonauts in se ...
was, in Ancient Greek mythology, the chief representative of the art of song and playing the lyre
The lyre () (from Greek λύρα and Latin ''lyra)'' is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute family of instruments. In organology, a ...
.
* Protagoras (c. 490–420 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Abdera, Thrace
Abdera () is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace, Greece. In classical antiquity, it was a major Greek ''polis'' on the Thracian coast.
The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its hono ...
. An expert in rhetoric
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion. It is one of the three ancient arts of discourse ( trivium) along with grammar and logic/ dialectic. As an academic discipline within the humanities, rhetoric aims to study the techniques that speakers or w ...
s and subjects connected to virtue and political life, often regarded as the first sophist
A sophist () was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BCE. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics and mathematics. They taught ''arete'', "virtue" or "excellen ...
. He is known primarily for three claims: (1) that man is the measure of all things, often interpreted as a sort of moral relativism
Moral relativism or ethical relativism (often reformulated as relativist ethics or relativist morality) is used to describe several Philosophy, philosophical positions concerned with the differences in Morality, moral judgments across different p ...
, (2) that he could make the "worse (or weaker) argument appear the better (or stronger)" (see Sophism
A sophist () was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BCE. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics and mathematics. They taught ''arete'', "virtue" or "excellen ...
), and (3) that one could not tell if the gods existed or not (see Agnosticism
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, the divine, or the supernatural is either unknowable in principle or unknown in fact. (page 56 in 1967 edition) It can also mean an apathy towards such religious belief and refer t ...
).
* Herodicus was a Greek physician of the fifth century BC who is considered the founder of sports medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the ...
. He is believed to have been one of Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
's tutors.
*Democritus
Democritus (, ; , ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, Thrace, Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an ...
(c. 460–370 BC) was a Greek philosopher and mathematician from Abdera, Thrace
Abdera () is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace, Greece. In classical antiquity, it was a major Greek ''polis'' on the Thracian coast.
The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its hono ...
. His main contribution is the atomic theory
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. The definition of the word "atom" has changed over the years in response to scientific discoveries. Initially, it referred to a hypothetical concept of ...
, the belief that all matter is made up of various imperishable indivisible elements which he called atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s.
*Spartacus
Spartacus (; ) was a Thracians, Thracian gladiator (Thraex) who was one of the Slavery in ancient Rome, escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major Slave rebellion, slave uprising against the Roman Republic.
Historical accounts o ...
was a Thracian who led a large slave uprising in what is now Italy in 73–71 BC. His army of escaped gladiator
A gladiator ( , ) was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their ...
s and slaves defeated several Roman legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 i ...
s in what is known as the Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directl ...
.
*A number of Roman emperors of the 3rd–5th century were of Thraco-Roman
The term Thraco-Roman describes the Romanization (cultural), Romanized culture of Thracians under the rule of the Roman Empire.
The Odrysian kingdom of Thrace became a Roman client kingdom c. 20 BC, while the Greek city-states on the Black Sea coa ...
backgrounds (Maximinus Thrax
Gaius Julius Verus Maximinus "Thrax" () was a Roman emperor from 235 to 238. Born of Thracian origin – given the nickname ''Thrax'' ("the Thracian") – he rose up through the military ranks, ultimately holding high command in the army of th ...
, Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Λικίνιος; c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign, he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan that ...
, Galerius
Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; Greek: Γαλέριος; 258 – May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. He participated in the system of government later known as the Tetrarchy, first acting as '' caesar'' under Emperor Diocletian. In th ...
, Aureolus
Aureolus was a Roman military commander during the reign of Emperor Gallienus before he attempted to usurp the Roman Empire. After turning against Gallienus, Aureolus was killed during the political turmoil that surrounded the Emperor's assass ...
, Leo the Thracian, etc.). These emperors were elevated via a military career (hence the resultant nickname for them, Barracks Emperor), from the condition of common soldiers in one of the Roman legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 i ...
s to the foremost positions of political power
In political science, power is the ability to influence or direct the actions, beliefs, or conduct of actors. Power does not exclusively refer to the threat or use of force (coercion) by one actor against another, but may also be exerted thro ...
.
Legacy
The Trakiya Heights inAntarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
"are named after the historical region."SCAR
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about th ...
.
See also
* 1989 expulsion of Turks from Bulgaria * Celtic settlement of Eastern Europe *Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ro ...
* Dardania
* Destruction of Thracian Bulgarians in 1913
* Hawks of Thrace
*Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
*Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
* Moesogoths
* Music of Thrace
* Paionia
* Thracian treasure
* Turkish Republic of Thrace
* List of kings of Thrace and Dacia
Notes
References
*Hoddinott, R. F., ''The Thracians'', 1981. *Ilieva, Sonya, ''Thracology'', 2001External links
Ethnological Museum of Thrace
comprehensive website on Thracian history and culture.
Bulgaria's most famous Thracian Treasure – The Panagyurishte Gold Treasure to return home after two years lapse
Bulgaria's Thracian Heritage.
including images of the comprehensive art collection of Thracian gold found on the territory of contemporary Bulgaria.
Information on Ancient Thrace
*The People of the God-Sun Ar and Areia (modern Thrace
The People of the God-Sun Ar and Areia (Modern Thrace)
{{coord, 42, N, 26, E, source:wikidata, display=title Thrace, Ancient Greek geography Historical regions in Greece History of Thrace Thracians Geography of Turkey Historical regions in Bulgaria Historical regions in Turkey