|
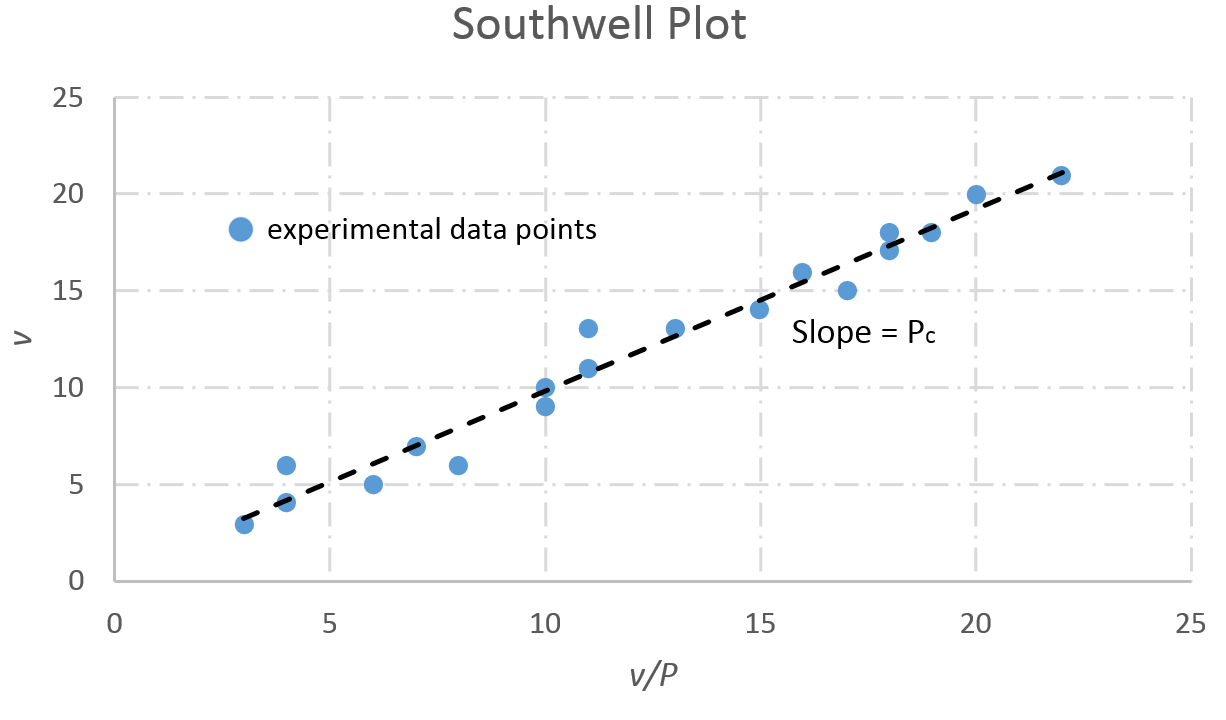
Southwell Plot
The Southwell plot is a graphical method of determining experimentally a structure's Structural load, critical load, without needing to subject the structure to near-critical loads.Mandal, P., & Calladine, C. (2002). Lateral-torsional buckling of beams and the Southwell plot. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 44(12), 2557-2571. doi:10.1016/s0020-7403(02)00192-3 The technique can be used for nondestructive testing of any structural elements that may fail by buckling.Stability Of Structures: Additional Topics. (n.d.). Retrieved November 20, 2016, from http://www.colorado.edu/engineering/CAS/courses.d/Structures.d/IAST.Lect26.d/IAST.Lect26.pdf Critical load Consider a simply supported beam under a compressive load ''P''. The differential equation of equilibrium is \frac + \alpha^2\frac(v-v^o)=0, \alpha^2=\frac where ''v''''o'' is the initial deflection, and the boundary conditions are v(0)=v^(0)=v(L)=v^(L)=0 Assuming that the deflected shape can be expressed as a Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Southwell Plot
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experiment, natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Method
This is a list of graphical methods with a mathematical basis. Included are diagram techniques, chart techniques, plot techniques, and other forms of visualization. There is also a list of computer graphics and descriptive geometry topics. Simple displays *Area chart *Bar chart **Histogram ** Variable-width bar chart *Box plot ** Dispersion fan diagram *Graph of a function ** Logarithmic graph paper *Heatmap *Line chart *Pie chart * Plotting *Radar chart *Scatterplot *Sparkline * Spiral graphic * Stemplot * Stripe graphic Set theory *Venn diagram * Karnaugh diagram Descriptive geometry *Isometric projection *Orthographic projection *Perspective (graphical) Engineering drawing *Technical drawing **Graphical projection *Mohr's circle *Pantograph *Circuit diagram * Smith chart * Sankey diagram Systems analysis * Binary decision diagram *Control-flow graph * Functional flow block diagram * Information flow diagram *IDEF * N2 chart * Sankey diagram *State diagram *System context ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Load
A structural load or structural action is a mechanical load (more generally a force) applied to Structural engineering#Structural elements, structural elements. A load causes stress (physics), stress, deformation (engineering), deformation, displacement (vector), displacement or acceleration in a structure. Structural analysis, a discipline in engineering, analyzes the effects of loads on structures and structural elements. Excess load may cause structural failure, so this should be considered and controlled during the design of a structure. Particular mechanical structures—such as aircraft, satellites, rockets, space stations, ships, and submarines—are subject to their own particular structural loads and actions. Engineers often evaluate structural loads based upon published regulations, contracts, or specifications. Accepted technical standards are used for acceptance testing and inspection. Types In civil engineering, specified loads are the best estimate of the actual l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current testing, eddy-current, magnetic-particle inspection, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant testing, liquid penetrant, radiographic testing, radiographic, ultrasonic testing, ultrasonic, and Visual inspection, visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Element
In structural engineering, structural elements are used in structural analysis to split a complex structure into simple elements (each bearing a structural load). Within a structure, an element cannot be broken down (decomposed) into parts of different kinds (e.g., beam or column). Structural building components are specialized structural building products designed, engineered and manufactured under controlled conditions for a specific application. They are incorporated into the overall building structural system by a building designer. Examples are wood or steel roof trusses, floor trusses, floor panels, I-joists, or engineered beams and headers. A structural building component manufacturer or truss manufacturer is an individual or company regularly engaged in the manufacturing of components. Structural elements can be lines, surfaces or volumes. Line elements: *Rod - axial loads * Beam - axial and bending loads * Pillar * Post (structural) * Struts or Compression member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buckling
In structural engineering, buckling is the sudden change in shape (Deformation (engineering), deformation) of a structural component under Structural load, load, such as the bowing of a column under Compression (physics), compression or the wrinkling of a plate under Shearing (physics), shear. If a structure is subjected to a gradually increasing load, when the load reaches a critical level, a member may suddenly change shape and the structure and component is said to have ''buckled''. Euler's critical load and Johnson's parabolic formula are used to determine the buckling stress of a column. Buckling may occur even though the Stress (mechanics), stresses that develop in the structure are well below those needed to cause Catastrophic failure, failure in the material of which the structure is composed. Further loading may cause significant and somewhat unpredictable deformations, possibly leading to complete loss of the member's load-carrying capacity. However, if the deformation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Conditions
In the study of differential equations, a boundary-value problem is a differential equation subjected to constraints called boundary conditions. A solution to a boundary value problem is a solution to the differential equation which also satisfies the boundary conditions. Boundary value problems arise in several branches of physics as any physical differential equation will have them. Problems involving the wave equation, such as the determination of normal modes, are often stated as boundary value problems. A large class of important boundary value problems are the Sturm–Liouville problems. The analysis of these problems, in the linear case, involves the eigenfunctions of a differential operator. To be useful in applications, a boundary value problem should be well posed. This means that given the input to the problem there exists a unique solution, which depends continuously on the input. Much theoretical work in the field of partial differential equations is devoted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Series
A Fourier series () is an Series expansion, expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems involving the function become easier to analyze because trigonometric functions are well understood. For example, Fourier series were first used by Joseph Fourier to find solutions to the heat equation. This application is possible because the derivatives of trigonometric functions fall into simple patterns. Fourier series cannot be used to approximate arbitrary functions, because most functions have infinitely many terms in their Fourier series, and the series do not always Convergent series, converge. Well-behaved functions, for example Smoothness, smooth functions, have Fourier series that converge to the original function. The coefficients of the Fourier series are determined by integrals of the function multiplied by trigonometric func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (structure)
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally across the beam's axis (an element designed to carry a load pushing parallel to its axis would be a strut or column). Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending, as loads produce reaction forces at the beam's support points and internal bending moments, shear, stresses, strains, and deflections. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile (shape of cross-section), equilibrium conditions, length, and material. Beams are traditionally descriptions of building or civil engineering structural elements, where the beams are horizontal and carry vertical loads. However, any structure may contain beams, such as automobile frames, aircraft components, machine frames, and other mechanical or structural systems. Any structural element, in any orientation, that primarily resists loads applied laterally across the element's axis is a beam. Overview Historically a beam is a squared ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwell Beam Theory
Southwell may refer to: Geography *Southwell, Dorset, a village *Southwell, Nottinghamshire, a town **Southwell Minster, historic cathedral *** Prebends of Southwell ** Southwell Racecourse, horse racing venue located near Newark-on-Trent, Nottinghamshire ** Southwell Rural District, a rural district in Nottinghamshire, England from 1894 to 1974 * Southwell, Eastern Cape, a settlement in South Africa Other * Southwell (surname) *Southwell, assumed name of Nathaniel Bacon (Jesuit) * Viscount Southwell Viscount Southwell ( ), of Castle Mattress in the County of Limerick, is a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created in 1776 for Thomas Southwell, 3rd Baron Southwell. The Southwell family descends from Thomas Southwell. In 1662 he was cr ..., a title in the Peerage of Ireland * Southwell School, a co-educational independent preparatory school in Hamilton, New Zealand {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |