Southwell Plot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Southwell plot is a
The Southwell plot is a
 Consider a simply supported beam under a compressive load ''P''. The differential equation of equilibrium is
,
where ''v''''o'' is the initial deflection, and the
Consider a simply supported beam under a compressive load ''P''. The differential equation of equilibrium is
,
where ''v''''o'' is the initial deflection, and the 
 The Southwell plot is a
The Southwell plot is a graphical method
This is a list of graphical methods with a mathematical basis.
Included are diagram techniques, chart techniques, plot techniques, and other forms of visualization.
There is also a list of computer graphics and descriptive geometry topics.
Sim ...
of determining experimentally a structure's critical load, without needing to subject the structure to near-critical loads.Mandal, P., & Calladine, C. (2002). Lateral-torsional buckling of beams and the Southwell plot. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 44(12), 2557-2571. doi:10.1016/s0020-7403(02)00192-3 The technique can be used for nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
of any structural element
In structural engineering, structural elements are used in structural analysis to split a complex structure into simple elements (each bearing a structural load). Within a structure, an element cannot be broken down (decomposed) into parts of dif ...
s that may fail by buckling
In structural engineering, buckling is the sudden change in shape (Deformation (engineering), deformation) of a structural component under Structural load, load, such as the bowing of a column under Compression (physics), compression or the wrin ...
.Stability Of Structures: Additional Topics. (n.d.). Retrieved November 20, 2016, from http://www.colorado.edu/engineering/CAS/courses.d/Structures.d/IAST.Lect26.d/IAST.Lect26.pdf
Critical load
 Consider a simply supported beam under a compressive load ''P''. The differential equation of equilibrium is
,
where ''v''''o'' is the initial deflection, and the
Consider a simply supported beam under a compressive load ''P''. The differential equation of equilibrium is
,
where ''v''''o'' is the initial deflection, and the boundary conditions
In the study of differential equations, a boundary-value problem is a differential equation subjected to constraints called boundary conditions. A solution to a boundary value problem is a solution to the differential equation which also satis ...
are
Assuming that the deflected shape can be expressed as a Fourier series
A Fourier series () is an Series expansion, expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems ...
,
Then after substitution into the differential equation,
,
This relates the deflected shape to the initial imperfections and the applied load. Specifically, at ''x''=''L''/2,
,
As ''P'' approaches ''P''1, ''v''(''L''/2) is dominated by ''V''1. Therefore, when ''P''''P''1, then the fundamental mode will dominate, resulting in
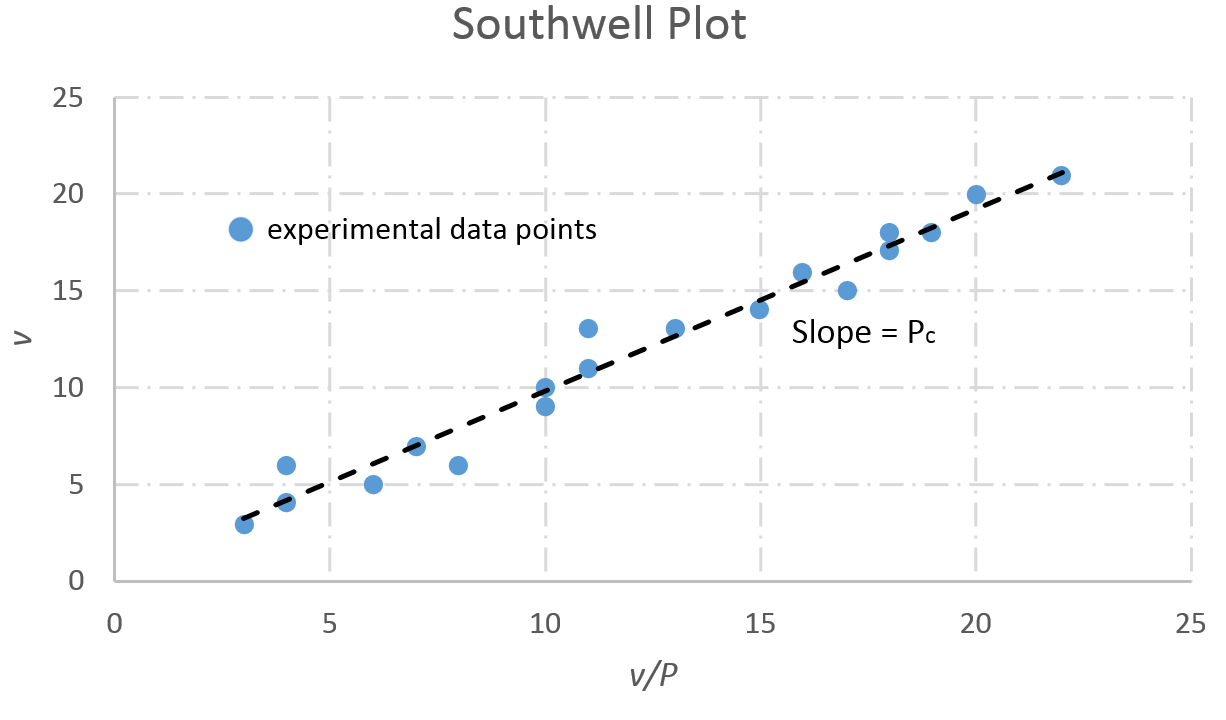
Southwell plots ''v''/''P'' against ''v'' and obtains ''P''1=''P''critical=''P''c from the slope of the predicted straight line graph.Experiment 2.5: Stability of Structures. (n.d.). Retrieved November 20, 2016, from https://mycourses.purdue.edu/bbcswebdav/pid-7803100-dt-content-rid-31348241_1/courses/wl_10033.201710/Lab 5 manual.pdf
This analysis was done for a specific point on a simply supported beam, but the concept can be extended to arbitrary structures. With any problem whose mathematical analog is the same fourth order ordinary differential equation as above, with similar boundary conditions, the first eigenvalue of the associated homogeneous problem can be obtained from the slope of the graph. Therefore, a point of large deflection can be chosen, and it does not need to be the center of a simply supported beam. 
Applications
Strictly speaking, Southwell's Plot is applicable only to structures with a neutral post-buckling path. Initially created for stability problems in column buckling, the Southwell method has also been used to determine critical loads in frame and plate buckling experiments. The method is particularly useful for field tests of structures that are likely to be damaged by applying loads near the critical load and beyond, such asreinforced concrete
Reinforced concrete, also called ferroconcrete or ferro-concrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having higher tensile strength or ...
columns or advanced composite materials. The method can also minimize parasitic effects in experiments and give values that are closer to the theoretically expected values. For example, in a real experiment setup it is impossible to reproduce any theoretical boundary condition perfectly. Additionally, the results of compressive tests can be very sensitive to imperfections and the actual boundary conditions. Therefore, the measured critical load during the experiment can be very different from what is predicted.
References
{{reflist Nondestructive testing Mechanics