|
Southern Flathead Sculpin
The southern flathead sculpin (''Megalocottus taeniopterus'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This species occurs in the northern Pacific Ocean. Taxonomy The southern flathead sculpin was first formally described as ''Cottus taeniopterus'' by the Austrian ichthyologist Rudolf Kner with its type locality given as Decastris Bay near the mouth of the Amur River in Russia. Some authorities consider that this species as a subspecies or junior synonym of '' M. platycephalus''. ''FishBase'' still recognises two species within the genus ''Megalocottus''. Distribution The southern flathead sculpin is found in the northwestern Pacific Ocean in Amur Liman, Peter the Great Gulf and around southern Sakhalin Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Kner
Rudolf Ignaz Kner (24 August 1810 – 27 October 1869) was an Austrian geologist, paleontologist, zoologist and ichthyologist. He also wrote some poems which were published by his brother-in-law K.A. Kaltenbrunner. Biography Kner was born in Linz where his father Johann Evangelist Georg Kner (1763-1845) was a tax officer. His mother Barbara (1770-1825), daughter of forester Johann von Adlersburg was earlier married to apothecary Felix Gulielmo until his death. Barbara had a daughter Marie Gulielmo from her earlier marriage before having Rudolf and his sister Pauline. Pauline Anna Barbara Kner (1809-1843) married the Austrian poet Karl Adam Kaltenbrunner (1804-1867) in 1834. Rudolf studied in the secondary school in Linz from 1818 and the high school from 1821. During this period he was encouraged in the natural sciences with a gift of minerals from his uncle Hallstatt Maximilian Kner (1755–1821). From 1823 he went to the Stiftsgymnasium Kremsmünster. His godfather, Ign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that now goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called '' Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, '' Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank – for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
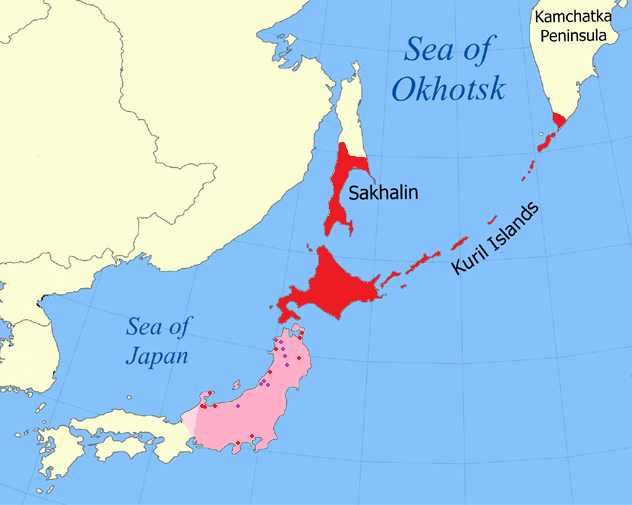
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An island of the West Pacific, Sakhalin divides the Sea of Okhotsk to its east from the Sea of Japan to its southwest. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast and is the largest island of Russia, with an area of . The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of whom are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (), which was the name of the Qing dynasty city of Aigun. The Ainu people of Sakhalin paid tribute to the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties and accepted official appointments from them. Sometimes the relationship was forced but control from dynasties in China was loose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great Gulf
The Peter the Great Gulf (Russian: Залив Петра Великого) is a gulf on the southern coast of Primorsky Krai, Russia, and the largest gulf of the Sea of Japan. The gulf extends for from the Russian–North Korean border, at the mouth of the Tumen River in the west, across to Cape Povorotny in the east, and its bays reach inland. Vladivostok (the largest city and capital of Primorsky Krai) and Nakhodka (the third-largest city in the krai) are located along the Gulf coast. Geography and nature The Peter the Great Gulf has a coastline of about , with the largest bay of the gulf, at about , divided by the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula and the Eugénie Archipelago into the major bays of Amur Bay to the west and the Ussuri Bay to the east. The coast is indented by many smaller, minor bays, including Posyet Bay, Zolotoy Rog (the "Golden Horn") and Diomede Bay, in the west, Lazurnaya Bay (the "Shamora", with its sandy beaches), at the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amur Liman
The Amur Liman is a liman of the Amur River, the northern part of the Strait of Tartary between Eurasia and Sakhalin. It connects the Sakhalin Gulf of the Sea of Okhotsk with the main body of the Strait of Tartary via the Nevelskoy Strait. "Amur Liman" is often translated as "Amur Estuary An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ..." or "Amur Mouth". References Bodies of water of Sakhalin Oblast Bays of the Sea of Okhotsk Bodies of water of Russia Estuaries of Russia {{russia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalocottus
''Megalocottus'' is a small genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. These fishes are found in the western Pacific Ocean. Taxonomy ''Megalocottus'' was first proposed as a monospecific genus in 1861 by the American biologist Theodore Gill with ''Cottus paltycephalus'' which had been described in 1814 by Peter Simon Pallas from Kamchatka and the Sea of Okhotsk as its only species. The 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' classifies this genus in the subfamily Cottinae of the family Cottidae but other authorities classify it in the subfamily Myoxocephalinae of the family Psychrolutidae, although others place the subfamily Myoxocephalinae within the Cottidae. Etymology ''Megalocottus'' prefixes ''megalo'' meaning "great" or large" with Cottus, presumed to be a reference to the large size of the type species. Species ''Megalocottus'' currently contains two recognized: * '' Megalocottus platycephalus'' (Pallas, 1814) (Belligere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FishBase
FishBase is a global species database of fish species (specifically finfish). It is the largest and most extensively accessed online database on adult finfish on the web.Marine Fellow: Rainer Froese ''Pew Environment Group''. Over time it has "evolved into a dynamic and versatile ecological tool" that is widely cited in scholarly publications. FishBase provides comprehensive species data, including information on , geographical distribution, biometrics and morpholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belligerent Sculpin
The belligerent sculpin (''Megalocottus platycephalus''), or flathead sculpin, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This species occurs in the northern Pacific Ocean. Taxonomy The belligerent sculpin was first formally described in 1814 as ''Cottus platycephalus'' by the German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas with its type locality given as Kamchatka and the Sea of Okhotsk. In 1861 the American biologist Theodore Gill classified this species in the monospecific genus ''Megalocottus''. Some authorities consider the belligerent sculpin to be the still the only species in its genus, either recognising the Southern flathead sculpin (''M. taeniopterus'') as a subspecies or junior synonym of ''M. platycephalus''. Fishbase still recognises two species within the genus ''Megalocottus''. The specific name ''playcephalus'' means "flat head", a reference to the wide, flat head with a projecting lower jaw. Description The belligerent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific name, infraspecific ranks, such as variety (botany), variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes, bacterial nomenclature and virus clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray-finned Fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spines called '' lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they dominate the subphylum Vertebrata, and constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 extant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amur River
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ''proper'' is long, and has a drainage basin of .Амур (река в Азии) If including its main stem , the Argun, the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De-Kastri
De-Kastri () is a rural locality (a settlement) in Ulchsky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: Etymology The settlement's name is the Russian phonetic transliteration of the name of the Marquis de Castries, who sponsored the expedition of the French explorer La Pérouse, who was the first European to sight the bay where the settlement is located. Geography The settlement is located on the Chikhachyova Bay, which was known as ''Bay of de Castries'' until 1952. History This locality was named De-Kastri for the former name of the bay on which it stands. The bay was discovered by La Pérouse on July 25, 1787 and named after the sponsor of the expedition—the then Secretary of State of the French Navy, the Marquis de Castries. The bay is a convenient natural refuge for vessels, giving it strategic importance from a military viewpoint. The settlement was founded in 1853, although the land where it was situated would not officially be Russian territory until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |