|
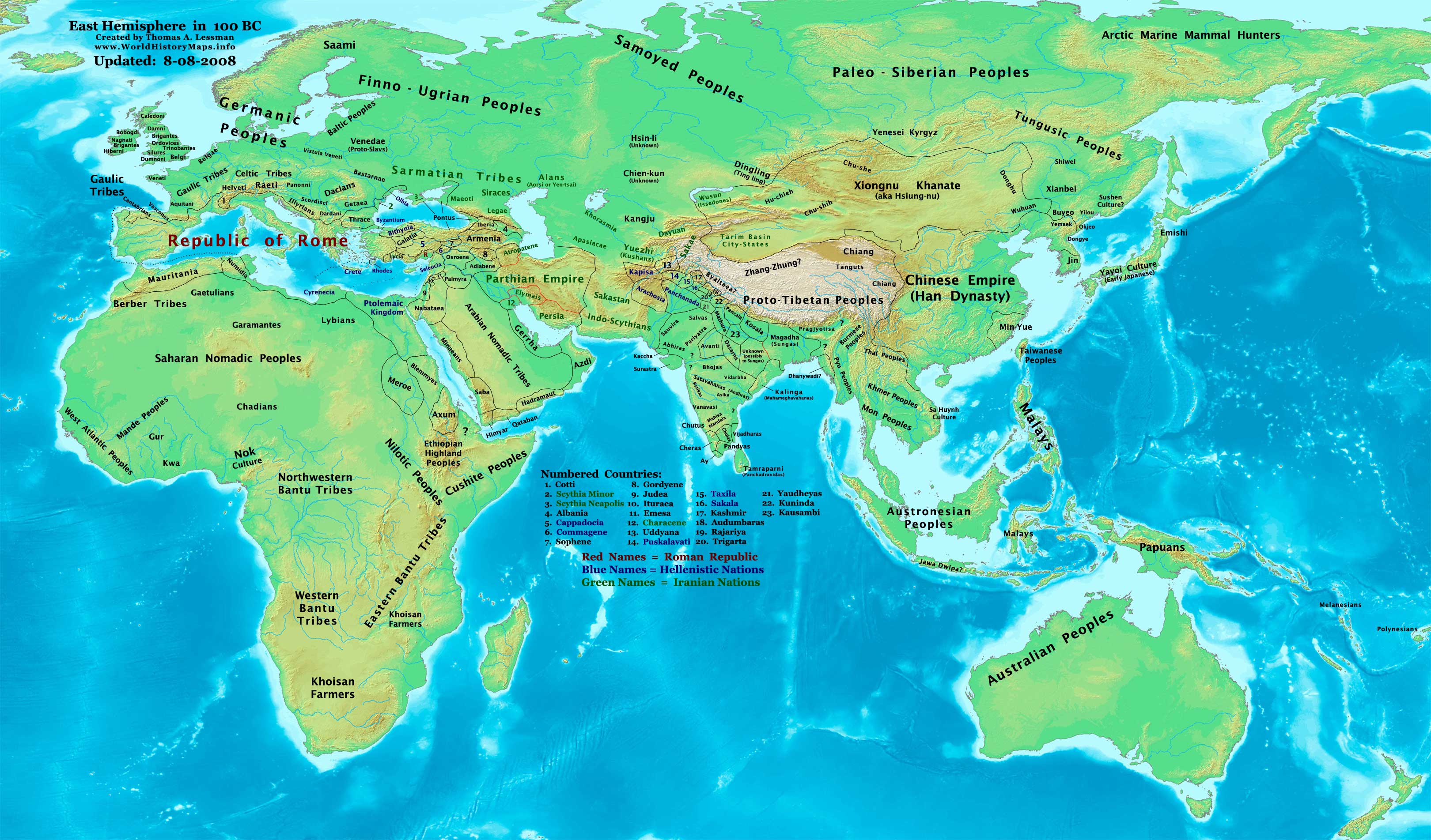
Songyun (monk)
Song Yun or Songyun ( & 520s) was a Chinese Buddhist monk who travelled to medieval India from the Tuoba Northern Wei kingdom during China's Northern and Southern dynastic period at the behest of the Empress Hu. He and his companions Huisheng, Fali, and Zheng or Wang Fouze left the Wei capital Luoyang on foot in 518 and returned in the winter of 522 with 170 Buddhist scriptures. Song and Hui's accounts of their journey are now lost but much of their information was preserved in other texts. Life Knowledge of Song Yun's bibliography is known primarily from sources derived from the accounts of the journey written by Song and his companion Huisheng or analysis of those sources. He was originally from Dunhuang. Surviving accounts of his journey to India vary in various details. According to the reconstruction of the trip by Édouard Chavannes, :Huisheng nd the otherswere sent in the 11th day of the second month of the second Zhengui year (518); he and his companions arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Chavannes
Émmanuel-Édouard Chavannes (5 October 1865 – 29 January 1918) was a French sinologist and expert on Chinese history and religion, and is best known for his translations of major segments of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'', the work's first ever translation into a Western language. Chavannes was a prolific and influential scholar, and was one of the most accomplished Sinologists of the modern era notwithstanding his relatively early death at age 52 in 1918. A successor of 19th century French sinologists Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat and Stanislas Julien, Chavannes was largely responsible for the development of Sinology and Chinese scholarship into a respected field in the realm of French scholarship. Life and career Édouard Chavannes was born on 5 October 1865 in Lyon, France. As a youth he studied at the ''lycée'' in Lyon, where, like most students of his era, his education focused mainly on the Latin and Greek classics. Chavannes was then sent to Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qaidam
The Qaidam, Tsaidam, or Chaidamu Basin is a hyperarid basin that occupies a large part of Haixi Prefecture in Qinghai Province, China. The basin covers an area of approximately , one-fourth of which is covered by saline lakes and playas. Around one third of the basin, about , is desert. Name ''Tshwa'i 'Dam'' is the Wylie romanization of the Tibetan name , meaning "Salt Marsh"; the Tibetan Pinyin romanization of the same name is ''Caidam''. ''Qaidam'' is the GNC romanization of its transcription into Mongolian; ''Tsaidam'' is a variant romanization of the same name. ''Chaidamu'' is the pinyin romanization of its transcription into Chinese characters; the same name was formerly romanized as the for the Chinese Postal Map. Geography Orographically, the Qaidam Basin is a comparatively low area in the northeastern part of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau.. With an elevation of around , Qaidam forms a kind of shelf between Tibet to the south (around ) and Gansu to the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai Lake
Qinghai Lake is the list of lakes by area, largest lakes of China, lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline lake, alkaline saline lake, salt lake. The lake has fluctuated in size, shrinking over much of the 20th century but increasing since 2004. It had a surface area of , an average depth of , and a maximum depth of in 2008. Names ''Qinghai'' is the Chinese tones, atonal pinyin romanization of Chinese, romanisation of the Standard Chinese, Mandarin pronunciation of the Chinese language, Chinese name Although modern Chinese distinguishes between the colors blue and green, Blue–green distinction in language, this distinction did not exist in classical Chinese. The color (''qīng'') was Blue–green distinction in language#Chinese, a "single" color inclusive of both blue and green as separate shades. The name is thus variously translated as "Blue Sea", "Green Sea", "Blue-Green Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
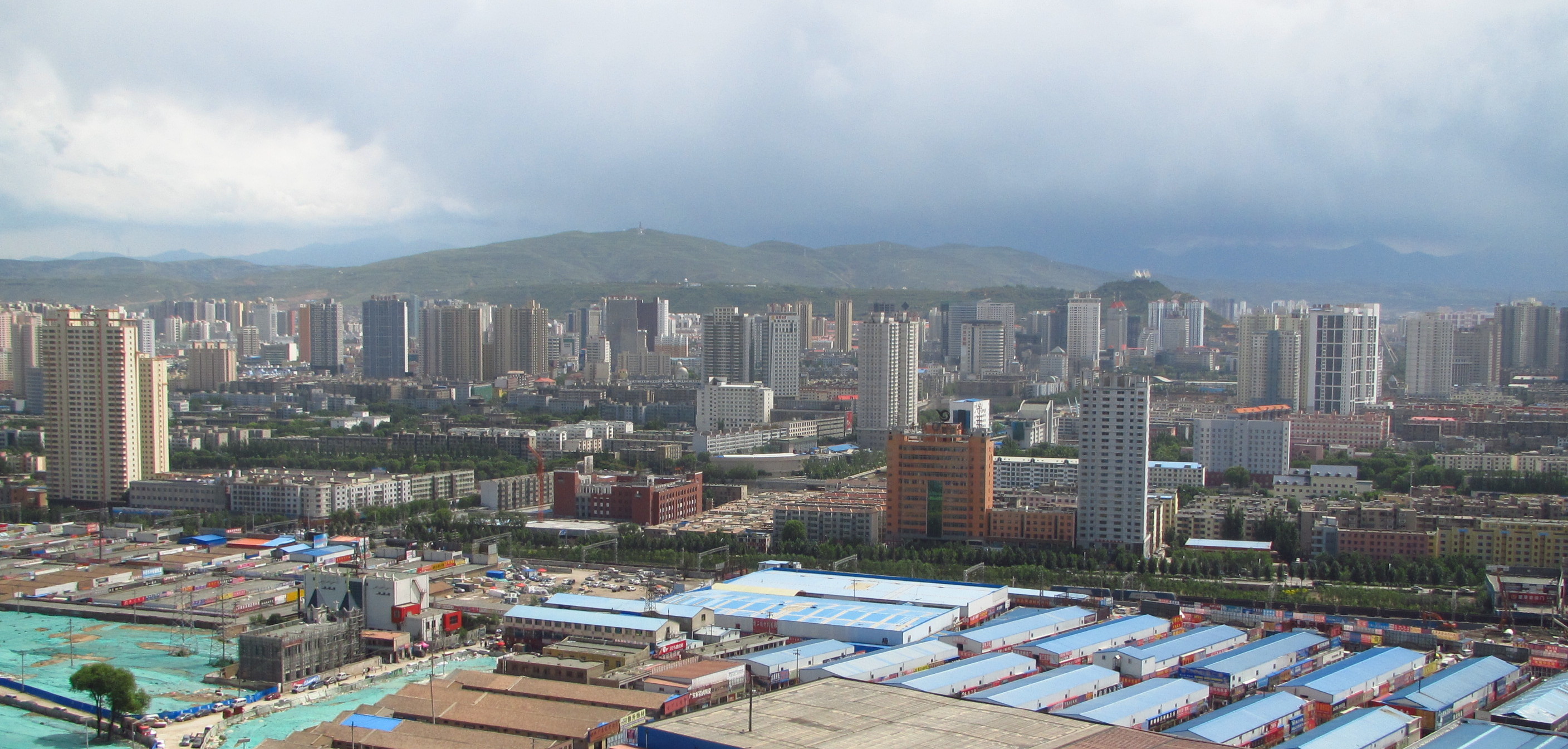
Xining
Xining is the Capital (political), capital and most populous city of Qinghai province in western China and the largest city on the Tibetan Plateau. As of the 2020 census, it had 2,467,965 inhabitants (2,208,708 as of 2010), of whom 1,954,795 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of 5 urban districts. The city lies in the Huangshui River, Huangshui River Valley, also known as Tsongkha (Tibetan script, Tibetan: ཙོང་ཁ་), and owing to its high altitude, has a cool climate on the borderline between Semi-arid climate#Cold semi-arid climates, cool semi-arid and dry winter humid continental climate, humid continental. Xining was a commercial hub along the Northern Silk Road's Hexi Corridor for over 2000 years, and was a stronghold of the Han dynasty, Han, Sui dynasty, Sui, Tang dynasty, Tang, and Song dynasty, Song dynasties' resistance against nomadic attacks from the west. Although long a part of Gansu province, Xining was added to Qinghai in 1928. Xining holds sites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Hui people, Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese language, Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat language, Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin, or simply pinyin, officially the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet, is the most common romanization system for Standard Chinese. ''Hanyu'' () literally means 'Han Chinese, Han language'—that is, the Chinese language—while ''pinyin'' literally means 'spelled sounds'. Pinyin is the official romanization system used in China, Singapore, Taiwan, and by the United Nations. Its use has become common when transliterating Standard Chinese mostly regardless of region, though it is less ubiquitous in Taiwan. It is used to teach Standard Chinese, normally written with Chinese characters, to students in mainland China and Singapore. Pinyin is also used by various Chinese input method, input methods on computers and to lexicographic ordering, categorize entries in some Chinese dictionaries. In pinyin, each Chinese syllable is spelled in terms of an optional initial (linguistics), initial and a final (linguistics), final, each of which is represented by one or more letters. Initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodhidharma
Bodhidharma was a semi-legendary Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk who lived during the 5th or 6th century CE. He is traditionally credited as the transmitter of Chan Buddhism to China, and is regarded as its first Chinese Lineage (Buddhism), patriarch. He is also popularly regarded as the founder of Shaolin kung fu, an idea popularized in the 20th century, but based on the 17th century Yijin Jing and the Daoist association of ''daoyin'' gymnastics with Bodhidharma. Little contemporary biographical information on Bodhidharma is extant, and subsequent accounts became layered with legend and unreliable details. According to the principal Chinese sources, Bodhidharma came from the Western Regions, which typically refers to Central Asia but can also include the Indian subcontinent, and is described as either a "Persians, Persian Central Asian" or a "South Indian [...] the third son of a great Indian king." Aside from the Chinese accounts, several popular traditions also exist regarding Bodhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congling
The Pamir Mountains are a range of mountains between Central Asia and South Asia. They are located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world's highest mountains. Much of the Pamir Mountains lie in the Gorno-Badakhshan region of Tajikistan. Spanning the border parts of four countries, to the south, they border the Hindu Kush mountains along Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in Badakhshan Province, Chitral and Gilgit-Baltistan regions of Pakistan. To the north, they join the Tian Shan mountains along the Alay Valley of Kyrgyzstan. To the east, they extend to the range that includes China's Kongur Tagh, in the "Eastern Pamirs", separated by the Yarkand valley from the Kunlun Mountains. Since the Victorian era, they have been known as the "Roof of the World", presumably a translation from Persian. Names and etymology In other languages The Pamir region is home to seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending as far east as the Pothohar Plateau in Punjab, though the cultural influence of Greater Gandhara extended westwards into the Kabul, Kabul valley in Afghanistan, and northwards up to the Karakoram range. The region was a central location for the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, spread of Buddhism to Central Asia and East Asia with many Chinese Buddhism, Buddhist pilgrims visiting the region. Between the third century BCE and third century CE, Gandhari language, Gāndhārī, a Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language written in the Kharosthi script and linked with the modern Dardic languages, Dardic language family, acted as the lingua franca of the region and through Buddhism, the language spread as far as China based on Gandhār ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udyana
(also: ''Uḍḍiyāna'', ''Uḍḍāyāna'', ''Udyāna'' or 'Oḍḍiyāna'), a small region in early medieval India, is ascribed importance in the development and dissemination of Vajrayāna Buddhism.‘Uḍḍiyāna and Kashmir’, pp 265-269 ‘The Śaiva Exegesis of Kashmir’, in Mélanges tantriques à la mémoire d’Hélène Brunner. Tantric Studies in Memory of Hélène Brunner, Collection Indologie 106, EFEO, Institut français de Pondichéry (IFP), ed. Dominic Goodall and André Padoux, 2007.) Tibetan Buddhist traditions view it as a Beyul (Tibetan: སྦས་ཡུལ, Wylie: sbas-yul), a legendary heavenly place inaccessible to ordinary mortals. Padmasambhava, the eighth-century Buddhist master who was instrumental in the introduction of Buddhism to Tibet, was believed to have been born in Oddiyana. The Dzogchen Siddha Garab Dorje is likewise attributed to this region. It is ascribed importance in the development and dissemination of Vajrayāna Buddhism. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitral
Chitral () is a city situated on the Kunar River, Chitral River in northern area of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. It serves as the capital of the Lower Chitral District, and was previously the capital of Chitral District, and before that the capital of Chitral (princely state), Chitral princely state. The region was encompassed into West Pakistan between the years 1969 and 1972. It has a population of 49,780 per the 2017 census. History Nothing definitive is recorded about the town's first settlers. In the 3rd century AD, Kanishka, the ruler of the Kushan Empire, occupied Chitral. In the 4th century AD, the Chinese overran the valley. Raees rule over Chitral began in 1320 and came to an end in the 15th century. From 1571 onwards Chitral was the capital of the princely state of Chitral under the rule of the Katur Dynasty. Ancient era file:Singoor.png, left, Gankoreneotek Grave in Singoor. The existence of the Gandhara grave culture, Gandharan Grave Culture in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |