|
Solid Earth Tide
Earth tide (also known as solid-Earth tide, crustal tide, body tide, bodily tide or land tide) is the displacement of the solid earth's surface caused by the gravity of the Moon and Sun. Its main component has meter-level amplitude at periods of about 12 hours and longer. The largest body tide constituents are semi- diurnal, but there are also significant diurnal, semi-annual, and fortnightly contributions. Though the gravitational force causing earth tides and ocean tides is the same, the responses are quite different. Tide raising force The larger of the periodic gravitational forces is from the Moon but that of the Sun is also important. The images here show lunar tidal force when the Moon appears directly over 30° N (or 30° S). This pattern remains fixed with the red area directed toward (or directly away from) the Moon. Red indicates upward pull, blue downward. If, for example the Moon is directly over 90° W (or 90° E), the red areas are centred on the western northern h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Earth
Solid earth refers to "the earth beneath our feet" or '' terra firma'', the planet's solid surface and its interior. It excludes the Earth's fluid envelopes, the atmosphere and hydrosphere (but includes the ocean basin), as well as the biosphere and interactions with the Sun. Solid-earth science refers to the corresponding methods of study, a subset of Earth sciences, predominantly geophysics and geology, excluding aeronomy, atmospheric sciences, oceanography, hydrology, and ecology. See also * ''Ad cœlum'' * Crust (geology) ** Earth's crust * Geosphere * Land * Landform * Landscape * Lithosphere * Pedosphere * Structure of the Earth * Terrain Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientati ... * ''Solid Earth'' (journal) * ''Journal of Geophysical Research'' - section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pole Tide
Pole or poles may refer to: People *Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland *Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name *Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist *Spot Poles (Spottswood Poles, 1887–1962), American baseball player * Pole Atanraoi-Reim (fl. from 1992), a Kiribati lawyer * Pole baronets, three titles in the UK Astronomy and geography *Poles of astronomical bodies **Celestial pole, two points where the axis of rotation intersects the celestial sphere **Orbital pole, two points at the end of the orbital normal **North magnetic pole of Earth ** South magnetic pole of Earth *Geographical pole, two points on Earth where its axis of rotation intersects its surface **North Pole **South Pole Arts and entertainment * ''Pole'' (album), by Pole, 2003 * ''Pole'' (Stockhausen), a 1970 composition by Karlheinz Stockhausen *Pole, a character in the game '' Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' *Jill Pole, a characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
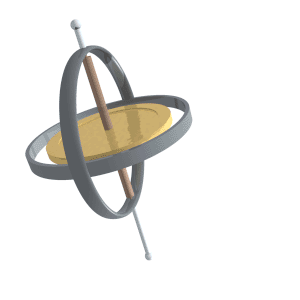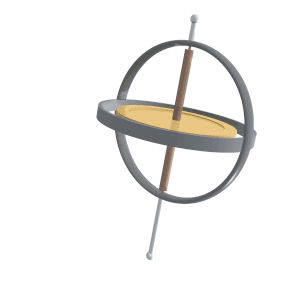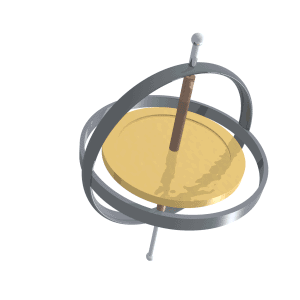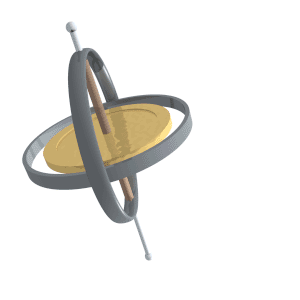
Nutation
Nutation () is a rocking, swaying, or nodding motion in the axis of rotation of a largely axially symmetric object, such as a gyroscope, planet, or bullet in flight, or as an intended behaviour of a mechanism. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the second Euler angle. If it is not caused by forces external to the body, it is called free nutation or Euler nutation (after Leonhard Euler). A pure nutation is a movement of a rotational axis such that the first Euler angle is constant. Therefore it can be seen that the circular red arrow in the diagram indicates the combined effects of precession and nutation, while nutation in the absence of precession would only change the tilt from vertical (second Euler angle). However, in spacecraft dynamics, precession (a change in the first Euler angle) is sometimes referred to as nutation. In a rigid body If a top is set at a tilt on a horizontal surface and spun rapidly, its rotational axis starts precess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precession (astronomy)
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called '' nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free or torque neglected Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluctuations In The Length Of Day
The length of the day (LOD), which has increased over the long term of Earth's history due to tidal effects, is also subject to fluctuations on a shorter scale of time. Exact measurements of time by atomic clocks and satellite laser ranging have revealed that the LOD is subject to a number of different changes. These subtle variations have periods that range from a few weeks to a few years. They are attributed to interactions between the dynamic atmosphere and Earth itself. The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS), formerly the International Earth Rotation Service, is the body responsible for maintaining global time and reference frame standards, notably through its Earth Orientation P ... monitors the changes. In the absence of external torques, the total angular momentum of Earth as a whole system must be constant. Internal torques are due to relative movements and mass redistribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Laser Ranging
Satellite laser ranging (SLR) is a method to measure the distance to satellites in a geocentric orbit. It consists of an astronomical observatory equipped with a laser that sends ultrashort pulses of light. The pulses hit the satellite and bounce back to be caught by the station, which measure the round trip time with the speed of light formula. These measurements are instantaneous and with millimeter level precision, which can be accumulated to provide accurate measurement of orbits and a host of important scientific data. Some satellites have retroreflectors, but the method also works on space debris. Satellite laser ranging is a proven geodesy, geodetic technique with significant potential for important contributions to scientific studies of the earth/atmosphere/ocean system. It is the most accurate technique currently available to determine the geocentric position of an Earth satellite, allowing for the precise calibration of radar altimeters and separation of long-term inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very-long-baseline Interferometry
Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. The distance between the radio telescopes is then calculated using the time difference between the arrivals of the radio signal at different telescopes. This allows observations of an object that are made simultaneously by many radio telescopes to be combined, emulating a telescope with a size equal to the maximum separation between the telescopes. Data received at each antenna in the array include arrival times from a local atomic clock, such as a hydrogen maser. At a later time, the data are correlated with data from other antennas that recorded the same radio signal, to produce the resulting image. The resolution achievable using interferometry is proportional to the observing frequency. The VLBI technique enables the distance between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephone or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls, and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. Overview The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft was launched in 1978 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional space, 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical body, astronomical bodies, such as planets or Natural satellite, circumplanetary systems. Geodynamics, Geodynamical phenomena, including crust (geology), crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national Geodetic control network, control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on Geodetic datum, datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific Classical antiquity, antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an government agency, agency of the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from List of NASA missions, U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
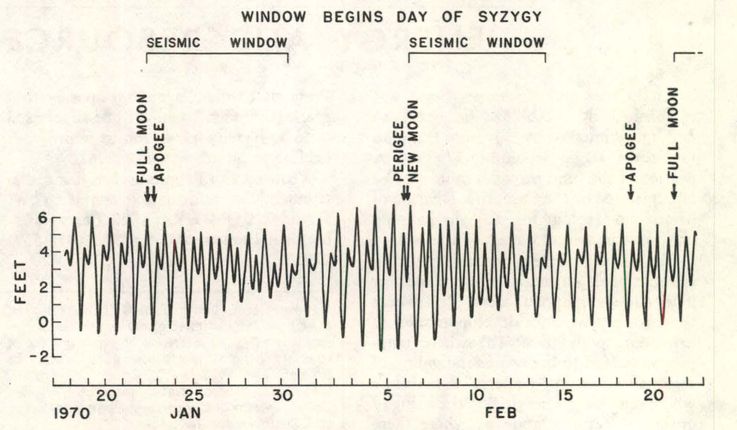
Tidal Triggering Of Earthquakes
Tidal triggering of earthquakes is the idea that tidal forces may induce seismicity. In connection with earthquakes, syzygy refers to the idea that the combined tidal effects of the sun and moon – either directly as earth tides in the crust itself, or indirectly by hydrostatic loading due to ocean tides – should be able to trigger earthquakes in rock that is already stressed to the point of fracturing, and therefore a higher proportion of earthquakes should occur at times of maximal tidal stress, such as at the new and full moons. Previously, scientists have searched for such a correlation for over a century, but with the exception of volcanic areas (including mid-ocean spreading ridges) the results have been mixed. It has been suggested that some negative results are due to failure to account for tidal phase and fault orientation ( dip), while "many studies reporting positive correlations suffer from a lack of statistical rigor." One systematic investigation found "no ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |