Tidal Triggering Of Earthquakes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
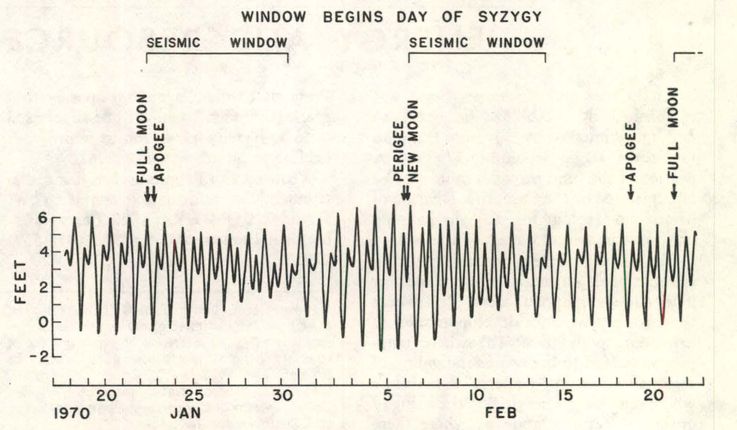 Tidal triggering of earthquakes is the idea that
Tidal triggering of earthquakes is the idea that Volcano watch
 Tidal triggering of earthquakes is the idea that
Tidal triggering of earthquakes is the idea that tidal forces
The tidal force or tide-generating force is the difference in gravitational attraction between different points in a gravitational field, causing bodies to be pulled unevenly and as a result are being stretched towards the attraction. It is the d ...
may induce seismicity
Seismicity is a measure encompassing earthquake occurrences, mechanisms, and magnitude at a given geographical location. As such, it summarizes a region's seismic activity. The term was coined by Beno Gutenberg and Charles Francis Richter in 194 ...
.
In connection with earthquakes, syzygy refers to the idea that the combined tidal effects of the sun and moon – either directly as earth tide
Earth tide (also known as solid-Earth tide, crustal tide, body tide, bodily tide or land tide) is the displacement of the solid earth's surface caused by the gravity of the Moon and Sun. Its main component has meter-level amplitude at periods of a ...
s in the crust itself, or indirectly by hydrostatic loading due to ocean tides – should be able to trigger earthquakes in rock that is already stressed to the point of fracturing, and therefore a higher proportion of earthquakes should occur at times of maximal tidal stress, such as at the new and full moons.
Previously, scientists have searched for such a correlation for over a century, but with the exception of volcanic areas (including mid-ocean spreading ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a d ...
s) the results have been mixed. It has been suggested that some negative results are due to failure to account for tidal phase and fault orientation ( dip), while "many studies reporting positive correlations suffer from a lack of statistical rigor." One systematic investigation found "no evidence for an increase in seismicity during intervals of large tidal range but there is clear evidence for small but significant increase in earthquake rates near low tide"; it did not find an increase of earthquakes near peak spring tides. Seismicity is favored at low tides, particularly for reverse fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic f ...
s, because unloading unclamps the fault, reducing friction. Ocean loading has no effect at all on strike-slip fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
s.
Research work has shown a robust correlation between small tidally induced forces and non-volcanic tremor activity.
Volcanologists use the regular, predictable Earth tide movements to calibrate and test sensitive volcano deformation monitoring instruments. The tides may also trigger volcanic events.
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an government agency, agency of the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geograp ...
.
See also
* Earthquake prediction#1990: New Madrid, U.S. (Browning) * Jim Berkland#Methodology * Love number * Tidal effect on plate tectonicsNotes
Sources
*. *. *. *. *. *. Tides Types of earthquake {{seismology-stub