|
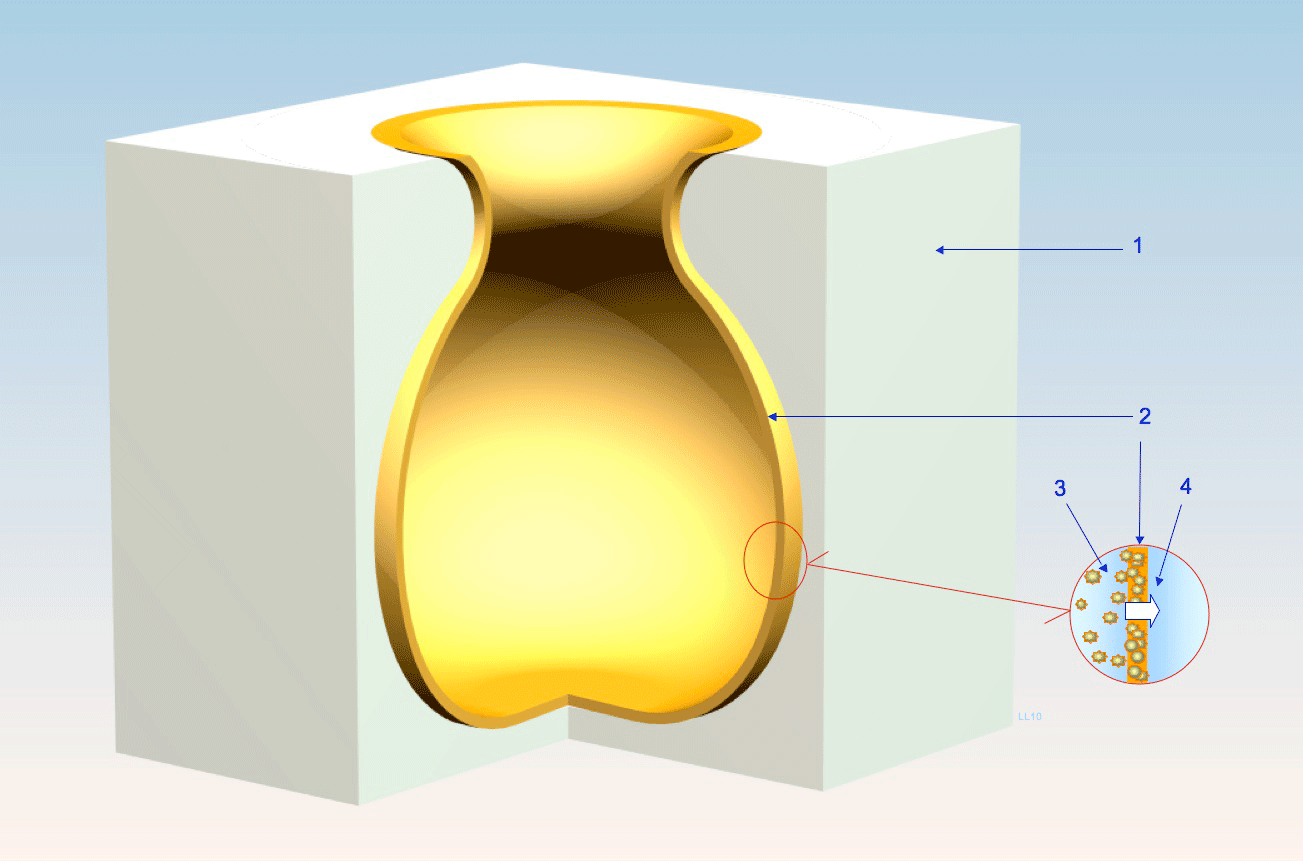
Slip Casting
Slip casting, or slipcasting, is a ceramic forming techniques, ceramic forming technique, and is widely used in industry and by craft potters to make ceramic forms. This technique is typically used to form complicated shapes like figurative ceramics that would be difficult to be reproduced by hand or other forming techniques. The technique involves a clay body slip (ceramics), slip, usually prepared in a blunger, being poured into plaster Molding (process), moulds and allowed to form a layer, the ''cast'', on the internal walls of the mould. It is suited for the consistent and precise shaping of complex shapes. It is the standard shaping technique for sanitaryware, such as toilets and basins, and is commonly used for smaller pieces like figurines and teapots. History The technique was first developed in China during the Tang dynasty (618–917), but was relatively little-used in China until recent times. It seems to have been reinvented independently in England around 1745 "r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sèvres - Grand Coulage 11
Sèvres (, ) is a French commune in the southwestern suburbs of Paris. It is located from the centre of Paris, in the Hauts-de-Seine department of the Île-de-France region. The commune, which had a population of 23,251 as of 2018, is known for its famous porcelain production at the ''Manufacture nationale de Sèvres'', which was also where the Treaty of Sèvres (1920) was signed. Geography Situation Sèvres is a commune in the western suburbs of Paris, to the southwest of the centre of Paris, with an eastern edge by the river Seine. The commune borders Île Seguin, an island in the Seine, in the commune of Boulogne-Billancourt, adjoining Sèvres. File:Map commune FR insee code 92072.png, Map of the commune File:Sèvres map.svg, View of the commune of Sèvres in red on the map of Paris and the "Petite Couronne" File:SEVRES - L'Embarcadaire.jpg, Banks of the Seine in the early 20th century. At that time, the river was an important transportation axis; river shuttles can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, opposite Estonia. Finland has a population of 5.6 million. Its capital and largest city is Helsinki. The majority of the population are Finns, ethnic Finns. The official languages are Finnish language, Finnish and Swedish language, Swedish; 84.1 percent of the population speak the first as their mother tongue and 5.1 percent the latter. Finland's climate varies from humid continental climate, humid continental in the south to boreal climate, boreal in the north. The land cover is predominantly boreal forest biome, with List of lakes of Finland, more than 180,000 recorded lakes. Finland was first settled around 9000 BC after the Last Glacial Period, last Ice Age. During the Stone Age, various cultures emerged, distinguished by differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geberit
Geberit () is a Swiss multinational group specialized in manufacturing and supplying sanitary parts and related systems. It is a leader in its field in Europe with a global presence through its subsidiaries. History The beginnings In 1874, Caspar Melchior Gebert started a plumbing business in Rapperswil (SG), Switzerland. In 1905, he began to manufacture parts. His toilet tank, the Phoenix, made of lead-coated wood and with lead fittings (particularly a flushing mechanism, the first of its kind), was revolutionary and a great success. When Gebert died in 1909 his sons Albert and Leo took over the business. In the following years, the company expanded within Switzerland as well as to neighboring countries, and added new products (pipes, taps and valves). In the 1930s, the company was a pioneer of plastic parts in the sanitary industry. The Second World War World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global confli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcelain
Porcelain (), also called china, is a ceramic material made by heating Industrial mineral, raw materials, generally including kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The greater strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arise mainly from Vitrification#Ceramics, vitrification and the formation of the mineral mullite within the body at these high temperatures. End applications include tableware, ceramic art, decorative ware such as figurines, and products in technology and industry such as Insulator (electricity), electrical insulators and laboratory ware. The manufacturing process used for porcelain is similar to that used for earthenware and stoneware, the two other main types of pottery, although it can be more challenging to produce. It has usually been regarded as the most prestigious type of pottery due to its delicacy, strength, and high degree of whiteness. It is frequently both glazed and decorated. Though definitions vary, po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compound (chemistry), compounds, produces unique physical property, physical properties including toughness, high rubber elasticity, elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form Amorphous solid, amorphous and crystallization of polymers, semicrystalline structures rath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacture Nationale De Sèvres
The ''Manufacture nationale de Sèvres'' () is one of the principal European porcelain factories. It is located in Sèvres, Hauts-de-Seine, France. It is the continuation of Vincennes porcelain, founded in 1740, which moved to Sèvres in 1756. It has been owned by the French crown or government since 1759. Its production is still largely based on the creation of contemporary objects today. It became part of the ''Sèvres – Cité de la céramique, Cité de la céramique'' in 2010 with the ''Musée national de céramique'', and since 2012 with the ''Musée national Adrien-Dubouché, Musée national Adrien Dubouché'' in Limoges. History Origins In 1740, the ''Vincennes porcelain, Manufacture de Vincennes'' was founded, thanks to the support of Louis XV's polish born wife, Queen Marie Leszczyńska who was noted as an avid porcelain collector in her early years as Queen. According to the memoirs of the Duke de Luynes it was Queen Marie who originally promoted porcelain in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandre Brongniart
Alexandre Brongniart (5 February 17707 October 1847) was a French chemist, mineralogist, geologist, paleontologist, and zoologist, who collaborated with Georges Cuvier on a study of the geology of the region around Paris. Observing fossil content as well as lithology in sequences, he classified Tertiary period, Tertiary Formation (geology), formations and was responsible for defining 19th century geological studies as a subject of science by assembling observations and classifications. Brongniart was also the founder of the Sèvres - Cité de la céramique, Musée national de Céramique-Sèvres (National Museum of Ceramics), having been director of the Manufacture nationale de Sèvres, Sèvres Porcelain Factory from 1800 to 1847. Life He was born in Paris, the son of the architect Alexandre-Théodore Brongniart and father of the botanist Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart. In 1788, he co-founded the French Philomathic Society of Paris. In 1797, he became an instructor of natural hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Silicate
Sodium silicate is a generic name for chemical compounds with the formula or ·, such as sodium metasilicate (), sodium orthosilicate (), and sodium pyrosilicate (). The anions are often polymeric. These compounds are generally colorless transparent solids or white powders, and soluble in water in various amounts. Sodium silicate is also the technical and common name for a mixture of such compounds, chiefly the metasilicate, also called waterglass, water glass, or liquid glass. The product has a wide variety of uses, including the formulation of cements, coatings, passive fire protection, textile and lumber processing, manufacture of refractory ceramics, as adhesives, and in the production of silica gel. The commercial product, available in water solution or in solid form, is often greenish or blue owing to the presence of iron-containing impurities. In industry, the various grades of sodium silicate are characterized by their SiO2:Na2O weight ratio (which can be converted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash, sal soda, and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the chloralkali process. Hydrates Sodium carbonate is obtained as three hydrates and as the anhydrous salt: * sodium carbonate decahydrate ( natron), Na2CO3·10H2O, which readily effloresces to form the monohydrate. * sodium carbonate heptahydrate (not known in mineral form), Na2CO3·7H2O. * sodium carbonate monohydrate ( thermonatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duravit
Duravit AG, founded in 1817 and headquartered in Hornberg, Germany, is primarily a manufacturer of porcelain bathroom fittings. In recent years, the company has diversified its scope to include other products. History Founded as a small earthenware factory by Georg Friedrich Horn in 1817 in the Black Forest The Black Forest ( ) is a large forested mountain range in the States of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is th ..., Duravit did not begin to produce sanitary fixtures until the early 20th century such as sinks, bidets, and toilets. In the 1980s, the product line was expanded to offer bathroom accessories. The 1980s and 1990s were also characterized by various corporate acquisitions, including "Ceramique de Bischwiller in 1991, "MISR TECH" in 1999, and a partial stake in Laufen. This period also saw the further growth of product lines, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance Education
Distance education, also known as distance learning, is the education of students who may not always be physically present at school, or where the learner and the teacher are separated in both time and distance; today, it usually involves online education (also known as online learning, remote learning or remote education) through an online school. A distance learning program can either be completely online, or a combination of both online and traditional in-person (also known as, offline) classroom instruction (called hybrid or blended). Massive open online courses (MOOCs), offering large-scale interactive participation and open access through the World Wide Web or other network technologies, are recent educational modes in distance education. A number of other terms (distributed learning, e-learning, m-learning, virtual classroom, etc.) are used roughly synonymously with distance education. E-learning has shown to be a useful educational tool. E-learning should be an interac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |