|
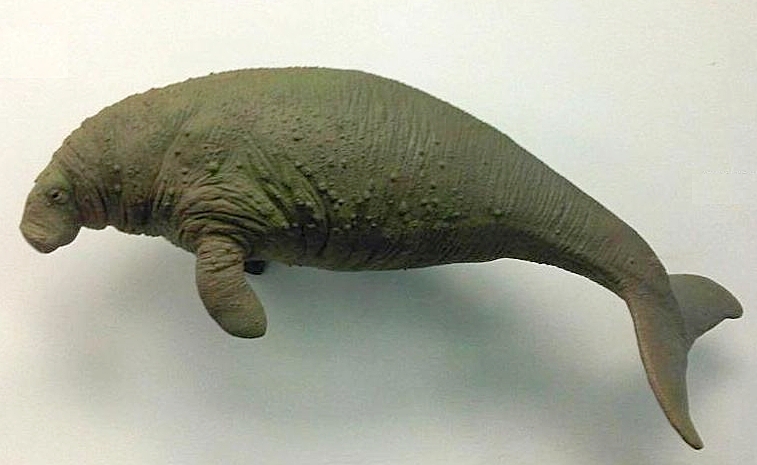
Sirenian
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The extant Sirenia comprise two distinct families: Dugongidae (the dugong and the now extinct Steller's sea cow) and Trichechidae (manatees, namely the Amazonian manatee, West Indian manatee, and West African manatee) with a total of four species. The Protosirenidae (Eocene sirenians) and Prorastomidae (terrestrial sirenians) families are extinct. Sirenians are classified in the clade Paenungulata, alongside the elephants and the hyraxes, and evolved in the Eocene 50 million years ago (mya). The Dugongidae diverged from the Trichechidae in the late Eocene or early Oligocene (30–35 mya). Sirenians grow to between in length and in weight. The recently extinct Steller's sea cow was the largest known sirenian to have lived, reaching lengths of and weights of . Sirenians have a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest modern relative, Steller's sea cow (''Hydrodamalis gigas''), was hunted to extinction in the 18th century. The dugong is the only sirenian in its range, which spans the waters of some 40 countries and territories throughout the Indo-West Pacific. The dugong is largely dependent on seagrass communities for subsistence and is thus restricted to the coastal habitats that support seagrass meadows, with the largest dugong concentrations typically occurring in wide, shallow, protected areas such as bays, mangrove channels, the waters of large inshore islands, and inter-reefal waters. The northern waters of Australia between Shark Bay and Moreton Bay are believed to be the dugong's contemporary stronghold. Like all modern sirenians, the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
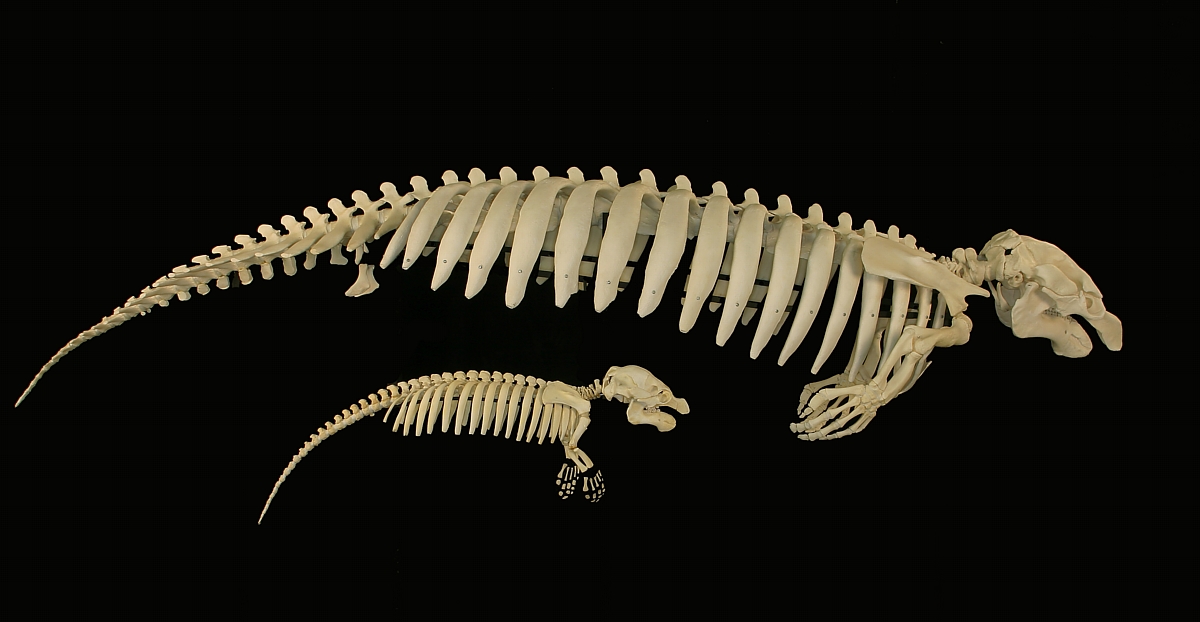
Steller's Sea Cow
Steller's sea cow (''Hydrodamalis gigas'') is an extinction, extinct sirenian described by Georg Wilhelm Steller in 1741. At that time, it was found only around the Commander Islands in the Bering Sea between Alaska and Russia; its range extended across the North Pacific during the Pleistocene epoch (geology), epoch, and likely contracted to such an extreme degree due to the Quaternary glaciation, glacial cycle. It is possible that indigenous populations interacted with the animal before Europeans. Steller first encountered it on Vitus Bering's Great Northern Expedition when the crew became shipwrecked on Bering Island. Much of what is known about its behavior comes from Steller's observations on the island, documented in his posthumous publication ''On the Beasts of the Sea''. Within 27 years of its discovery by Europeans, the slow-moving and easily-caught mammal was hunted into extinction for its meat, fat, and hide. Some 18th-century adults would have reached weights of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prorastomidae
Prorastomidae is a Family (biology), family of Extinction, extinct sirenians from Jamaica, related to the Extant taxon, extant manatees and dugong. The family includes the oldest known fossils of Sirenians, represented in two genera: *''Pezosiren'' ''Pezosiren'' comprises one known species, ''Pezosiren portelli'', that was discovered in modern-day Jamaica. One of the earliest true Sirenian species, ''P. portelli'' is distinct from extant Sirenians due to its quadrupedal stature. The species is estimated to have lived 50 million years ago during the Mid Eocene, and the skeletal elements suggest that ''P. portelli'' was able to properly support its body weight while out of the water. However, several morphological features suggest that this species spent significant amounts of time in an aquatic environment, such as ''P. portellis Pachyosteosclerosis, pachyosteosclerotic ribs. Similar to an extant manatee's ribs, these ribs provided a ballast and allowed the animal to achieve neutral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Manatee
The African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''), also known as the West African manatee, is a species of manatee that inhabits much of Western Africa – from Senegal to Angola. It is the only manatee species to be found in the Old World. Taxonomy The African manatee was officially declared a species under the ''Trichechus senegalensis'' taxon in 1795 by naturalist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. No subspecies of this taxon are known. Although African manatees live in both coastal areas and isolated inland areas, genetic evidence suggests no significant differences between the two populations. The African manatee falls under the genus ''Trichechus'' with only two other species, the Amazonian manatee and the West Indian manatee, which are also sirenians. Range and habitat African manatees inhabit the widest ranges of habitats of any sirenian species, ranging from offshore islands in the Atlantic to rivers in the western Sahel, equatorial rainforest rivers, and so on. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazonian Manatee
The Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis'') is a species of manatee that lives in the Amazon Basin in Brazil, Peru, Colombia and Ecuador. It has thin, wrinkled brownish or gray colored skin, with fine hairs scattered over its body and a white chest patch. It is the smallest of the three extant species of manatee. Taxonomy The specific name, ''inunguis'' is Latin for "nailless". The genus name ''Trichechus'', comes from Latin meaning "hair", referencing the whiskers around the manatee's mouth. Physical characteristics The Amazonian manatee is the smallest member of the manatee family and can be distinguished by its smoother rubbery skin and lack of vestigial nails on its flippers. Ranges of body weight and size observed are and for captive males, and for captive females, and and for free-ranging manatees, respectively. The maximum actual Amazonian manatee weight reported is . Calves of the species are born weighing and long. The Amazonian Manatees increase in length a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyrax
Hyraxes (), also called dassies, are small, stout, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the family Procaviidae within the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Modern hyraxes are typically between in length and weigh between . They are superficially similar to marmots or over-large pikas but are much more closely related to elephants and sirenians. Hyraxes have a life span of 9 to 14 years. Both types of "rock" hyrax ( ''P. capensis'' and ''H. brucei'') live on rock outcrops, including cliffs in Ethiopia and isolated granite outcrops called koppies in southern Africa. Almost all hyraxes are limited to Africa; the exception is the rock hyrax (''P. capensis'') which is also found in adjacent parts of the Middle East. Hyraxes were a much more diverse group in the past encompassing species considerably larger than modern hyraxes. The largest known extinct hyrax, '' Titanohyrax ultimus'', has been estimated to weigh , comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indian Manatee
The West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), also known as the North American manatee, is a large, aquatic mammal native to warm coastal areas of the Caribbean, from the Eastern United States to northern Brazil. Living alone or in herds, it feeds on underwater plants and uses its whiskers to navigate. It is divided into two subspecies, the Florida manatee (''T. m. latirostris'') in the United States and the Antillean manatee (''T. m. manatus'') in the Caribbean, both of which are endangered and face pressure from habitat loss, pollution, and other human activity. The West Indian manatee is the largest living member of the sirenians (order Sirenia), a group of large aquatic mammals that includes the dugong, other manatees, and the extinct Steller's sea cow. Manatees are herbivores, have developed vocal communication abilities, and are covered in highly sensitive whiskers (called vibrissae) that are used for feeding and navigation. In breeding season, several males form mating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protosirenidae
Protosirenidae is an extinct primitive family of the order Sirenia. Protosirenids are thought to have been amphibious quadrupeds, meaning that they spent their time both on land and in the water and had four legs. See also * Dugongidae * Evolution of sirenians *Manatee Manatees (, family (biology), family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivory, herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing t ... References External links ''Protosiren''at The Paleobiology Database. Eocene sirenians Prehistoric mammal families {{Paleo-sirenian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manatee
Manatees (, family (biology), family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivory, herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species in the order Sirenia: the Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis''), the West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), and the West African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''). They measure up to long, weigh as much as , and have paddle-like tails. Manatees are Herbivory, herbivores and eat over 60 different freshwater and saltwater plants. Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the Amazon basin, and West Africa. The main causes of death for manatees are human-related issues, such as habitat destruction and human objects. Their slow-moving, curious nature has led to violent collisions with propeller-driven boats and ships. Some manatees h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus''). They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears and convex or level backs. Elephants are scatter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dugongidae
Dugongidae is a Family (biology), family in the Order (biology), order of Sirenia. The family has one surviving species, the dugong (''Dugong dugon''), one recently Extinction, extinct species, Steller's sea cow (''Hydrodamalis gigas''), and a number of extinct Genus, genera known from fossil records. Dugongidae's body weight ranges from 217 to 307 kg for juveniles, 334 to 424 kg for subadults, and 435 to 568.5 kg for adults. Oral temperatures for individual dugongs is determined from 24° to 34.2 °C. Heart rate readings are from 40 to 96 bpm and vary between individual dugongs. Respiration rate during the out-of-water phase is from 1 to 33. Taxonomy * Family Dugongidae ** Genus extinction, †''Anisosiren'' ** Genus †''Caribosiren'' ** Genus †''Indosiren'' ** Genus †''Lentiarenium'' ** Genus †''Kaupitherium'' ** Genus †''Paralitherium'' ** Genus †''Priscosiren'' ** Genus †''Prohalicore'' ** Genus †''Sirenavus'' ** Subfamily †Halitheriinae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |