|
Prorastomidae
Prorastomidae is a family of extinct sirenians from Jamaica, related to the extant manatees and dugong The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its close .... The family includes the oldest known fossils of Sirenians, represented in two genera: *'' Pezosiren'' ''Pezosiren'' comprises one known species, ''Pezosiren portelli'', that was discovered in modern-day Jamaica. One of the earliest true Sirenian species, ''P. portelli'' is distinct from extant Sirenians due to its quadrupedal stature. The species is estimated to have lived 50 million years ago during the Mid Eocene, and the skeletal elements suggest that ''P. portelli'' was able to properly support its body weight while out of the water. However, several morphological features suggest that this species spent significant amounts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirenia
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea-cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The Sirenia currently comprise two distinct families: Dugongidae (the dugong and the now extinct Steller's sea cow) and Trichechidae (manatees, namely the Amazonian manatee, West Indian manatee, and West African manatee) with a total of four species. The Protosirenidae (Eocene sirenians) and Prorastomidae (terrestrial sirenians) families are extinct. Sirenians are classified in the clade Paenungulata, alongside the elephants and the hyraxes, and evolved in the Eocene 50 million years ago (mya). The Dugongidae diverged from the Trichechidae in the late Eocene or early Oligocene (30–35 mya). Sirenians grow to between in length and in weight. The historic Steller's sea cow was the largest known sirenian to have lived, and could reach lengths of and weights of . Sirenia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Sirenians
Sirenia is the order of placental mammals which comprises modern "sea cows" (manatees and the Dugong) and their extinct relatives. They are the only extant herbivorous marine mammals and the only group of herbivorous mammals to have become completely aquatic. Sirenians are thought to have a 50-million-year-old fossil record (early Eocene-recent). They attained modest diversity during the Oligocene and Miocene, but have since declined as a result of climatic cooling, oceanographic changes, and human interference. Two genera and four species are extant: ''Trichechus'', which includes the three species of manatee that live along the Atlantic coasts and in rivers and coastlines of the Americas and western Africa, and ''Dugong'', which is found in the Indian and Pacific oceans. Origins Sirenians, along with Proboscidea (elephants), group together with the extinct Desmostylia and likely the extinct Embrithopoda to form the Tethytheria. Tethytheria is thought to have evolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prorastomus
''Prorastomus sirenoides'' is an extinct species of primitive sirenian that lived during the Eocene Epoch 40 million years ago in Jamaica. Taxonomy The generic name ''Prorastomus'', a combination of Greek (''prōra''), prow, and (''stoma''), mouth, refers to the lower jaw of the animal "resembling the prow of a wherry". The genus name ''Prorastomus'' comes from Greek ''prora'' meaning "prow" and Latin ''stomus'' meaning "mouth." In 1892, naturalist Richard Lydekker respelled it as ''Prorastoma'' with a feminine ending, however this was unjustified as ''stomus'' is masculine in Latin. ''Prorastomus'' is one of two genera of the family Prorastomidae, the other '' Pezosiren''. These two species are the oldest sirenians, dating to the Eocene. The first specimen was described by paleontologist Sir Richard Owen in 1855, and, being found in Jamaica in the Yellow Limestone Group, pointed to the origin of Sirenia as being in the New World rather than the Old World as was previously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
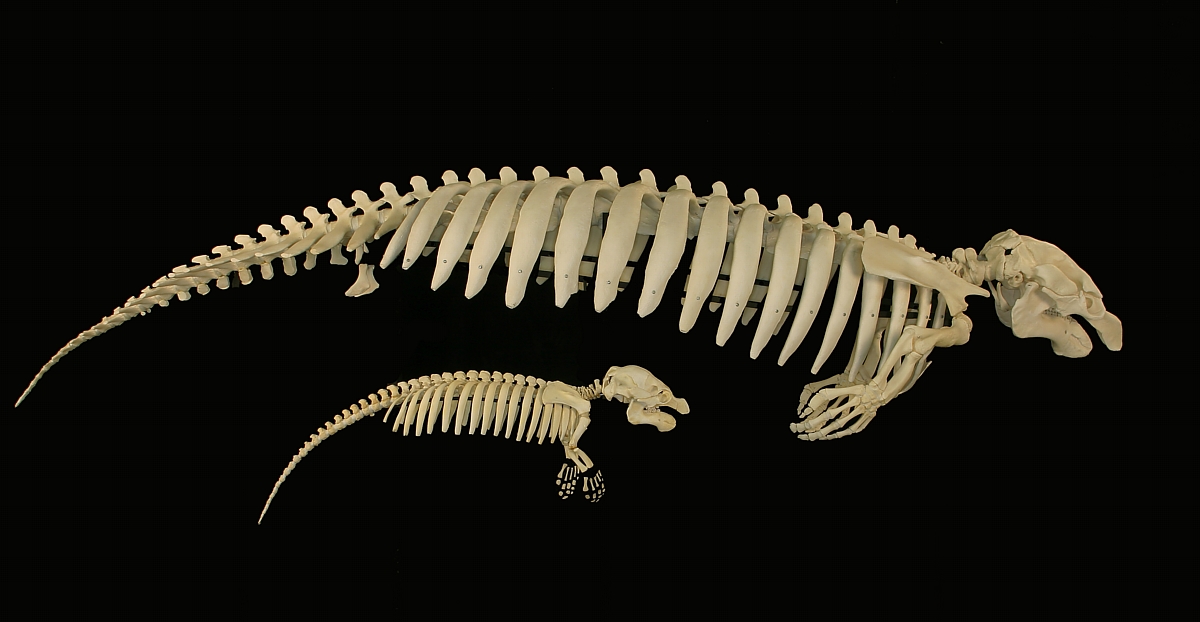
Pezosiren
''Pezosiren portelli'', also known as the "walking manatee", is a basal sirenian from the early Eocene of Jamaica, 50 million years ago. The type specimen is represented by a Jamaican fossil skeleton, described in 2001 by Daryl Domning, a marine mammal paleontologist at Howard University in Washington, DC. It is believed to have had a hippopotamus-like amphibious lifestyle, and is considered a transitional form between land and sea mammals:.Prothero, Donald R. 2007. ''Evolution: What the Fossils Say and Why It Matters''. With original illustrations by Carl Buell. New York, Columbia University Press. Discovery In the 1990s, vertebrate fossils were found in lagoon deposits at Seven Rivers in Jamaica by Daryl Domning and colleagues. The site is rich in fossils, and yielded hundreds of bones of mainly aquatic vertebrates, a primitive rhinoceros, and possibly a primate. In 2001, Domning named ''Pezosiren portelli'' based on sirenian bones found at Seven Rivers. The Seven Rivers site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds ( taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola (the island containing the countries of Haiti and the Dominican Republic); the British Overseas Territory of the Cayman Islands lies some to the north-west. Originally inhabited by the indigenous Taíno peoples, the island came under Spanish rule following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people either were killed or died of diseases, after which the Spanish brought large numbers of African slaves to Jamaica as labourers. The island remained a possession of Spain until 1655, when England (later Great Britain) conquered it, renaming it ''Jamaica''. Under British colonial rule Jamaica became a leading sugar exporter, with a plantation economy dependent on the African slaves and later their descenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extant Taxon
Neontology is a part of biology that, in contrast to paleontology, deals with living (or, more generally, ''recent'') organisms. It is the study of extant taxa (singular: extant taxon): taxa (such as species, genera and families) with members still alive, as opposed to (all) being extinct. For example: * The moose (''Alces alces'') is an extant species, and the dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct species. * In the group of molluscs known as the cephalopods, there were approximately 600 extant species and 7,500 extinct species. A taxon can be classified as extinct if it is broadly agreed or certified that no members of the group are still alive. Conversely, an extinct taxon can be reclassified as extant if there are new discoveries of living species (" Lazarus species"), or if previously-known extant species are reclassified as members of the taxon. Most biologists, zoologists, and botanists are in practice neontologists, and the term neontologist is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manatee
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species in the order Sirenia: the Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis''), the West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), and the West African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''). They measure up to long, weigh as much as , and have paddle-like tails. Manatees are herbivores and eat over 60 different freshwater and saltwater plants. Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the Amazon basin, and West Africa. The main causes of death for manatees are human-related issues, such as habitat destruction and human objects. Their slow-moving, curious nature has led to violent collisions with propeller-driven boats and ships. Some manatees have been found with over 50 scars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest modern relative, Steller's sea cow (''Hydrodamalis gigas''), was hunted to extinction in the 18th century. The dugong is the only sirenian in its range, which spans the waters of some 40 countries and territories throughout the Indo-West Pacific. The dugong is largely dependent on seagrass communities for subsistence and is thus restricted to the coastal habitats which support seagrass meadows, with the largest dugong concentrations typically occurring in wide, shallow, protected areas such as bays, mangrove channels, the waters of large inshore islands and inter-reefal waters. The northern waters of Australia between Shark Bay and Moreton Bay are believed to be the dugong's contemporary stronghold. Like all modern sirenians, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pezosiren Clean
''Pezosiren portelli'', also known as the "walking manatee", is a basal sirenian from the early Eocene of Jamaica, 50 million years ago. The type specimen is represented by a Jamaican fossil skeleton, described in 2001 by Daryl Domning, a marine mammal paleontologist at Howard University in Washington, DC. It is believed to have had a hippopotamus-like amphibious lifestyle, and is considered a transitional form between land and sea mammals:.Prothero, Donald R. 2007. ''Evolution: What the Fossils Say and Why It Matters''. With original illustrations by Carl Buell. New York, Columbia University Press. Discovery In the 1990s, vertebrate fossils were found in lagoon deposits at Seven Rivers in Jamaica by Daryl Domning and colleagues. The site is rich in fossils, and yielded hundreds of bones of mainly aquatic vertebrates, a primitive rhinoceros, and possibly a primate. In 2001, Domning named ''Pezosiren portelli'' based on sirenian bones found at Seven Rivers. The Seven Rivers si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)