|
Single-molecule Real-time
A single-molecule experiment is an experiment that investigates the properties of individual molecules. Single-molecule studies may be contrasted with measurements on an ensemble or bulk collection of molecules, where the individual behavior of molecules cannot be distinguished, and only average characteristics can be measured. Since many measurement techniques in biology, chemistry, and physics are not sensitive enough to observe single molecules, single-molecule fluorescence techniques (that have emerged since the 1990s for probing various processes on the level of individual molecules) caused a lot of excitement, since these supplied many new details on the measured processes that were not accessible in the past. Indeed, since the 1990s, many techniques for probing individual molecules have been developed. The first single-molecule experiments were patch clamp experiments performed in the 1970s, but these were limited to studying ion channels. Today, systems investigated using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuming Nie
Shuming Nie () is a Chinese-American chemist. He is the Grainger Distinguished Chair in Bioengineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He was the Wallace H. Coulter Distinguished Faculty Chair in Biomedical Engineering at Emory University. In 2007, Nie was elected as a fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE). In 2012, Nie was elected as a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). He is a pioneer of single-molecular SERS. He is one of the pioneers of quantum dots for biomedical imaging. Recent publications * Shuming Nie. "Remembering Dr. Richard P. Van Duyne (1945–2019): Gentleman, Scholar, and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Pioneer". ''ACS Nano'' 2020, 14(1), 26-27. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.9b09759 * * * * Warren C. W. Chan, Shuming Nie. Quantum Dot Bioconjugates for Ultrasensitive Nonisotopic Detection. ''Science'' 1998. 281(5385): 2016-2018.https://www.science.org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a Protein dimer, dimer of two globular proteins, Tubulin#Eukaryotic, alpha and beta tubulin into #Structure, protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesin
A kinesin is a protein complex belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells. Kinesins move along microtubule (MT) filaments and are powered by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (thus kinesins are ATPases, a type of enzyme). The active movement of kinesins supports several cellular functions including mitosis, meiosis and transport of cellular cargo, such as in axonal transport, and intraflagellar transport. Most kinesins walk towards the plus end of a microtubule, which, in most cells, entails transporting cargo such as protein and membrane components from the center of the cell towards the periphery. This form of transport is known as anterograde transport. In contrast, dyneins are motor proteins that move toward the minus end of a microtubule in retrograde transport. Discovery The first kinesins to be discovered were microtubule-based anterograde intracellular transport motors in 1985, based on their motility in cytoplasm extruded from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Limit
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolution. It is used in optics applied to light waves, in antenna theory applied to radio waves, and in acoustics applied to sound waves. The colloquial use of the term "resolution" sometimes causes confusion; when an optical system is said to have a high resolution or high angular resolution, it means that the perceived distance, or actual angular distance, between resolved neighboring objects is small. The value that quantifies this property, ''θ,'' which is given by the Rayleigh criterion, is low for a system with a high resolution. The closely related term spatial resolution refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to space, which is directly connected to angular resolution in imaging instruments. The Rayleigh criterion shows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
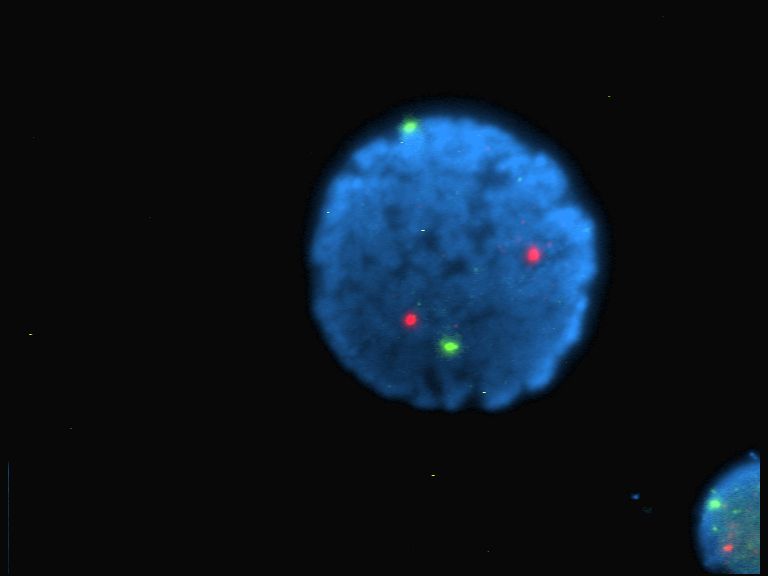
Fluorophores
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to macromolecules, serving as a markers (or dyes, or tags, or reporters) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, such as fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
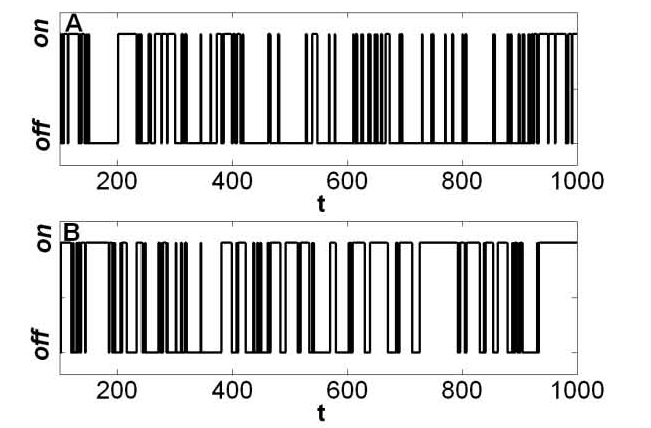
Two-state Trajectory
A two-state trajectory (also termed two-state time trajectory or a trajectory with two states) is a dynamical signal that fluctuates between two distinct values: ON and OFF, open and closed, +/-, etc. Mathematically, the signal X(t) has, for every t, either the value X(t)=c_\mathrm or X(t)=c_\mathrm. In most applications, the signal is stochastic; nevertheless, it can have deterministic ON-OFF components. A completely deterministic two-state trajectory is a square wave. There are many ways one can create a two-state signal, e.g. flipping a coin repeatedly. A stochastic two-state trajectory is among the simplest stochastic processes. Extensions include: three-state trajectories, higher discrete state trajectories, and continuous trajectories in any dimension. Two state trajectories in biophysics, and related fields Two state trajectories are very common. Here, we focus on relevant trajectories in scientific experiments: these are seen in measurements in chemistry, physics, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-state Trajectories
A two-state trajectory (also termed two-state time trajectory or a trajectory with two states) is a dynamical signal that fluctuates between two distinct values: ON and OFF, open and closed, +/-, etc. Mathematically, the signal X(t) has, for every t, either the value X(t)=c_\mathrm or X(t)=c_\mathrm. In most applications, the signal is stochastic; nevertheless, it can have deterministic ON-OFF components. A completely deterministic two-state trajectory is a square wave. There are many ways one can create a two-state signal, e.g. flipping a coin repeatedly. A stochastic two-state trajectory is among the simplest stochastic processes. Extensions include: three-state trajectories, higher discrete state trajectories, and continuous trajectories in any dimension. Two state trajectories in biophysics, and related fields Two state trajectories are very common. Here, we focus on relevant trajectories in scientific experiments: these are seen in measurements in chemistry, physics, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Tweezers
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers. If the object is held in air or vacuum without additional support, it can be called optical levitation. The laser light provides an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the relative refractive index between particle and surrounding medium. Levitation is possible if the force of the light counters the force of gravity. The trapped particles are usually micron-sized, or even smaller. Dielectric and absorbing particles can be trapped, too. Optical tweezers are used in biology and medicine (for example to grab and hold a single bacterium, a cell like a sperm cell or a blood cell, or a molecule like DNA), nanoengineering and nanochemistry (to study and build materials from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Force Microscope
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the diffraction-limited system, optical diffraction limit. Overview Atomic force microscopy (AFM) gathers information by "feeling" or "touching" the surface with a mechanical probe. Piezoelectric elements that facilitate tiny but accurate and precise movements on (electronic) command enable precise scanning. Despite the name, the Atomic Force Microscope does not use the nuclear force. Abilities and spatial resolution The AFM has three major abilities: force measurement, topographic imaging, and manipulation. In force measurement, AFMs can be used to measure the forces between the probe and the sample as a function of their mutual separation. This can be applied to perform force spectroscopy, to measure the mechanical properties of the sample, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodamine 6G
Rhodamine 6G is a highly fluorescent rhodamine family dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. Forms Rhodamine 6G usually comes in three different forms. Rhodamine 6G chloride is a bronze/red powder with the chemical formula C28H31ClN2O3. Although highly soluble, this formulation is very corrosive to all metals except stainless steel. Other formulations are less soluble, but also less corrosive. Rhodamine 6G perchlorate (C28H31ClN2O7) comes in the form of red crystals, while rhodamine 6G tetrafluoroborate (C28H31BF4N2O3) appears as maroon crystals. Solubility Butanol (40 g/L), ethanol (80 g/L), methanol (400 g/L), pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |