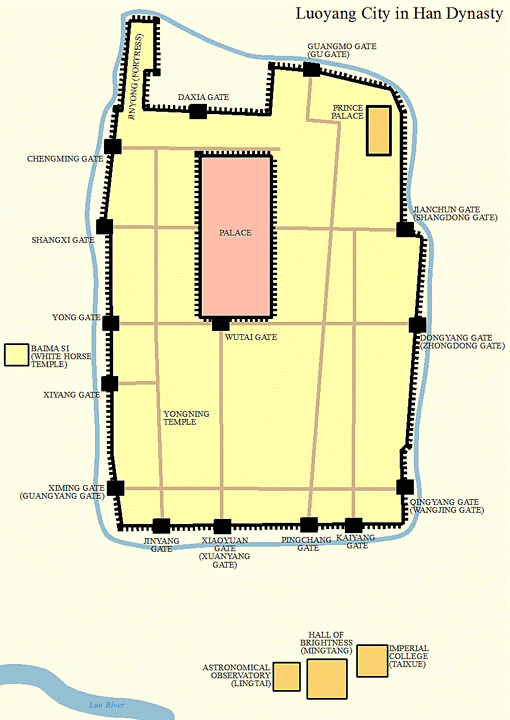
|
Sima Tan (Jin Dynasty)
Sima Tan (295 – 24 March 308) was a crown prince of the Western Jin. He was installed to the position in 302 to serve as heir apparent for his uncle, Emperor Hui of Jin, but was removed in 304. After his removal, there were several plots to restore him to the position before he was finally put to death by the Prince of Donghai, Sima Yue in 308. Life Background Sima Tan was born the eldest son to Sima Xia (司馬遐; 273 - 15 July 300), Prince Kang of Qinghe and the 13th son of Emperor Wu of Jin, and Xia's wife Lady Zhou (周氏). Lady Zhou's father was Zhou Hui (周恢) and her mother was a paternal aunt of Sima Yue, Prince Xiaoxian of Donghai, and daughter of Sima Kui, brother of Sima Xia's great-grandfather Sima Yi. According to a story in his biography in ''Book of Jin'', while Tan was still his father's heir, he wore a golden bell that one day shrivelled up like millet. A fortune teller believe that the gold represented the prosperity of the Jin dynasty, and was a good ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dangyin
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gou Xi
Gou Xi (died November 311), courtesy name Daojiang, was a Chinese military commander of the Western Jin Dynasty. He came to prominence as a general under the Prince of Donghai, Sima Yue, after he quelled the rebellions of Gongshi Fan (公師藩), Ji Sang and Shi Le. Sima Yue initially valued Gou Xi, but after Gou Xi was constantly antagonized by Yue, their relationship broke down in 310. Gou Xi plotted with Emperor Huai of Jin to depose Yue as regent, which caused Yue to die of stress shortly after, and Gou Xi being instated to the positions of Grand General and Grand Commander. However, their victory was short-lived due to the Disaster of Yongjia, which saw Emperor Huai's and Luoyang’s capture at the hands of Han-Zhao forces in 311. That same year, Gou Xi was captured and later executed by Shi Le. War of the Eight Princes and suppressing Sima Ying's loyalists Early career Gou Xi hailed from Shanyang County in Henei Commandery and was of humble origins. He was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disaster Of Yongjia
The Disaster of Yongjia (simplified Chinese: 永嘉之乱; traditional Chinese: 永嘉之亂) occurred in 311 CE, when forces of the Han-Zhao dynasty captured and sacked Luoyang, the capital of the Western Jin dynasty. The Han's army committed a massacre of the city's inhabitants, killing the Jin crown prince, a host of ministers, and over 30,000 civilians. They also burnt down the palaces and dug up the Jin dynasty's mausoleums. Though the Western Jin would survive for a few more years, this event is often seen as one of the worst disasters in Chinese history, as both the emperor and one of the ancient capitals fell to the hands of "barbarian" forces. Background Despite the War of the Eight Princes concluding in early 307, the Western Jin court, under the paramountcy of the Prince of Donghai, Sima Yue, had to deal subsequently with an assortment of rebellions throughout the empire. Most concerning was the Five Divisions in Bing province, descendants of the Southern Xiongnu wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Le
Shi Le (; 274 –17 August 333), courtesy name Shilong, also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Ming of Later Zhao, was the founding emperor of the Jie-led Later Zhao dynasty of China. He was initially sold as a slave by Western Jin officials, but after attaining freedom, he helped start a rebellion and eventually became a powerful general for the Han-Zhao dynasty, conquering most of northern China in Han-Zhao's name but holding the territory under his own control. In 319, after a dispute with the Han-Zhao emperor Liu Yao, he broke away from Han and formed his own state, Later Zhao (named as such due to Liu Yao changing his state's name from Han to Zhao, which is distinguished as the Former Zhao). In 321, he defeated Duan Pidi, the last remaining Jin power in northern China besides Murong Hui, and in 329 he captured Liu Yao and conquered the Han-Zhao, adding western China to his empire as well. For the next 21 years, the Later Zhao would dominate northern China. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Teng
Sima Teng (司馬腾) (died June or July 307), courtesy name Yuanmai (元迈), posthumously known as Prince Wu'ai of Xincai, was a Western Jin imperial prince. He was a younger brother of Sima Yue, Prince Xiaoxian of Donghai, a regent for Emperor Hui and Emperor Huai, and the elder brother of Sima Lue and Sima Mo. Background Sima Teng was the second son of Sima Tai (司馬泰; posthumously known as Prince Wenxian of Gaomi (高密文献王)), who was a son of Sima Yi's brother Sima Kui (司馬馗), making Teng a second cousin of Jin's founding emperor Emperor Wu. Sima Teng's first title was Duke of Dongying. When his father Sima Tai died on 17 July 299, during the reign of Emperor Hui, his younger brother Sima Lüe inherited the title of Prince of Gaomi, as Sima Teng was made heir to an unnamed elder of the Sima clan. Despite their distant relationship to the emperor's family, Teng and his brothers, Sima Yue, Sima Lue and Sima Mo were all renowned members of the imperial cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuge Xu
Zhuge Xu ( 250 – 260s) was a Chinese general and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Life Zhuge Xu was from Yangdu County (), Langya Commandery (), which is in present-day Yinan County, Shandong. He was probably a distant relative of other famous Zhuges in the Three Kingdoms period, such as Zhuge Jin, Zhuge Liang and Zhuge Dan, since he shared the same Ancestral home (Chinese), ancestral home as them. He served in the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period. In 255, when the Wei generals Guanqiu Jian and Wen Qin started Guanqiu Jian and Wen Qin's Rebellion, a rebellion in Shouchun (壽春; present-day Shou County, Anhui), Zhuge Xu was then serving as the Administrator () of Taishan Commandery (泰山郡; around present-day Tai'an, Shandong). He led troops from Taishan Commandery to assist other Wei imperial forces led by the regent Sima Shi to suppress the rebellion. Zhuge Xu was later promoted to the position of Inspector () of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hua Xin
Hua Xin (157 – 30 January 232), courtesy name Ziyu, was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period of China. He initially served directly under the central government of the Eastern Han dynasty. Later, he served under the warlord Sun Ce and then under the warlord Cao Cao. He continued to serve in the Cao Wei state during the Three Kingdoms period. Biography As a clerk in Gaotang County, Hua Xin was nominated as xiaolian, and appointed as Langzhong (郎中). In 187, Hua was appointed as Shangshu Lang (尚书郎). When Dong Zhuo evacuated the court from Luoyang to Chang'an, Hua requested a position as the administrator of Shanggui County (上邽) . He encountered Yuan Shu's army en route and was accepted to the latter's court. However, Hua left after his advice for Yuan to attack Dong Zhuo was dismissed. In 192, Hua was appointed as the administrator of Yuzhang (豫章) Commandery. After Liu Yao, governor of Yang Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Xianrong
Yang Xianrong (羊獻容) (died 13 May 322), posthumous name (as honored by Former Zhao) Empress Xianwen (獻文皇后, literally "the wise and civil empress"), was an empress—uniquely in the history of China, for two different dynastic empires and two different emperors. Her first husband was Emperor Hui of Jin, and her second husband was Liu Yao of Former Zhao. Also unique was that she was deposed four times and restored four times as empress of the Western Jin (five, if one counts the brief usurpation by Sima Lun against her husband in 301). Background and as empress of Jin Yang Xianrong was from Taishan Commandery (roughly modern Tai'an, Shandong). Her father was the mid-level official Yang Xuanzhi. Her maternal grandfather was the general Sun Qi, a distant relative of Sun Xiu, the chief strategist for Sima Lun the Prince of Zhao. Therefore, after Sima Lun and Sun overthrew Empress Jia Nanfeng in May 300, Sun had Yang Xianrong selected as the new empress in December of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Eight Princes
The War of the Eight Princes, Rebellion of the Eight Kings, or Rebellion of the Eight Princes ( zh, t=八王之亂, s=八王之乱, p=bā wáng zhī luàn, w=pa wang chih luan) was a series of coups and civil wars among kings/princes (Chinese: ''wáng'' 王) of the Chinese Jin dynasty (266–420)#Western Jin (266–316), Western Jin dynasty from 291 to 306 AD. The key point of contention in these conflicts was the paramountcy over the empire in light of the developmentally disabled Emperor Hui of Jin. The name of the conflict is derived from the biographies of the eight princes collected in Chapter 59 of the ''Book of Jin''. The "War of the Eight Princes" is somewhat of a misnomer: rather than one continuous conflict, the War of the Eight Princes saw intervals of peace interposed with short and intense periods of internecine conflict. At no point in the whole conflict were all of the eight princes on one side of the fighting (as opposed to, for example, the Rebellion of the Seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Huai Of Jin
Emperor Huai of Jin (; 284 – March 14, 313), personal name Sima Chi (司馬熾), courtesy name Fengdu (豐度), was an emperor of the Jin dynasty. Emperor Huai was captured in July 311 ( Disaster of Yongjia) and later executed in 313 under the order of Liu Cong, ruler of the Xiongnu state of Han-Zhao. As Prince of Yuzhang and crown prince Sima Chi was one of the youngest sons of Sima Yan, the founding emperor of Jin, by his concubine Consort Wang Yuanji (王媛姬). Just prior to Emperor Wu's death in May 290, Prince Chi was created the Prince of Yuzhang on 22 December 289. During the early stages of the War of the Eight Princes during the reign of his developmentally disabled half-brother Sima Zhong, unlike the other princes fighting for power, Prince Chi did not involve himself in political or military matters, but spent his time studying history instead. In late 304, when Emperor Hui was forcibly taken from the capital Luoyang to Chang'an, then under the control of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Fang
Zhang Fang (died February 306) was a military general of the Jin dynasty (266–420). He was the influential general of the Prince of Hejian, Sima Yong during the War of the Eight Princes who helped him in subduing the Prince of Changshan, Sima Ai, and had the imperial family briefly under his control in 304. Though capable, he was infamous for his transgressions against the emperor and the cruelty that he and his soldiers displayed, with one account claiming that he had them engage in cannibalism. His act of forcibly moving Emperor Hui of Jin from Luoyang to Chang'an provided the Prince of Donghai, Sima Yue and his allies with pretext to start a coalition to punish him and Sima Yong in 305. In a desperate attempt to settle for peace, Sima Yong had Zhang Fang assassinated the following year. Life Coalition against Sima Lun and Sima Jiong (301 and 302) Zhang Fang was born in a poor family in Sima Yong's princely fief, Hejian commandery. Despite his upbringing, he was talente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |