|
Silylene
Silylene is a chemical compound with the formula SiR2. It is the silicon analog of carbene. Silylene rapidly when condensed. Silylenes are formal derivatives of silylene with its hydrogens replaced by other substituents. Most examples feature amido (NR2) or alkyl/aryl groups. Silylenes have been proposed as reactive intermediates. They are carbene analogs. Synthesis and properties Silylenes have been generated by thermolysis or photolysis of polysilanes, by silicon atom reactions ( insertion, addition or abstraction), by pyrolysis of silanes, or by reduction of 1,1-dihalosilane. It has long been assumed that the conversion of metallic Si to tetravalent silicon compounds proceeds via silylene intermediates: :Si + Cl2 → SiCl2 :SiCl2 + Cl2 → SiCl4 Similar considerations apply to the direct process, the reaction of methyl chloride and bulk silicon. Early observations of silylenes involved generation of dimethylsilylene by dechlorination of dimethyldichlorosilane: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-heterocyclic Silylene
An ''N''-Heterocyclic silylene (NHSi) is a neutral Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic Chemical compounds, chemical compound consisting of a Silylene, divalent silicon atom bonded to two nitrogen atoms. The isolation of the first stable NHSi, also the first stable dicoordinate silicon compound, was reported in 1994 by Michael Denk and Robert West (chemist), Robert West three years after Anthony Joseph Arduengo III, Anthony Arduengo first isolated an N-heterocyclic carbene, the lighter Congener (chemistry), congener of NHSis. Since their first isolation, NHSis have been synthesized and studied with both saturated and unsaturated central rings ranging in size from 4 to 6 atoms. The stability of NHSis, especially 6π aromatic unsaturated five-membered examples, make them useful systems to study the structure and reactivity of silylenes and low-valent main group elements in general. Though not used outside of academic settings, complexes containing NHSis are known to be competent catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silenes
In inorganic chemistry, silenes, or disilalkenes,Philip P. Power "pi-Bonding and the Lone Pair Effect in Multiple Bonds between Heavier Main Group Elements" Chemical Reviews, 1999, 99, 3462. are silicon compounds that contain double bonds, where the oxidation state of Si is +2. The parent molecule is disilene, Si2H4. Structure The first transient disilene was reported in 1972 by D. N. Roark and Garry J. D. Peddle. Simple disilenes easily polymerize. To suppress this tendency, bulky substituents are used. Indeed the first isolable disilene, tetramesityldisilene, was described in 1981 by West, Fink, and Michl. It was prepared by UV-photolysis of the related cyclic trisilane: : 2 i(mesityl)2sub>3 → 3 (mesityl)2Si=Si(mesityl)2 Structure of tetramesityldisilene Tetramesityldisilene is a yellow-orange solid. The Si=Si double bond lengths of disilenes vary between 2.14 and 2.29 Å and are nearly 5 to 10% shorter than the Si-Si single bond lengths of corresponding disilane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
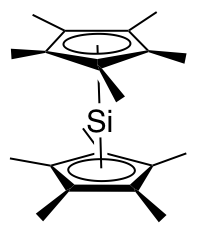
Decamethylsilicocene
Decamethylsilicocene, (C5Me5)2Si, is a group 14 sandwich compound. It is an example of a main-group cyclopentadienyl complex; these molecules are related to metallocenes but contain p-block elements as the central atom. It is a colorless, air sensitive solid that sublimes under vacuum. Synthesis The first synthesis of decamethylsilicocene was reported by Jutzi and coworkers in 1986. It involved reduction of bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)silicon(IV) dichloride with two equivalents of sodium naphthalenide to generate decamethylsilicocene, naphthalene, and sodium chloride. Generation of the sterically crowded bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)silicon(IV) dichloride required several steps, beginning with double deprotonation of (C5Me4H)2SiCl2 using ''tert''-butyllithium, followed by treatment of the resultant (C5Me4Li)2SiCl2 with methyl iodide. Decamethylsilicocene is soluble in aprotic solvents such as hexane, benzene, and chlorinated solvents. Molecular weight determinations s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbene Analog
Carbene analogs in chemistry are carbenes with the carbon atom replaced by another chemical element. Just as regular carbenes they appear in chemical reactions as reactive intermediates and with special precautions they can be stabilized and isolated as chemical compounds. Carbenes have some practical utility in organic synthesis but carbene analogs are mostly laboratory curiosities only investigated in academia. Carbene analogs are known for elements of group 13, group 14, group 15 and group 16. Group 13 carbene analogs In group 13 elements the boron carbene analog is called a borylene or boranylidene. Group 14 carbene analogs The heavier group 14 carbenes are silylenes, R2Si:, germylenes R2Ge: (example diphosphagermylene), stannylenes R2Sn: and plumbylenes R2Pb:, collectively known as metallylenes and regarded as monomers for polymetallanes. The oxidation state for these compounds is +2 and stability increases with principal quantum number (moving down a row in the perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Trap
In chemistry, a chemical trap is a chemical compound that is used to detect unstable compounds. The method relies on efficiency of bimolecular reactions with reagents to produce a more easily characterize trapped product. In some cases, the trapping agent is used in large excess. Case studies Cyclobutadiene A famous example is the detection of cyclobutadiene released upon oxidation of cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl. When this degradation is conducted in the presence of an alkyne, the cyclobutadiene is trapped as a bicyclohexadiene. The requirement for this trapping experiment is that the oxidant (ceric ammonium nitrate) and the trapping agent be mutually compatible. : Diphosphorus Diphosphorus is an old target of chemists since it is the heavy analogue of N2. Its fleeting existence is inferred by the controlled degradation of certain niobium complexes in the presence of trapping agents. Again, a Diels-Alder strategy is employed in the trapping: : Silylene Another classic but e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silylium Ion
A silylium ion is a reactive organosilicon compound, silyl-containing cation with the formula . With three rather than the usual four bonds to Si, silylium ions are the silicon analogues of carbenium ions. They can be viewed as protonated silylenes. Early efforts to generate these cations produced salts of the pyridine complex [(CH3)3Si-NC5H5]+, the hydride-bridged species [(Et3Si)2H]+, and the toluene complex [(mes)3Si(toluene)]+. Well-characterized silylium salts with well-defined three-coordinate silicon cations trimesitylsilylium and tris(pentamethylphenyl) . These cations are related to trityl (), with the extra methyl groups providing steric protection, compensating for the greater size of Si vs C. Its 29Si NMR chemical shift is 225.5 ppm, downfield of TMS, which indicates that the cation is quite "naked". Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (Me3SiOTf), normally considered a source of electrophilic silicon, has a 29Si NMR shift of 43 ppm. Salts of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysilane
Polysilanes are organosilicon compounds with the formula (R2Si)n. They are relatives of traditional organic polymers but their backbones are composed of silicon atoms. They exhibit distinctive optical and electrical properties. They are mainly used as precursors to silicon carbide. The simplest polysilane would be (SiH2)n, which is mainly of theoretical, not practical interest. Synthesis left, Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane shares some properties of high molecular weight polysilanes. The first polysilane, poly(dimethylsilylene), CH3)2Sisub>''x'', was reported in 1949 by Charles A. Burkhard (1916 - 1991) of General Electric. It was prepared by heating sodium metal with dimethyldichlorosilane: :(CH3)2SiCl2 + 2 Na → CH3)2Sisub>n + 2 NaCl The modified Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes remains a viable and general route to high molecular weight, linear polysilane derivatives. This reaction is conducted at elevated temperature in an inert solvent using a dispersion of the alkali me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Photolysis
Flash photolysis is a pump-probe laboratory technique, in which a sample is first excited by a strong pulse of light from a pulsed laser of nanosecond, picosecond, or femtosecond pulse width or by another short-pulse light source such as a flash lamp. This first strong pulse is called the pump pulse and starts a chemical reaction or leads to an increased population for energy levels other than the ground state within a sample of atoms or molecules. Typically the absorption of light by the sample is recorded within short time intervals (by a so-called test or probe pulses) to monitor relaxation or reaction processes initiated by the pump pulse. Flash photolysis was developed shortly after World War II as an outgrowth of attempts by military scientists to build cameras fast enough to photograph missiles in flight. The technique was developed in 1949 by Manfred Eigen, Ronald George Wreyford Norrish and George Porter, who won the 1967 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this invention. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken or new bonds formed or both. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |