silylene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Silylene is a
 The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
 In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by flash photolysis of a trisilane:
:
In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by flash photolysis of a trisilane:
: In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two
In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two
chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
with the formula SiR2. It is the silicon analog of carbene. Silylene rapidly when condensed.
Silylenes are formal derivatives of silylene with its hydrogens replaced by other substituents. Most examples feature amido (NR2) or alkyl/aryl groups.
Silylenes have been proposed as reactive intermediates. They are carbene analogs.
Synthesis and properties
Silylenes have been generated by thermolysis or photolysis of polysilanes, by silicon atom reactions ( insertion,addition
Addition (usually signified by the Plus and minus signs#Plus sign, plus symbol, +) is one of the four basic Operation (mathematics), operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication, and Division (mathematics), divis ...
or abstraction), by pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
of silanes, or by reduction of 1,1-dihalosilane. It has long been assumed that the conversion of metallic Si to tetravalent silicon compounds proceeds via silylene intermediates:
:Si + Cl2 → SiCl2
:SiCl2 + Cl2 → SiCl4
Similar considerations apply to the direct process, the reaction of methyl chloride and bulk silicon.
Early observations of silylenes involved generation of dimethylsilylene by dechlorination of dimethyldichlorosilane:
:SiCl2(CH3)2 + 2 K → Si(CH3)2 + 2 KCl
The formation of dimethylsilylene was demonstrated by conducting the dechlorination in the presence of trimethylsilane: the trapped product being pentamethyldisilane:
:Si(CH3)2 + HSi(CH3)3 → (CH3)2Si(H)−Si(CH3)3
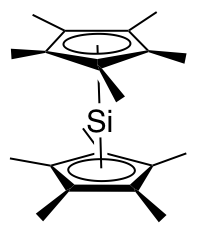
A room-temperature isolable ''N''-heterocyclic silylene is :
 The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
Related reactions
 In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by flash photolysis of a trisilane:
:
In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by flash photolysis of a trisilane:
: In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two
In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two microsecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is to one second, ...
s. Added methanol acts as a chemical trap with a second order rate constant of which is close to diffusion control.
See also
* Carbene analogs * ''N''-heterocyclic silylene * Silenes, R2Si=SiR2 * Silylium ions, protonated silylenesReferences
{{Reflist Inorganic silicon compounds Free radicals Octet-deficient functional groups