|
Silver Zinc Battery
A silver zinc battery is a secondary cell that utilizes silver(I,III) oxide and zinc. Overview Silver zinc cells share most of the characteristics of the silver-oxide battery, and in addition, is able to deliver one of the highest specific energies of all presently known electrochemical power sources. Long used in specialized applications, it is now being developed for more mainstream markets, for example, batteries in laptops and hearing aids. Silver–zinc batteries, in particular, are being developed to power flexible electronic applications, where the reactants are integrated directly into flexible substrates, such as polymers or paper, using printing or chemical deposition methods. Experimental new silver–zinc technology (different to silver-oxide) may provide up to 40% more run time than lithium-ion batteries and also features a water-based chemistry that is free from the thermal runaway and flammability problems that have plagued the lithium-ion alternatives. Chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
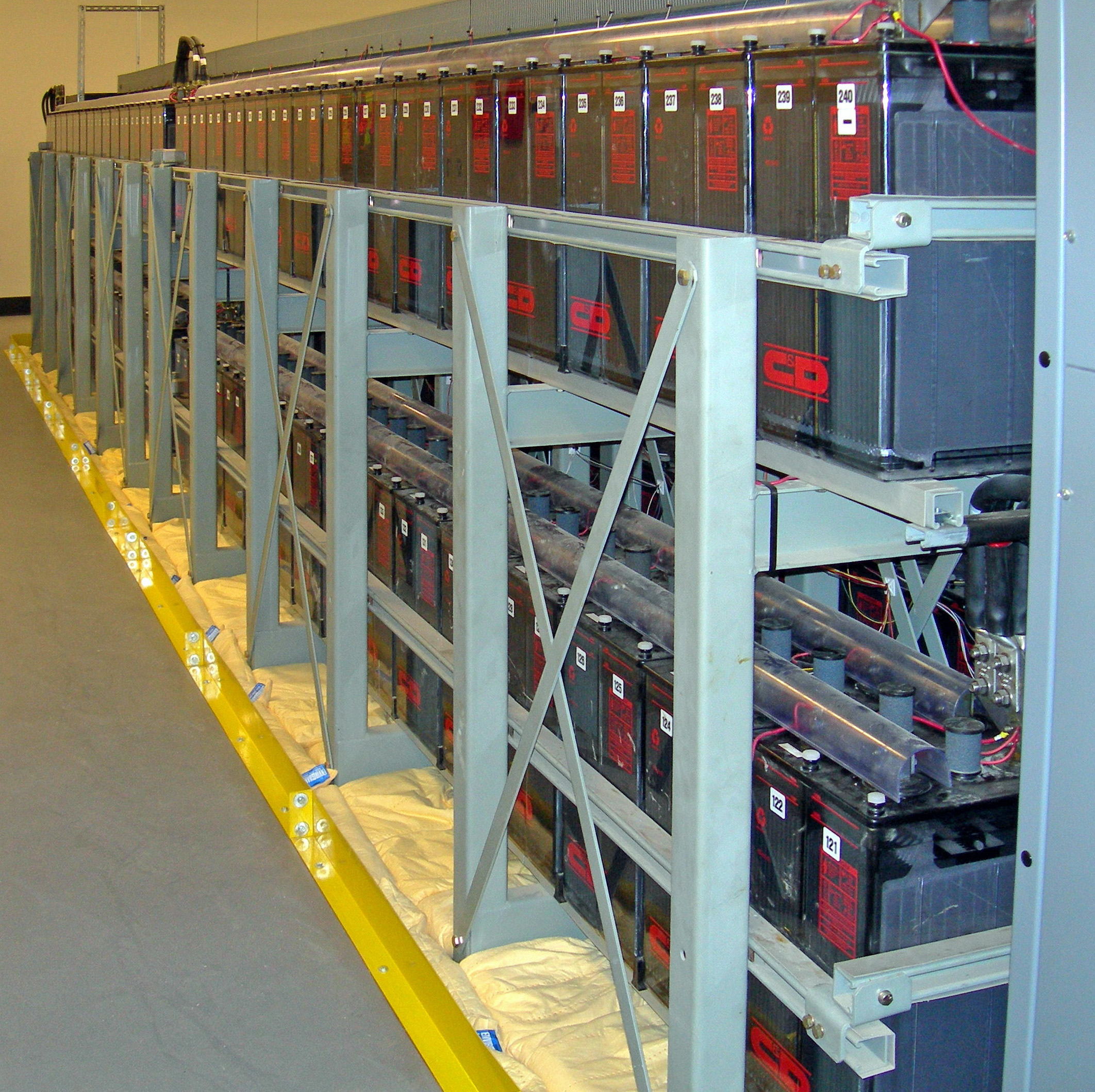
Secondary Cell
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of Accumulator (energy), energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or primary battery, which is supplied fully charged and discarded after use. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. The term "accumulator" is used as it accumulator (energy), accumulates and energy storage, stores energy through a reversible electrochemical Chemical reaction, reaction. Rechargeable batteries are produced in many different shapes and sizes, ranging from Button cell#Rechargeable variants, button cells to megawatt systems connected to grid energy storage, stabilize an electrical distribution network. Several different combinations of electrode materials and electrolytes are used, including lead–acid battery, lead–acid, zinc–air battery, zinc–air, nickel–cadmium battery, nickel–cadmium (NiC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Density
In physics, energy density is the quotient between the amount of energy stored in a given system or contained in a given region of space and the volume of the system or region considered. Often only the ''useful'' or extractable energy is measured. It is sometimes confused with stored energy per unit mass, which is called ''specific energy'' or . There are different types of energy stored, corresponding to a particular type of reaction. In order of the typical magnitude of the energy stored, examples of reactions are: Nuclear power, nuclear, Chemical energy, chemical (including Electrochemistry, electrochemical), electrical, pressure, Deformation (engineering), material deformation or in Electromagnetic field, electromagnetic fields. Nuclear reactions take place in stars and nuclear power plants, both of which derive energy from the binding energy of nuclei. Chemical reactions are used by organisms to derive energy from food and by automobiles from the combustion of gasoline. Liqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Motors
General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing four automobile brands: Chevrolet, Buick, GMC (marque), GMC, and Cadillac, each a separate division of GM. By total sales, it has continuously been the largest automaker in the United States, and was the List of manufacturers by motor vehicle production, largest in the world for 77 years before losing the top spot to Toyota in 2008. General Motors operates manufacturing plants in eight countries. In addition to its four core brands, GM also holds interests in Chinese brands Baojun and SAIC-GM-Wuling, Wuling via SAIC-GM-Wuling, SAIC-GM-Wuling Automobile. GM further owns GM Defense, a namesake defense vehicles division which produces military vehicles for the United States government and military, the vehicle safety, security, and information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfa-class Submarine
The Alfa class, Soviet designation Project 705 Lira (, meaning "Lyre", NATO reporting name Alfa), was a class of nuclear-powered attack submarines in service with the Soviet Navy from 1971 into the early 1990s, with one serving in the Russian Navy until 1996. They were among the fastest military submarines ever built, with only the prototype submarine (NATO reporting name Papa-class) exceeding them in submerged speed. The Project 705 submarines had a unique design among other submarines. In addition to the revolutionary use of titanium for its hull, it used a powerful lead-bismuth liquid metal cooled reactor as a power source, which greatly reduced the size of the reactor compared to conventional designs, thus reducing the overall size of the submarine, and allowing for very high speeds. However, it also meant that the reactor had a short lifetime and had to be kept warm when it was not being used. As a result, the submarines were used as interceptors, mostly kept in port ready ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 37 Torpedo
The Mark 37 torpedo is a torpedo with electrical propulsion, developed for the US Navy after World War II. It entered service with the US Navy in the early 1950s, with over 3,300 produced. It was phased out of service with the US Navy during the 1970s, and the stockpiles were sold to foreign navies. Development Its engineering development began in 1946 by Westinghouse. It was largely based on the concept of the passive homing Mark 27, with added active homing system tested on modified Mark 18s, and a new torpedo body. Between 1955 and 1956, thirty torpedoes were produced for development testing, with large-scale production commenced shortly afterwards. Due to its electric propulsion, the torpedo swam smoothly out of the launch tube, instead of having to be ejected by pressurized air, therefore significantly reducing its acoustic launch signature. To allow for water flow around the torpedo while swimming out, several 1" thick guide studs were attached to the torpedo, which al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructed from a repurposed Saturn V third stage (the S-IVB), and took the place of the stage during launch. Operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation and hundreds of experiments. Skylab's orbit eventually decayed and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. Overview Skylab was the only space station operated exclusively by the United States. A permanent station was planned starting in 1988, but its funding was canceled and U.S. participation shifted to the International Space Station in 1993. Skylab had a mass of with a Apollo command and service module (CSM) attached and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 13
Apollo 13 (April 1117, 1970) was the seventh crewed mission in the Apollo program, Apollo space program and would have been the third Moon landing. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center on April 11, 1970, but the landing was aborted after an oxygen tank in the Apollo command and service module#Service module (SM), service module (SM) exploded two days into the mission, disabling its electrical and life-support system. The crew, supported by backup systems on the Apollo Lunar Module, lunar module (LM), instead looped around the Moon in a circumlunar trajectory and returned safely to Earth on April 17. The mission was commanded by Jim Lovell, with Jack Swigert as Apollo command and service module#Command module (CM), command module (CM) pilot and Fred Haise as Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module (LM) pilot. Swigert was a late replacement for Ken Mattingly, who was grounded after exposure to rubella. A routine stir of an oxygen tank ignited damaged wire insulation insid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cells
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came almost a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for satellites and space capsules. Since then, fuel cells hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
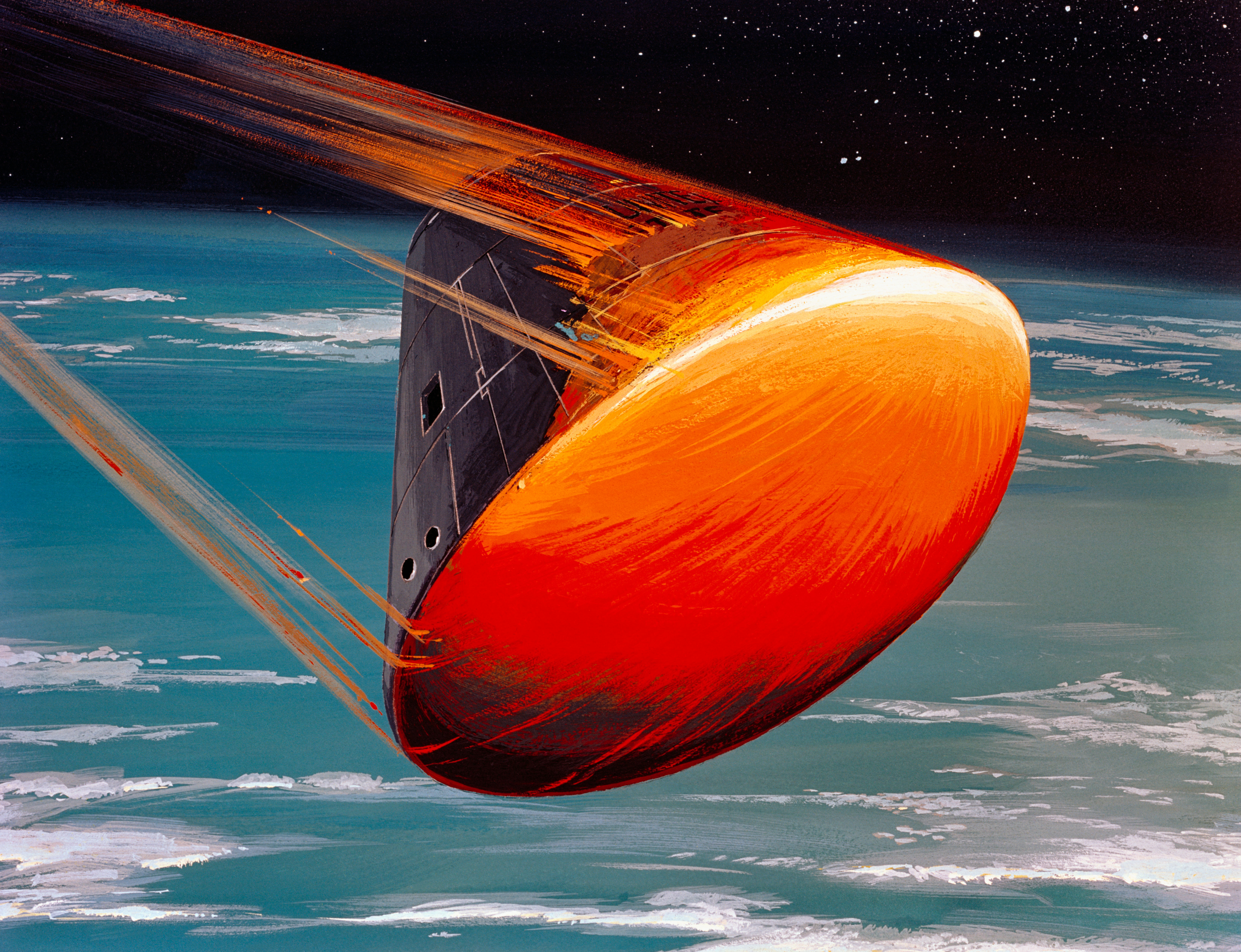
Apollo Command/Service Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo (spacecraft), Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown (spacecraft landing), splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical cable, umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Rover
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration Rover (space exploration), vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, Apollo 16, 16, and Apollo 17, 17. Other rovers have been partially or fully autonomous robots, such as the Soviet Union's Lunokhods, Chinese ''Yutu (rover), Yutus'', Indian ''Pragyan (Chandrayaan-3), Pragyan'', and Japan's Smart Lander for Investigating Moon#Rovers, LEVs. Five countries have had operating rovers on the Moon: the Soviet Union, the United States, China, India, and Japan. Variations in design Lunar rover designs have varied in several ways. Size and speed Lunokhod rovers were in length. The LRVs were long with a wheelbase, and achieved a top speed of during Apollo 17. Power The Lunokhod rovers, and others, used photovoltaic solar power. The LRV rovers were battery powered. Lunokhod and the Chinese ''Yutu'' rovers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |