|
Siege Of Gaza (332 BCE)
The siege of Gaza, as part of the Wars of Alexander the Great, took place in October of 332 BC. Resulting in a victory for Macedon, it ended the 31st Dynasty of Egypt, which functioned as a satrapy under the Achaemenid Persian Empire. Alexander succeeded in breaching the walls of Gaza by utilizing the engines that he had employed earlier that year, during the siege of Tyre brought by Hephaestion. Following three unsuccessful assaults, the Macedonian army was able to storm and take the Gazan stronghold. Batis, the military commander of Gaza's fortress, expected to hold the city as well as the rest of Egypt in complete subjection until the raising of another army by Persian king Darius III; confronting Alexander at Gaza was crucial to denying the Macedonians a route into the Egyptian mainland. The fortress was located on an eminence, on the edge of a desert from which the surrounding area could be easily controlled, including the main road from Assyria to Egypt. The city, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula and the South Caucasus. The region is separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. West Asia contains the majority of the similarly defined Middle East. The ''Middle East'' is a political term invented by Western geographers that has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granicus River
Granicus may refer to: * Granicus River, also called Biga River (Turkish: Biga Çayı) * Battle of the Granicus The Battle of the Granicus in May 334 BC was the first of three major battles fought between Alexander the Great of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon and the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The battle took place on the road from Abydos (Hellespont ... River, between Alexander the Great and the Persian Empire in May 334 BC * Granicus (band), a band formed in 1969 * Granicus Valles, a network of valleys on Mars {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Persian Gate
The Battle of the Persian Gate took place as part of the Wars of Alexander the Great. In the winter of 330 BC, Ariobarzanes of Persis led a last stand with his outnumbered Persian army at the Persian Gates, Persian Gate, near Persepolis, and held back the Ancient Macedonian army, Macedonian army for approximately a month. However, through captured prisoners of war or a local shepherd, Alexander the Great, Alexander found a path around to flank the Persian troops from the rear, allowing him to capture half of Persia proper in another decisive victory against the Achaemenid Empire. Background The Achaemenid Empire suffered a series of defeats against the Macedonian forces at Battle of the Granicus, Granicus (334 BC), Battle of Issus, Issus (333 BC) and Battle of Gaugamela, Gaugamela (331 BC), and by the end of 331 BC Alexander had advanced to Babylon and Susa. A Royal Road connected Susa (the first Persian capital city in Elam) with the more eastern capitals of Persepolis and Pasar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital of Elam and the winter capital of the Achaemenid Empire, and remained a strategic centre during the Parthian Empire, Parthian and Sasanian Empire, Sasanian periods. The site currently consists of three archaeological mounds, covering an area of around . The city of Shush, Iran, Shush is located on the site of ancient Susa. Name The name Susa is of Elamiate origin and has appeared in many languages: *Middle *Middle and Neo- *Neo-Elamite language, Elamite and Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid *Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid * * * * or *New * Literary references Susa was one of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East. In Historiography, historic literature, Susa appears in the very earliest Sumerian records: for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Uxian Defile
The Battle of Uxian Defile was fought by Alexander the Great against the Uxian tribe of the Persian Empire. The battle raged on the mountain range between the key Persian cities of Susa and Persepolis. Persepolis was the ancient capital of the Persian Empire and held a symbolic value among the native Persian population. They believed that if this city were to fall into enemy hands, then, in effect, the whole Persian Empire would fall into the hands of the enemy. Background Alexander had recently defeated Darius III Codomannus at the Battle of Gaugamela on the eastern side of the Tigris river, the result of which had been a disaster for Darius and the Persian Empire. Darius had prematurely fled the battle, and his army had dispersed. Thus Alexander had been unable to achieve his goal of capturing Darius during the course of the battle. Instead, Alexander chased Darius and, as a result, captured the important cities of the Persian Empire along the way. Immediately after the bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erbil
Erbil (, ; , ), also called Hawler (, ), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. The city is the capital of the Erbil Governorate. Human settlement at Erbil may be dated back to the 5th millennium BC. At the heart of the city is the ancient Citadel of Erbil and Mudhafaria Minaret. The earliest historical reference to the region dates to the Third Dynasty of Ur of Sumer, when King Shulgi mentioned the city of Urbilum. The city was later conquered by the Assyrian people, Assyrians. In the 3rd millennium BC, Erbil was an independent power in its area. It was conquered for a time by the Gutians. Beginning in the late 2nd millennium BC, it came under Assyrian control. Subsequent to this, it was part of the geopolitical province of Assyria under several empires in turn, including the Median Empire, the Achaemenid Empire (Achaemenid Assyria), Macedonian Empire, Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenian Empire, Parthian Empire, Assyria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela ( ; ), also called the Battle of Arbela (), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Ancient Macedonian army, Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Army, Persian Army under Darius III, King Darius III. It was the second and final battle between the two kings, and is considered to be the final blow to the Achaemenid Empire, resulting in its complete conquest by Alexander. The fighting took place in Gaugamela, a village on the banks of the river Khazir River, Bumodus, north of Arbela (modern-day Erbil, in Iraqi Kurdistan). Despite being heavily outnumbered, the Army of Macedon emerged victorious due to the employment of superior tactics and the clever usage of light infantry forces. It was a decisive victory for the League of Corinth, and it led to the fall of the Achaemenid Empire and of Darius III. Background In November 333 BC, Darius III, King Darius III had lost the Battle of Issus to Alexander the Great, which res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile Delta, Nile River delta. Founded in 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, Egypt, Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" and "Pearl of the Mediterranean Coast" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and petroleum, oil pipeline transport, pipelines from Suez. The city extends about along the northern coast of Egypt and is the largest city on the Mediterranean, the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second-largest in Egypt (after Cairo), the List of largest cities in the Arab world, fourth- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyre, Lebanon
Tyre (; ; ; ; ) is a city in Lebanon, and one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. It was one of the earliest Phoenician metropolises and the legendary birthplace of Europa (consort of Zeus), Europa, her brothers Cadmus and Phoenix (son of Agenor), Phoenix, and Carthage's founder Dido (Elissa). The city has many ancient sites, including the Tyre Hippodrome, and was added as a whole to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1984. The historian Ernest Renan noted that "One can call Tyre a city of ruins, built out of ruins". Tyre is the fifth-largest city in Lebanon after Beirut, Tripoli, Lebanon, Tripoli, Sidon, and Baalbek. It is the capital of the Tyre District in the South Governorate. There were approximately 200,000 inhabitants in the Tyre urban area in 2016, including many refugees, as the city hosts three of the twelve Palestinian refugee camps in Lebanon: Burj el-Shamali, Burj El Shimali, El-Buss refugee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Tyre (332 BC)
The siege of Tyre was orchestrated by Alexander the Great in 332 BC during his campaigns against the Persians. At first, the Macedonian army was unable to capture the city of Tyre, which was a strategic coastal base on the Mediterranean Sea, through conventional means because it was on an island that was 1 kilometer off the coast of Modern day Lebanon (at the time Phoenicia) and had walls right up to the sea. Alexander responded to this problem by first blockading and besieging Tyre for seven months, and then by building a causeway and placing siege towers with catapults built on top at the end after his soldiers discovered that they could not extend it any further due to a steep drop under the surface of the water. This allowed him to breach the fortifications. It is said that Alexander was so enraged at the Tyrians' defence of their city and the loss of his men that he destroyed half the city. According to Arrian, 8,000 Tyrian civilians were massacred after the city fell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
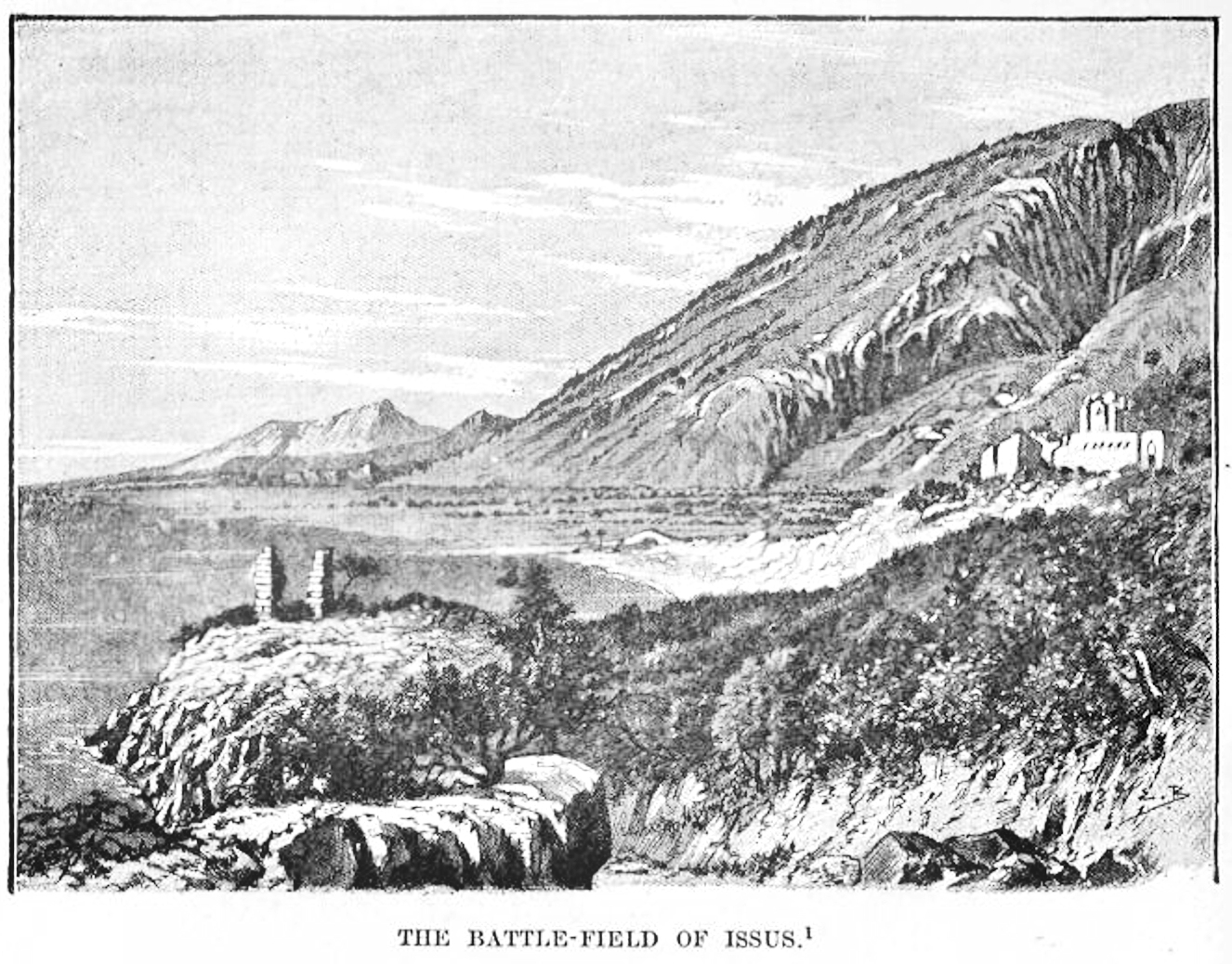
Issus (Cilicia)
Issus (Latin; Phoenician: ''Sissu'') or Issos (, ''Issós'', or , ''Issoí'') was an ancient settlement on the strategic coastal plain straddling the small Pinarus river (a fast melt-water stream several metres wide) below the navigationally difficult inland mountains towering above to the east in the Turkish Province of Hatay, near the border with Syria. It can be identified with Kinet Höyük in the village of Yeşilköy near Dörtyol in Turkey's Hatay Province. Excavations on the mound occurred between 1992 and 2012 by Bilkent University. It is most notable for being the place of no fewer than three decisive ancient or medieval battles each called in their own era the Battle of Issus: # The Battle of Issus (333 BC) or the First Battle of Issus, in which Alexander the Great of Macedonia defeated Darius III of Persia # Battle of Issus (194) or the Second Battle of Issus, in which P. Cornelius Anullinus defeated Septimius Severus's rival Pescennius Niger # Battle of Issus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Issus
The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on 5 November 333 BC between the League of Corinth, Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III of Persia, Darius III. It was the second great battle of Alexander's conquest of Asia, and the first encounter between Darius III and Alexander the Great. The battle resulted in the Macedonian troops defeating the Persian forces. After the Hellenic League soundly defeated the Persian satraps of Asia Minor (led by Greek mercenary Memnon of Rhodes) at the Battle of the Granicus, Darius took personal command of his army. He gathered reinforcements and proceeded to lead his men in a surprise march behind the Hellenic advance, in order to cut off their line of supply. Alexander was forced to countermarch, and the stage was set for the battle near the mouth of the Pinarus River and the city of Issus (town), Issus. Location The battle took place south of the ancient city Issus (town) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |