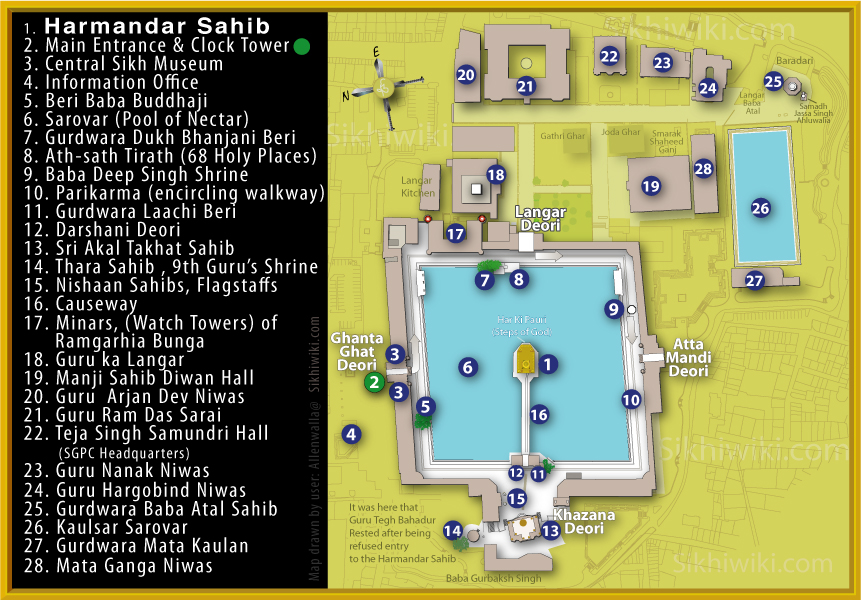
|
Shri Khuralgarh Sahib
Khuralgarh Sahib ( pa, ਖੁਰਾਲਗੜ ਸਾਹਿਬ) is one of the most prominent historical place of Ravidasi communities like Ad-Dharmi, Chamar, Ramdasia Sikhs and Mochis. It is situated at village Kharali, Garhshanker, Hoshiarpur district. Khuralgarh Sahib is also called ''Charan Choh Ganga Sri Guru Ravidas Ji'' as this place was visited by Sri Guru Ravidas Minar-e-Begampura Minar-e-Begampura is 151 feet high hallmark of ''Guru Ravidass Memorial'' at Shri Khuralgarh Sahib in Khuralgarh village. This memorial is said to have a spacious congregation hall having the capacity to accommodate 10000 pilgrims. Also there is state-of-the art auditorium equipped with all the modern audio-visual aids to showcase the life works of Guru Ravidass Ravidas or Raidas, was an Indian mystic poet-saint of the bhakti movement during the 15th to 16th century CE. Venerated as a ''guru'' (teacher) in the modern regions of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharali
Kharali (sometimes spelled as Khurali or Khuralgarh) is a village located in Garhshanker area of Hoshiarpur district, Punjab, India. Village is known for Shri Khuralgarh Sahib, a place visited by the social reformer and spiritual figure Ravidas. Demographics Kharali village has total population of 343 families. The village has population of 1786 persons having 901 males and 885 females. Children population with age 0-6 is 201 which makes up 11.25% of total population. Average Sex Ratio is 982 higher than Punjab state average of 895. As in 2011 census, literacy rate of the village was 76.53%. 37.79% of total population is Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Schedule Caste/Dalit at the village. See also *Shri Khuralgarh Sahib, religious place in Kharali. References Villages in Hoshiarpur district {{Hoshiarpur district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhshanker
Garhshankar is a city in Hoshiarpur district in the state of Punjab, India India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the .... History It was founded by Doad Rajput king named Shankar Sahai in 1000 AD. Garhshankar was converted as a Tehsil in the year of 1844 by the British administration. Politics Jai Krishan Singh Rouri, (AAP) is the second term MLA from Garhshankar Assembly Constituency, elected in 2022 Punjab Assembly Elections. He was first elected as MLA in 2017 Punjab Assembly Elections. Demographics As per 2011 census, Garhshankar had a population of . Males constitute 52% of the population and females 48%. Garhshankar has an average literacy rate of 73%, higher than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 76%, and female literacy is 70%. Railways Garhshank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoshiarpur District
Hoshiarpur district is a district of Punjab state in northern India. Hoshiarpur, one of the oldest districts of Punjab, is located in the North-east part of the Punjab state and shares common boundaries with Gurdaspur district in the north-west, Jalandhar district and Kapurthala district in south-west, Kangra district and Una district of Himachal Pradesh in the north-east. Hoshiarpur district comprises 4 sub-divisions, 10 community development blocks, 9 urban local bodies and 1417 villages. The district has an area of 3365 km2. and a population of 1,586,625 persons as per census 2011. Hoshiarpur along with the districts of Nawanshehar, Kapurthala and parts of Jalandhar represents one of the cultural region of Punjab called Doaba or the Bist Doab - the tract of land between two rivers namely Beas and Sutlej. The area along with the Shivalik foothills on the right side of Chandigarh-Pathankot road in Hoshiarpur is submountainous and this part of the district is also known as K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab, India
Punjab (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the States and union territories of India, Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the north and northeast, Haryana to the south and southeast, and Rajasthan to the southwest; by the Indian union territory, union territories of Chandigarh to the east and Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir to the north. It shares an international border with Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab, a Pakistani province, province of Pakistan to the west. The state covers an area of 50,362 square kilometres (19,445 square miles), which is 1.53% of India's total geographical area, making it List of states and union territories of India by area, the 19th-largest Indian state by area out of 28 Indian states (20th largest, if UTs are considered). With over 27 million inhabitants, Punjab is List of states and union territories of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad-Dharmi
The Ad-Dharmi is a Dalit religion in the state of Punjab in India Ad-Dharmis are 11.48% of the total of lower status communities in Punjab. Origin The Ad-Dharm movement was started in 1920s, for the purpose of getting a distinct religious identity same as Adi Dravida movement of Tamil Nadu. The founder of the Ad-Dharm Movement was Mangu Ram Mugowalia (founding member of Ghadar Party), Master Gurbanta Singh (senior Congress leader) B. L. Gherra and also Pandit Hari Ram (Pandori Bibi) who was the secretary of the organization. The movement projected Guru Ravidas, the 14th century Bhakti Movement saint as their spiritual guru and a sacred book ''Ad Parkash'' for separate ritual traditions. The Ad-Dharmi Dalits came together as a faith was in 1925 when the British ruled India. In the 1931 census, more than 450,000 registered themselves as members of the new indigenous faith called ''Ad Dharam'' (or ''Original Religion''). But this faith and movement vanished after India's independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhagat
Bhagat is a term used in the Indian subcontinent to describe religious personalities who have obtain high acclaim in their community for their services and devoutness.It is also one of the clan in Mahar caste with clan totem as King Cobrahttp://lsi.gov.in:8081/jspui/bitstream/123456789/2806/1/41944_1961_ETH.pdf and also a surname found among Marathas, Bania communities and Punjabi Brahmins. Definition ''Bhagat'' is a Punjabi word derived from the Sanskrit word ''Bhagavata'', which means: a devotee of the Lord ('' Bhagvan''). It usually defines the relationship between a lord and his devotee and the pure offering from a bhagat to his bhagvaan. Many such Hindu devotees are followers of the ''bhakti'' tradition, who adhere to a prayer-led path of realization. ''Bhagat'' is also a Hindu, Buddhist and Jain surname, found in various communities though it is most prevalent in the northern states of India. Sikhism Sikhism's central scriptural book, Guru Granth Sahib, has teachings of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravidassia Religion
Ravidassia or the Ravidas Panth is an Indian religion based on the teachings of Ravidass, who is revered as a satguru. Historically, Ravidassia represented a range of beliefs in the Indian subcontinent, with some devotees of Ravidass counting themselves as Ravidassia, but first formed in the early 20th-century in colonial British India.Paramjit Judge (2014), Mapping Social Exclusion in India: Caste, Religion and Borderlands, Cambridge University Press, , pages 179-182 The Ravidassia tradition began to take on more cohesion following 1947, and the establishment of successful Ravidassia tradition in the diaspora. Estimates range between two to five million for the total number of Ravidassias. Ravidassias believe that Ravidas is their Guru (saint) whereas the Sikhs have traditionally considered him one of many bhagats (holy person), a lower position to Guru in Sikhism. Further, Ravidassias accept living sants of Ravidass Deras as ''Guru'' A new Ravidassia religion was laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramdasia
The Ramdasia were historically a Sikh Hindu sub-group that originated from the caste of leather tanners and shoemakers known as Chamar Terminology Ramdasia is a term used in general for Sikhs whose ancestors belonged to Chamar caste. Originally they are followers of Guru Ravidass who belongs to Chamar community. Both the words Ramdasia and Ravidasia are also used inter changeably while these also have regional context. In Puadh and Malwa, largely Ramdasia in used while Ravidasia is predominantly used in Doaba. Ramdasia Sikhs are enlisted as scheduled caste by Department of Social justice, Empowerment and Minorities- Government of Punjab. On Department's list of Scheduled Caste, this caste is listed on serial number 9 along with other Chamar caste synonymous such as Ravidasia, Jatav and so on. Military service British Raj During World War I the single-battalion regiments of the Mazhabi and Ramdasia Sikh Pioneers – the 23rd, 32nd and 34th Pioneer Regiments – wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh Architecture
Sikh architecture is a style of architecture that was developed under Sikh Empire during 18th and 19th century in the Punjab region. Due to its Modernism, progressive style, it is constantly evolving into many newly developing branches with new contemporary styles. Although Sikh architecture was initially developed within Sikhism its style has been used in many non-religious buildings due to its beauty. 300 years ago, Sikh architecture was distinguished for its many curves and straight lines; Keshgarh Sahib, Shri Keshgarh Sahib and the Sri Harmandir Sahib (Harmandir Sahib, Golden Temple) are prime examples. Sikh Architecture is heavily influenced by Mughal architecture, Mughal and Islamic architecture, Islamic styles. The onion dome, frescoes, in-lay work, and multi-foil arches, are Mughal influences, more specially from Shah Jahan's period, whereas ''Chhatri, chattris'', oriel windows, bracket supported eaves at the string-course, and ornamented friezes are derived from elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamar
Chamar is a Dalit community classified as a Scheduled Caste under modern India's system of affirmative action. Historically subject to untouchability, they were traditionally outside the Hindu ritual ranking system of castes known as varna. They are found throughout the Indian subcontinent, mainly in the northern states of India and in Pakistan and Nepal. History Ramnarayan Rawat posits that the association of the Chamar community with a traditional occupation of tanning was constructed, and that the Chamars were instead historically agriculturists. The term ''chamar'' is used as a pejorative word for dalits in general. It has been described as a casteist slur by the Supreme Court of India and the use of the term to address a person as a violation of the Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989. Chamars have remained one of the most discriminated community within Hinduism. In reference to villages of Rohtas and Bhojpur district of Bihar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mochi (Sikh)
Mochi are the sub-caste and sub-community of Chamar Caste. Mochi are a community found mainly in the Punjab state of India, in the districts of Patiala, Ludhiana and Nabha. However, the majority of the Mochis in Punjab remain Hindu, with only a smaller minority converting Sikhism. Almost all Sikh Mochi are members of the Ravidasi sect. Most are involved in their traditional occupation of shoemaking.People of India Punjab Volume XXXVII edited by I.J.S Bansal and Swaran Singh pages 353 to 357 Manohar Although the Sikh Mochi practice endogamy and clan exogamy, there are occasional cases of intermarriage with the Chamar community. There clans are referred to as ''gots'' from the Sanskrit gotra include the Biswan, Sinh and Suman Mochi. See also * Mochi (Hindu) The Mochi are a Hindu caste found mainly in North India. They are the traditional shoemakers of South Asia. History and origin Historically, the community was involved in the manufacture of protective leather craft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravidas
Ravidas or Raidas, was an Indian mystic poet-saint of the bhakti movement during the 15th to 16th century CE. Venerated as a ''guru'' (teacher) in the modern regions of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab and Haryana, he was a poet, social reformer and spiritual figure. The life details of Ravidas are uncertain and contested. Scholars believe he was born in 1450 CE. But some Scholars believe he was born in 1377 CE and dead in 1528 CE. He taught removal of social divisions of caste and gender, and promoted unity in the pursuit of personal spiritual freedom. Ravidas's devotional verses were included in the Sikh scriptures known as ''Guru Granth Sahib''. The ''Panch Vani'' text of the Dadu Panthi tradition within Hinduism also includes numerous poems of Ravidas. He is also the central figure within the Ravidassia religious movement. Life The details of Guru Ravidas's life are not well known. Scholars state he was born in 1377 CE and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |