Sikh architecture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sikh architecture is a style of
Sikh architecture is a style of
 Apart from religious buildings, Sikh architecture includes secular fo rts, ''bungas'' (residential places), palaces, and colleges. The religious structure is called ''
Apart from religious buildings, Sikh architecture includes secular fo rts, ''bungas'' (residential places), palaces, and colleges. The religious structure is called ''
File:Gurdwara Dera Sahib and Samadhi of Ranjit Singh.jpg, Golden dome of Gurdwara Dera Sahib in
Article on Sikh Architecture
{{Architecture of India Architectural styles Indian architectural history Pakistani architectural history
 Sikh architecture is a style of
Sikh architecture is a style of architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
that was developed under the Sikh Confederacy
The Sikh Confederacy was a confederation of twelve sovereign Sikh states (each known as a Misl, derived from the Arabic word مِثْل meaning 'equal'; sometimes spelt as Misal) which rose during the 18th century in the Punjab region in the n ...
and Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, Br ...
during the 18th and 19th centuries in the Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
region. Due to its progressive style, it is constantly evolving into many newly developing branches with new contemporary
Contemporary history, in English-language historiography, is a subset of modern history that describes the historical period from about 1945 to the present. In the social sciences, contemporary history is also continuous with, and related t ...
styles. Although Sikh architecture was initially developed within Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
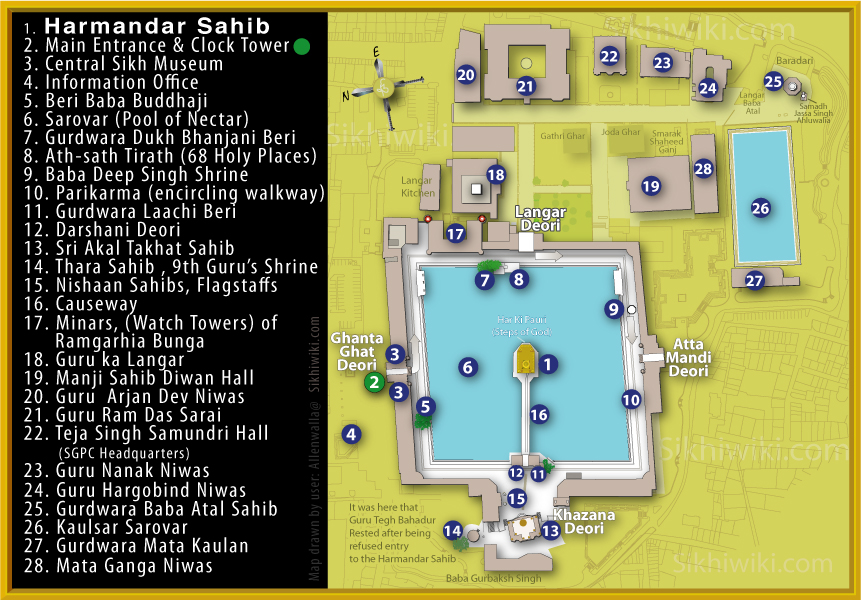
its style has been used in many non-religious buildings due to its beauty. 300 years ago, Sikh architecture was distinguished for its many curves and straight lines; Keshgarh Sahib and the Harmandir Sahib
The Golden Temple is a gurdwara located in Amritsar, Punjab, India. It is the pre-eminent spiritual site of Sikhism. It is one of the Holy place, holiest sites in Sikhism, alongside the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Kartarpur, Pakistan, ...
(Golden Temple
The Golden Temple is a gurdwara located in Amritsar, Punjab, India. It is the pre-eminent spiritual site of Sikhism. It is one of the Holy place, holiest sites in Sikhism, alongside the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Kartarpur, Pakistan, ...
) are prime examples.
Background
Sikh Architecture is heavily influenced by Mughal andIslamic
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
styles. The onion dome, fresco
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting become ...
es, in-lay work, and multi-foil arches, are Mughal influences, more specially from Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the ...
's period, whereas '' chattris'', oriel windows, bracket supported eaves
The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural sty ...
at the string- course, and ornamented friezes
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neithe ...
are derived from elements of Rajput architecture
Rajput architecture is an architectural style associated with the forts and palaces of the many Rajput rulers. Many of the Rajput forts are UNESCO World Heritage Sites and popular tourist attractions.
Rajput architecture represents differen ...
.
 Apart from religious buildings, Sikh architecture includes secular fo rts, ''bungas'' (residential places), palaces, and colleges. The religious structure is called ''
Apart from religious buildings, Sikh architecture includes secular fo rts, ''bungas'' (residential places), palaces, and colleges. The religious structure is called ''gurdwara
A gurdwara or gurudwara () is a place of assembly and place of worship, worship in Sikhism, but its normal meaning is "place of guru" or "home of guru". Sikhism, Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths and rel ...
'' (a place where the Guru dwells). The word ''gurdwara'' is a compound of ''guru'' (guide or master) and ''dwara'' (gateway or seat). So, it has an architectural connotation. Sikh ''gurdwaras'' are generally commemorative buildings connected with the ten gurus in some way, or with places and events of historical significance. Some examples are Gurdwara Dera Sahib (encampment place), in Batala in Gurdaspur district. It was erected in memory of the brief stay of Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is t ...
along with his companions on the occasion of his marriage. Gurdwara Shahid Ganj (Martyrdom Memorial) in Muktsar in Faridkot district commemorates the cremation spot of Sikhs who were killed in a battle between Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; born Gobind Das; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708) was the tenth and last human Sikh gurus, Sikh Guru. He was a warrior, poet, and philosopher. In 1675, at the age of nine he was formally installed as the leader of the ...
and the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of pre ...
in 1705. Gurdwara Shish Mahal (palace of mirrors) in Kiratpur in Ropar district was made where Guru Har Kishan was born.
There are over 500 historical ''gurdwaras''.
Conservation
Many priceless Sikh heritage sites (including their architecture) have been destroyed or altered beyond recognition under the guise of '' "kar seva"'' renovations by various institutions and groups in recent-times, especially vulnerable are Sikh heritage sites in both India and Pakistan according to one scholar, who states it is due to "...the lack of will on the part of the authorities concerned to preserve them". An example of these haphazard and destructive renovations is an incident involving the top section of the historical ''Darshani Deori''gatehouse
A gatehouse is a type of fortified gateway, an entry control point building, enclosing or accompanying a gateway for a town, religious house, castle, manor house, or other fortification building of importance. Gatehouses are typically the most ...
at the Gurdwara Tarn Taran Sahib complex, which was demolished by Kar Seva groups in March 2019. Many groups are rushing to digitize what historical architecture and structures remains for posterity before they are lost, such as Panjab Digital Library. In July 2021, the SGPC launched a project to archive and document the heritage structures of the community and have set up the old doors of the Golden Temple
The Golden Temple is a gurdwara located in Amritsar, Punjab, India. It is the pre-eminent spiritual site of Sikhism. It is one of the Holy place, holiest sites in Sikhism, alongside the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Kartarpur, Pakistan, ...
as museum display when they were replaced. However, around the same time the SGPC denied the importance of a historical Sikh structure discovered underground near the Golden Temple complex, which experts at the Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexander ...
(ASI) deemed as 'historic'. Also, the SGPC made plans to raze a historical building known as ''Guru Ram Das Sarai'', even in the face of criticism of the decision by experts. As many as ninety percent of Sikh heritage monuments have been destroyed in Punjab in the name of renovation and kar seva. Many historical Sikh structures that were destroyed by Kar Seva renovations include original houses of the Sikh gurus and their relatives.
According to the Sikh historian, Harjinder Singh Dilgeer:
According to Sikh scholar, Gurtej Singh, on who is to blame for the plight of Sikh historical heritage: Peter Bance, when evaluating the status of Sikh sites in present-day India, where the majority of Sikhs live today, criticizes the destruction of the originality of 19th-century-era Sikh sites under the guise of "renovation", whereby historical structures are toppled and new buildings take their former place. An example cited by him of sites losing their originality relates to nanakshahi bricks, which are characteristic of Sikh architecture from the 19th century, being replaced by renovators of historical Sikh sites in India by marble and gold. Bance advocates that a grassroots movement advocating for the proper restoration and preservation of historical Sikh sites and their original architecture is necessary, which works together with private enthusiasts and government bodies in-cooperation with one another. Bance further claims that a lack of willpower rather than a lack of funds is responsible for the poor conservation of Sikh historical sites. Bance believes that the way forward in the modern-age to conserve Sikh heritage must be a digital approach, where social networking and technology is utilized to share research, build-up archives, and promote tourism to these sites. Increased tourism has the potential to increase efforts to preserve and restore Sikh heritage sites. Bance uses the Instagram platform to bring light to forgotten Sikh heritage lying in Pakistan with the wider community, using engagements there to generate social awareness and passion. Through his Instagram account, Bance has been contacted by persons interested in restoring Sikh heritage sites, which have allowed them to be connected with others who specialize in this field. Furthermore, he claims that on a weekly-basis hundreds of members of the general public from both India and Pakistan contact him through social media requesting him to visit their locality to document the Sikh heritage located there, as they lack the know-how on how to do this themselves.
Shahid Shabbir is a Pakistani historian and journalist who has documented countless Sikh heritage sites (most often neglected, dilapidated, or abandoned) located in his country, including their extant artwork and architecture. Sikh architecture remains a seldom studied or researched subject.
Gallery
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
File:The Entrance of Janam Asthan-2.jpg, The Gurdwara Janam Asthan in Nankana Sahib, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, commemorates the site where Guru Nanak is believed to have been born. It was rebuilt by the Pakistani Government
File:Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur 04.jpg, Darbar Sahib, gurdwara commemorating Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is t ...
, in Kartarpur, Pakistan
File:Hazur Sahib, Nanded, Maharashtra, September 2012.jpg, Shri Hazoor Sahib is a gurdwara in Nanded
Nanded is a city in Maharashtra state, India. It is the List of cities in Maharashtra, tenth largest city in the state and the List of cities in India by population, seventy-ninth most populated city in India. It is the second largest city in ...
, Maharashtra, India
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the so ...
; is one of the five .
File:Front view of Gurudwara Bangla Sahib, Delhi.jpg, Gurudwara Bangla Sahib
Gurdwara Bangla Sahib () is one of the most prominent Sikh gurdwaras, or Sikh house of worship, in Delhi, India, and known for its association with the eighth Sikh Guru, Guru Har Krishan, as well as the holy pond inside its complex, known as t ...
is one of the most prominent Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
gurdwara in Delhi, India and known for its association with the eighth Sikh Guru
The Sikh gurus (Punjabi language, Punjabi: ਸਿੱਖ ਗੁਰੂ; Hindi: सिख गुरु) are the spiritual masters of Sikhism, who established the religion over the course of about two and a half centuries, beginning in 1469. The year ...
, Guru Har Krishan, as well as the pool inside its complex, known as the " sarovar."
File:Original structure of Gurudwara Sri Sheesh Mahal Sahib, Kiratpur Sahib.jpg, Original structure of Gurudwara Sri Sheesh Mahal Sahib, Kiratpur Sahib
File:Photograph of a Sikh temple at Dacca (Dhaka) in Bengal, India (now Bangladesh), circa 1920–21.jpg, Photograph of a Sikh gurdwara at Dacca (Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; , ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital city, capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh. It is one of the list of largest cities, largest and list o ...
) in Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
(now Bangladesh), circa 1920–21
File:True-colour photograph - Lahore, India (now Pakistan). Sikh Temple in 1914 (Gurdwara Dera Sahib in Lahore).jpg, True-colour photograph of Gurdwara Dera Sahib in Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
, India (now Pakistan), taken in 1914 by Stéphane Passet.
File:True-colour photograph - ‘Interior decoration of the western door of the Darbar Sahib (Golden Temple)’, 15 January 1914.jpg, True-colour photograph titled ‘Interior decoration of the western door of the Darbar Sahib’, taken on 15 January 1914 by Stéphane Passet.
See also
* Sikh architecture in Karnataka * Nanak Shahi bricks * Sikh art and culture * Sikh scriptures * History of Sikhism * Sikh Ajaibghar * Mehdiana SahibReferences
Bibliography
*Arshi, Pardeep Singh, ''Sikh Architecture in the Punjab'', Intellectual Pub. House, 1986. *Brown, Percy, Indian Architecture (Islamic Period), Fifth Edition, 1965, Bombay. *Brown, Percy, Indian Architecture (Hindu and Buddhist Period), Fifth Edition, 1965, Bombay. *Singh, Mehar, ''Sikh Shrines In India'', Publications Division, Government of India, 1974, New Delhi. *Singh, Darshan, ''The Sikh art and architecture'', Dept. of Guru Nanak Sikh Studies, Panjab University, 1987. *Marg, Volume XXX, Number 3, June 1977, Bombay.Further reading
* *External links
*Article on Sikh Architecture
{{Architecture of India Architectural styles Indian architectural history Pakistani architectural history