|
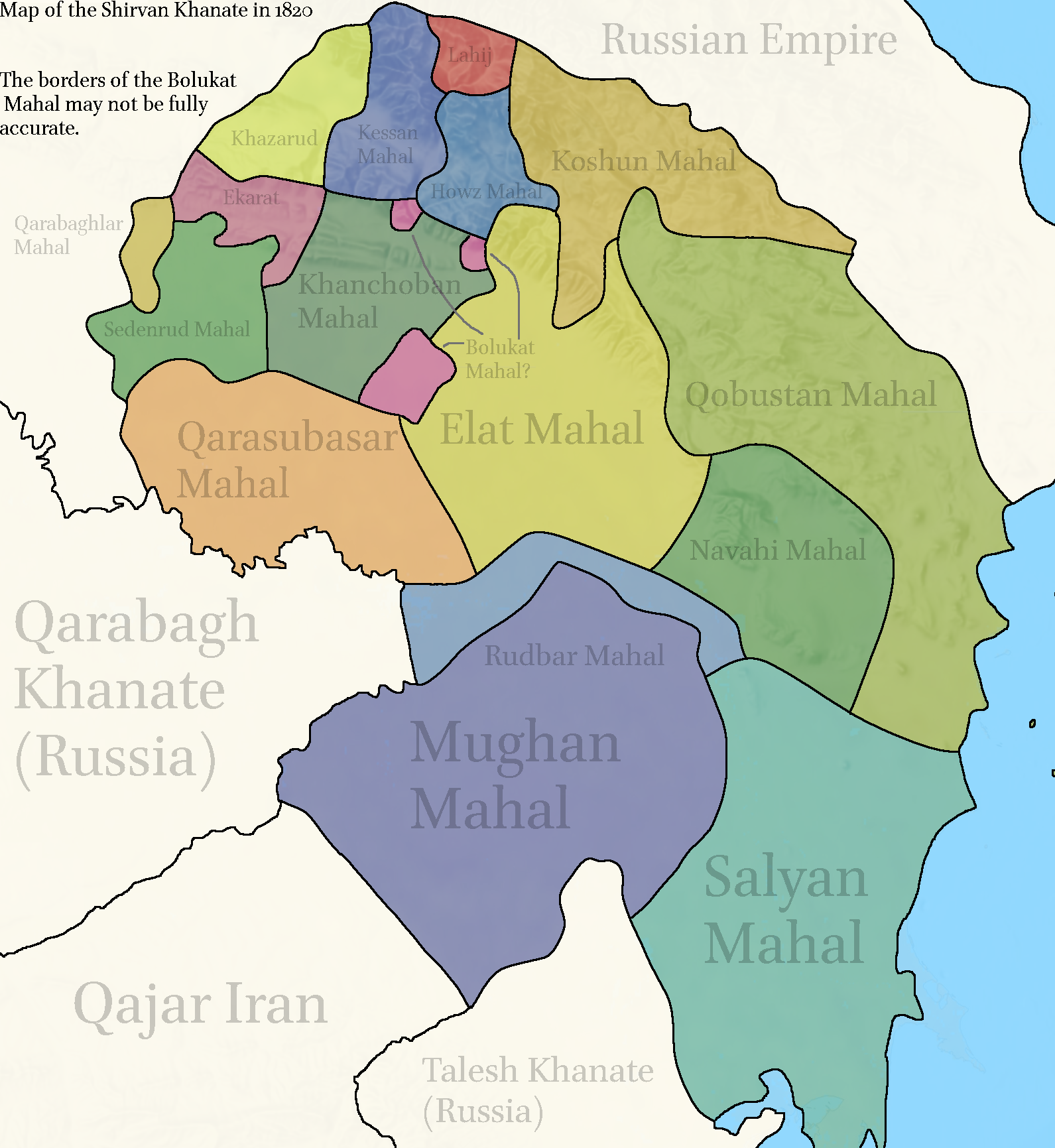
Shirvan Khanate
Shirvan Khanate () was a Caucasian khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the Shirvan region from 1761 to 1820. Background Under the Safavid dynasty of Iran, Shirvan was a leading silk manufacturer and its principal city, Shamakhi, became an important place for trade. In 1724, most of Shirvan was annexed to the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of Constantinople. In 1734, the Iranian military leader Nader recovered Shirvan and installed Mohammad Mehdi Khan as its '' beglarbegi'' (governor-general). The following year, Mohammad Mehdi Khan was killed by rebellious dignitaries of the province. They had been incited by the governor of Darband, Morad-Ali Soltan Ostajlu. Mohammad Qasem Beg, who was a prominent dignitary of Shirvan and Nader's ''ishikaghasi-bashi'' (chamberlain), successfully appealed to Nader to pardon Shirvan. In 1735, Nader had the inhabitants of Shamakhi resettled in New Shamakhi ( Aqsu), situated 18 miles north of the Kur River. He then installed as Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zand Dynasty
The Zand dynasty () was an Iranian dynasty, founded by Karim Khan Zand (1751–1779) that initially ruled southern and central Iran in the 18th century. It later expanded to include much of the rest of contemporary Iran (except for the provinces of Baluchestan and Khorasan) as well as parts of Iraq. The lands of present-day Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia were controlled by khanates which were de jure part of the Zand realm, but the region was de facto autonomous. The island of Bahrain was also held for the Zands by the autonomous Al-Mazkur sheikhdom of Bushehr. The reign of its most important ruler, Karim Khan, was marked by prosperity and peace. With its capital at Shiraz, arts and architecture flourished under Karim Khan's reign, with some themes in architecture being revived from nearby sites of pre-Islamic Achaemenid (550–330 BC) and Sasanian (224–651 AD) eras. The tombs of the medieval Persian poets Hafez and Saadi Shirazi were also renovated by Karim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shia Islam
Shia Islam is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political Succession to Muhammad, successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (Imamah (Shia doctrine), imam). However, his right is understood to have been usurped by a number of Companions of the Prophet, Muhammad's companions at the meeting of Saqifa where they appointed Abu Bakr () as caliph instead. As such, Sunni Muslims believe Abu Bakr, Umar (), Uthman () and Ali to be 'Rashidun, rightly-guided caliphs' whereas Shia Muslims only regard Ali as the legitimate successor. Shia Muslims assert imamate continued through Ali's sons Hasan ibn Ali, Hasan and Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn, after whom different Shia branches have their own imams. They revere the , the family of Muhammad, maintaining that they possess divine knowledge. Shia holy sites include the Imam Ali Shrine, shrine of Ali in Naj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kura (South Caucasus River)
The Kura, also known in Georgian as Mtkvari ( ), is an east-flowing transboundary river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus, while its main tributary, the Aras, drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, the Kura flows through to Georgia, then into Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and finally enters the Caspian Sea. The total length of the river is . People have inhabited the Caucasus region for thousands of years and first established agriculture in the Kura Valley over 4,500 years ago. Large, complex civilizations eventually grew on the river, but by 1200 CE most were reduced to ruin by natural disasters and foreign invaders. The increasing human use, and eventual damage, of the watershed's forests and grasslands, contributed to a rising intensity of floods through the 20th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbent
Derbent, also historically known as Darband, or Derbend, is the southernmost city in Russia. It is situated along the southeastern coast of the Dagestan, Republic of Dagestan, occupying the narrow gateway between the Caspian Sea and the Caucasus Mountains, and connecting the Eurasian Steppe to the north and the Iranian Plateau to the south. Derbent covers an area of with a population of roughly 120,000 residents. Derbent is considered the oldest city in Russia, with historical documentation dating to the 8th century BC, making it List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Due to its strategic location, over the course of history, the city changed ownership many times, particularly among the History of Iran, Persian, Umayyad Caliphate, Arab, Mongol Empire, Mongol, Timurid Empire, Timurid, and Shirvanshah, Shirvan kingdoms. In the early 19th century, the city came under control of the Russian Empire through the Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beglarbegi
''Beylerbey'' (, meaning the 'commander of commanders' or 'lord of lords’, sometimes rendered governor-general) was a high rank in the western Islamic world in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, from the Anatolian Seljuks and the Ilkhanids to Safavid Iran and the Ottoman Empire. Initially designating a commander-in-chief, it eventually came to be held by senior provincial governors. In Ottoman usage, where the rank survived the longest, it designated the governors-general of some of the largest and most important provinces, although in later centuries it became devalued into a mere honorific title. The title is originally Turkic and its equivalents in Arabic were ''amir al-umara'', and in Persian, ''mir-i miran''. Early use The title originated with the Seljuks, and was used in the Sultanate of Rum initially as an alternative for the Arabic title of ''malik al-umara'' ("chief of the commanders"), designating the army's commander-in-chief. Among the Mongol Ilkha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar (; 6 August 1698 or 22 October 1688 – 20 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian history, ruling as shah of Iran (Persia) from 1736 to 1747, when he was assassinated during a rebellion. He fought numerous campaigns throughout the Middle East, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and South Asia, emerging victorious from the battles of Herat, Mihmandust, Murche-Khort, Kirkuk, Yeghevārd, Khyber Pass, Karnal, and Kars. Because of his military genius,The Sword of Persia: Nader Shah, from Tribal Warrior to Conquering Tyrant "Nader commanded the most powerful military force in Asia, if not the world" (quote from publisher's summary) some historians have described him as the '' |
Treaty Of Constantinople (1724)
The Treaty of Constantinople (,) Russo-Ottoman Treaty or Treaty of the Partition of Persia (''Iran Mukasemenamesi'') was a treaty concluded on 24 June 1724 between the Ottoman Empire and the Russian Empire, dividing large portions of the territory of mutually neighbouring Safavid Iran between them. The Russians and the Ottomans were engaged in a race to occupy more Iranian territories and were about to engage in a war over the occupation of Gandjeh when France intervened. In the Russo-Persian War (1722–1723), Russia had managed to conquer swaths of Safavid Iran's territories in the North Caucasus, Transcaucasia, and northern mainland Iran, while the Ottoman Turks had invaded and conquered all Iranian territories in the west, most notably Georgia and Armenia. Still, the news of a Russo-Iranian accord that would settle the 1722–1723 Russo-Iranian War precipitated a crisis between Imperial Russia and Ottoman Empire, who openly stated that it would not permit any other power to es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safavid Iran
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the beginning of History of Iran, modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires. The Safavid List of monarchs of Persia, Shāh Ismail I, Ismā'īl I established the Twelver denomination of Shia Islam, Shīʿa Islam as the Safavid conversion of Iran to Shia Islam, official religion of the empire, marking one of the most important turning points in the history of Islam. An Iranian dynasty rooted in the Sufi Safavid order founded by sheikhs claimed by some sources to be of Kurds, Kurdish origin, it heavily intermarried with Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman, Georgians, Georgian, Circassians, Circassian, and Pontic Greeks, Pontic GreekAnthony Bryer. "Greeks and Türkmens: The Pontic Exception", ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 29'' (1975), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safavid Dynasty
The Safavid dynasty (; , ) was one of Iran's most significant ruling dynasties reigning from Safavid Iran, 1501 to 1736. Their rule is often considered the beginning of History of Iran, modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires. The Safavid List of monarchs of Persia, Shah Ismail I established the Twelver denomination of Shia Islam, Shi'a Islam as the Safavid conversion of Iran to Shia Islam, official religion of the Persian Empire, marking one of the most important turning points in the history of Islam. The Safavid dynasty had its origin in the Safavid order, Safavid Sufi order, which was established in the city of Ardabil in the Azerbaijan (Iran), Iranian Azerbaijan region. It was an Iranian dynasty of Kurdish people, Kurdish origin, but during their rule they intermarried with Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman, Georgians, Georgian, Circassians, Circassian, and Pontic Greeks, Pontic GreekAnthony Bryer. "Greeks and Türkmens: The Pontic Exception", ''Dumbarton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirvan
Shirvan (from ; ; Tat: ''Şirvan'') is a historical region in the eastern Caucasus, as known in both pre-Islamic Sasanian and Islamic times. Today, the region is an industrially and agriculturally developed part of the Republic of Azerbaijan that stretches between the western shores of the Caspian Sea and the Kura River, centered on the Shirvan Plain. History Etymology Vladimir Minorsky believes that names such as Sharvān (Shirwān), Lāyzān and Baylaqān are Iranian names from the Iranian languages of the coast of the Caspian Sea. There are several explanations about this name: * Shirvan or Sharvan are corrupted forms of the word "Shahrbān" () which means "the governor". The word "Shahrban" has been used since Achaemenian Dynasty as "Xshathrapawn" (satrap) to refer to different states of the kingdom. * Shervan in Persian means cypress tree (the same as 'sarv' in Middle Persian and in New Persian, as well as in ArabicDehkhoda dictionary). It is also used as a male n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanates Of The Caucasus
The khanates of the Caucasus, also known as the Azerbaijani khanates, Persian khanates, or Iranian Khanates, were various administrative units in the South Caucasus governed by a hereditary or appointed ruler under the official rule of Iran. The title of the ruler was khan, which was identical to the Ottoman rank of pasha. Following the assassination of Nader Shah () in 1747, internal chaos erupted in Iran, particularly in the South Caucasus, where semi-independent khanates emerged as a result of the lack of a centralized government. The khans neither had territorial or religious unity, nor an ethnic/national identity. They were mostly interested in preserving their positions and income. In Persian, the khanates were historically referred to as ''ulka'' or ''tuman'', governed by a ''hakem'' (governor). The English word "khanate" is a translation of the Russian word ''khanstvo'' and the Armenian word ''khanut'iun''. The shah could promote a ''hakem's'' status to that of a khan, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |