|
Shabad Hazare
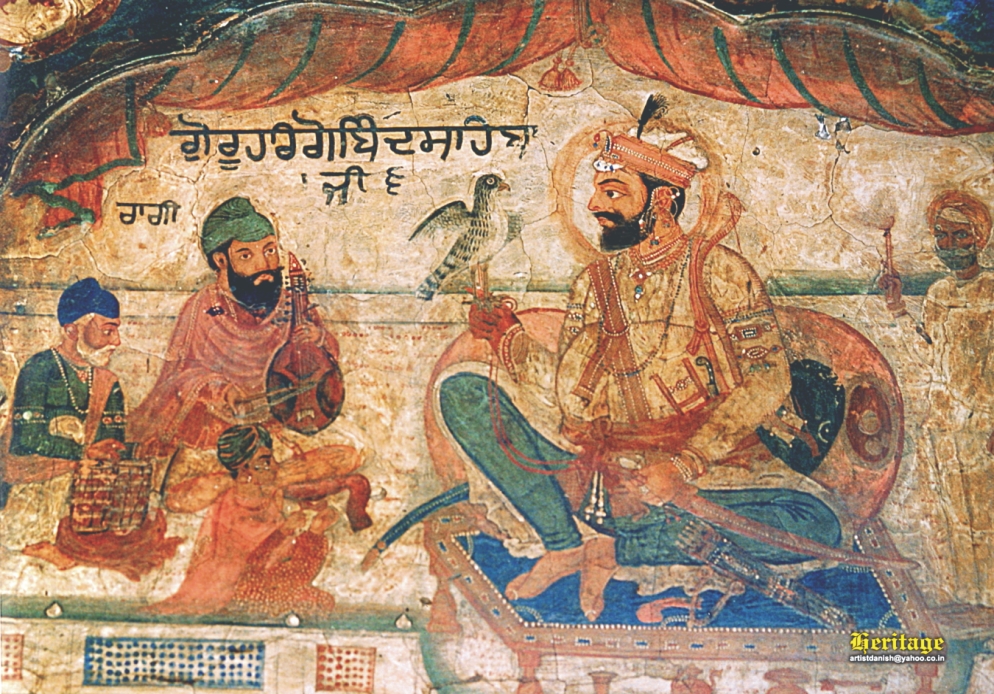
Shabad Hazare, also known as Sabad Patshahi 10 (, pronunciation: , also known as the Shabad Hazare Padishah), under the title Shabad (), are ten religious hymns (or '' shabads'') composed by Guru Gobind Singh that are present in Dasam Granth. These hymns have comments on ritualistic practices in Sanyas, Jogis and Bairagis, and also against any form of idolatry, human or deity worship. Description These hymns are primarily composed in Braj and Punjabi languages, written in Gurmukhi, with plentiful use of Sanskrit words, except sixth hymn, which is composed in Punjabi with some Persian words. Excluding the sixth, all other hymns have three ''Padash'' and ''Rahau'' (The Pause) placed in the beginning of the Shabads. Sixth hymn Mittar Pyare nu was composed at Machhiwara whereas others were composed at Anandpur Sahib. The ordering of hymns was given by Bhai Mani Singh. The shabads are similar in theme to Vaishnavist poetry regarding avatars. The only six Ragas present in Das ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religions and among the largest in the world with about 25–30million adherents, known as Sikhs. Sikhism developed from the spiritual teachings of Guru Nanak (1469–1539), the faith's first guru, and the nine Sikh gurus who succeeded him. The tenth guru, Guru Gobind Singh (1666–1708), named the Guru Granth Sahib, which is the central religious scripture in Sikhism, was their successor. This brought the line of human gurus to a close. Sikhs regard the Guru Granth Sahib as the 11th and eternally living guru. The core beliefs and practices of Sikhism, articulated in the Guru Granth Sahib and other Sikh scriptures, include faith and meditation in the name of the one creator (''Ik Onkar''), the divine unity and equality of all humankind, engaging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machhiwara
Machhiwara is one of the developing cities in the Samrala tehsil of Ludhiana district in the Indian state of Punjab. Machhiwara is famous for Gurudwara Sri Charan Kanwal Sahib associated with Guru Gobind Singh ji and named after the Guru's feet that are compared to the lotus flower. The Ghorewaha were given the title of Mian by Emperor Jehangir. During Emperor Akbar's time, the Ghorewaha Raja was Rana Udho II, The Raja of Machhiwara, Rana Udho actively assisted Emperor Akbar in his fight for the Delhi Throne, he captured the rebellious Bairam Khan and subsequently the Raja was allowed to retain the Jagir of Rahon worth 750 villages. The division of the Ghorewaha country took place after Rana Udho's death when all the Branches were Hindu, including that of the famed Rai Rup Chand. The principal Jagirs were taken, Rahon by the Tikka and Jadla by Bhoj Singh, who returned from Jaipur. History Machhiwara name came from ''machhi'' (fish) + ''wara'' (ground). Satluj River runs 13 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilaval
Bilaval or Bilawal () is a raga and the basis for the eponymous ''thaat'' (musical mode) in Hindustani classical music. Raga Bilaval is named after Veraval, Gujarat. Bilaval has been the standard for North Indian music since the early 19th century. Its tonal relationships are comparable to the Western music C major scale. Bilaval appears in the '' Ragamala'' as a ragini of Bhairav but today it is the head of the Bilaval thaat. The Ragamala names Bilaval as a Putra (son) of Bhairav but no relationship between these two ragas are made today. Bilaval is a morning raga that is intended to be sung with a feeling of deep devotion and repose and is often performed during the hot months. The Bilaval is equivalent to the Carnatic raga melakarta, Sankarabharanam, as well as the Western Ionian mode (major scale), and contains the notes S R G M P D N S'. The pitches of Bilaval thaat are all ' (natural). Flat () or sharp () pitches always occur regarding the interval pattern in Bilav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilang
Tilang is a raga in Indian classical music, that belongs to the Khamaj Thaat. Scale * Arohana (ascending scale): * Avarohana (descending scale): This raga has a lowered seventh, () in the descending scale. Its defining characteristics are: , . Some performers add a '' Re'' to create the following pattern: . Vādī and Samvādī * Vadi : Ga * Samvadi : Ni In Carnatic music This raga originated in Hindustani classical music and has been taken into Carnatic music.''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications It is derived from the 28th Melakarta (parent scale) Harikambhoji. It is an audava-audava raga (pentatonic asymmetrical scale) with the following structure. * Arohana: * Avarohana: Compositions *''Shree Ganesha Charanam'' by Papanasam Sivan *''Ramakrishnaru Manege'', ''Tarakka Bindige'' and ''Dasara Nindisa Beda'' by Purandara Dasa *''Satyavantara Sangaviralu'' by Kanaka Dasa *''Shanthi Nilava Vendum'' by Sethumadava Rao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khayal
Khyal or Khayal (ख़याल / خیال) is a major form of Hindustani classical music in the Indian subcontinent. Its name comes from a Persian language, Persian/Arabic language, Arabic word meaning "imagination". Khyal is associated with romantic poetry, and allows the performer greater freedom of expression than dhrupad and is sung with the tabla instead of the pakhavaj. In khyal, ragas are extensively ornamented, and the style calls for more technical virtuosity. Etymology () is an Urdu word of Arabic origin which means "imagination, thought, ideation, meditation, reflection". Hence khyal connotes the idea of a song that is imaginative and creative in either its nature or execution. The word entered India through the medium of the Persian language, Persian language. Just as the word reflects ideas of imagination and imaginative composition, the musical form is imaginative in conception, artistic and decorative in execution and romantic in appeal.Francis Joseph Steingass� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
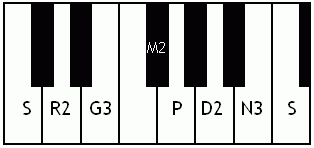
Kalyani (raga)
Kalyani is a melakarta raga (parent musical scale) in the Carnatic music. It is the prati madhyama equivalent of the raga Sankarabharanam. It was called Kalyan but is now more popularly called Yaman in Hindustani Music. Its Western equivalent is the Lydian mode. Kalyani in Carnatic music In South Indian weddings it is a very prominently played raga. The word ''Kalyani'' means ''she who causes auspicious things''. It is the 65th melakarta raga under the Katapayadi sankhya. It is also called ''Mechakalyani''. The notes for Kalyani are S R2 G3 M2 P D2 N3. Kalyani is the first Prathi Madhyama raga that was ever discovered. It was obtained by the process of Graha Bhedam or modal shift of tonic of the ancient Shadja Grama. Specifics on this raga Kalyani has scope for elaborate alapana. One should not remain too long on panchamam (pa) or alternate between shadjamam and panchamam too frequently. Kalyani is prominently known among the public. It is often performed at the begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorath Raga
Sorath is an India musical raga (musical mode) that appears in the Sikh tradition from northern India and is part of the Sikh holy scripture called Sri Guru Granth Sahib. Every raga has a strict set of rules which govern the number of notes that can be used; which notes can be used; and their interplay that has to be adhered to for the composition of a tune. In the Guru Granth Sahib, the Sikh holy Granth (book) there are a total of 60 raga compositions and this raga is the twenty fifth raga to appear in the series. The composition in this raga appear on a total of 65 pages from page numbers 595 to 660. Raga Sorath belongs to the Khamaj thaat. Besides Guru Nanak, Sorath was used by Guru Amar Das, Guru Ram Das, Guru Arjan and Guru Tegh Bahadar for a total of 150 hymns plus numerous slokas. Raag Sorath (ਸੋਰਠਿ) – Sorath conveys the feeling of having such a strong belief in something that you want to keep repeating the experience. In fact this feeling of certainty is so s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramkali
Raga Ramkali is a raga in Hindustani classical music and can be themed around soothing things a man would say to please a discontent wife, it is an early morning raga belonging to Bhairav Thaat. In this raga, as in Bhairav, Rishabh and Dhaivat are Komal( flat), but the Teevra and the flat nishad are added. The vadi-samvadi are Pancham and Shadja. The aroha is S r G M P, G M d N S' and the avroha is S' N d P m P, d (N)d P, G M r S. Flat nishad (seventh degree) and sharp madhyama (fourth degree) are used often. Ramkali also appears in Sikh tradition in North India and is a part of Sikh Scripture Sri Guru Granth Sahib Ji. Another form of this Raga present in Sri Guru Granth Sahib Ji isRaga Ramkali Dakhni. Theory Arohana and avarohana Arohana: Avarohana: Vadi : Pa Samavadi : Sa Pakad In Hindustani music, a ''pakad'' (Hindi: पकड़) is a generally accepted musical phrase (or set of phrases) thought to encapsulate the essence of a particular raga. The pakad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh Music
Sikh music, also known as Gurbani Sangeet (; meaning ''music of'' ''the speech of wisdom'')'','' and as Gurmat Sangeet (; meaning ''music of the counsel or tenets of the Guru'')'','' or even as Shabad Kirtan (), is the classical music style that is practised within Sikhism. It exists in institutional, popular, and folk traditions, forms, and varieties. Three types of Sikh musicians are rababis, ragis, and dhadhis. Sikh music exists in various melodic modes, musical forms, styles, musicians, and performance contexts. Terminology Whilst the term ''Gurmat Sangeet'' has come to be used as a name for all Sikh ''kirtan'' performed as per the prescribed ragas found within the Sikh scripture, Inderjit Kaur believes a more fitting term for the raga genre is "rāg-ādhārit shabad kīrtan". She further believes that the Sikh musicology as a whole should be referred to as "''gurmat sangīt shāstar/vigyān''", of which, raga kirtan is a genre found within. History Period of the Sikh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fountain
A fountain, from the Latin "fons" ( genitive "fontis"), meaning source or spring, is a decorative reservoir used for discharging water. It is also a structure that jets water into the air for a decorative or dramatic effect. Fountains were originally purely functional, connected to springs or aqueducts and used to provide drinking water and water for bathing and washing to the residents of cities, towns and villages. Until the late 19th century most fountains operated by gravity, and needed a source of water higher than the fountain, such as a reservoir or aqueduct, to make the water flow or jet into the air. In addition to providing drinking water, fountains were used for decoration and to celebrate their builders. Roman fountains were decorated with bronze or stone masks of animals or heroes. In the Middle Ages, Moorish and Muslim garden designers used fountains to create miniature versions of the gardens of paradise. King Louis XIV of France used fountains in the Gard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragas
A raga ( ; , ; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a melodic mode. It is central to classical Indian music. Each raga consists of an array of melodic structures with musical motifs; and, from the perspective of the Indian tradition, the resulting music has the ability to "colour the mind" as it engages the emotions of the audience. Each raga provides the musician with a musical framework within which to improvise. Improvisation by the musician involves creating sequences of notes allowed by the raga in keeping with rules specific to the raga. Ragas range from small ragas like Bahar and Sahana that are not much more than songs to big ragas like Malkauns, Darbari and Yaman, which have great scope for improvisation and for which performances can last over an hour. Ragas may change over time, with an example being Marwa, the primary development of which has been going down into the lower octave, in contrast with the traditional middle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole Para Brahman, supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. Its followers are called Vaishnavites or ''Vaishnava''s (), and it includes sub-sects like Krishnaism and Ramanandi Sampradaya, Ramaism, which consider Krishna and Rama as the supreme beings respectively. According to a 2020 estimate by The World Religion Database (WRD), hosted at Boston University’s Institute on Culture, Religion and World Affairs (CURA), Vaishnavism is the largest Hindu sect, constituting about 399 million Hindus. The ancient emergence of Vaishnavism is unclear, and broadly hypothesized as a History of Hinduism, fusion of various regional non-Vedic religions with worship of Vishnu. It is considered a merger of several popular non-Vedic theistic traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |