|
Sesquioxides
A sesquioxide is an oxide of an element (or radical), where the ratio between the number of atoms of that element and the number of atoms of oxygen is 2:3. For example, aluminium oxide and phosphorus(III) oxide are sesquioxides. Many sesquioxides contain a metal in the +3 oxidation state and the oxide ion , e.g., aluminium oxide , lanthanum(III) oxide and iron(III) oxide . Sesquioxides of iron and aluminium are found in soil. The alkali metal sesquioxides are exceptions because they contain both peroxide and superoxide ions, e.g., rubidium sesquioxide is formulated . Sesquioxides of metalloids and nonmetals are better formulated as covalent, e.g. boron trioxide , dinitrogen trioxide and phosphorus(III) oxide ; chlorine trioxide and bromine trioxide do not have oxidation state +3 on the halogen. Many transition metal oxides crystallize in the corundum structure type, with space group Rc. Sesquioxides of rare earth elements crystalize into one or more of three crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidium Sesquioxide
Rubidium sesquioxide is a chemical compound with the formula or more accurately . In terms of oxidation states, Rubidium in this compound has a nominal charge of +1, and the oxygen is a mixed peroxide () and superoxide () for a structural formula of . It has been studied theoretically as an example of a strongly correlated material. The compound was predicted to be a rare example of a ferromagnetic Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagne ... compound that is magnetic due to a p-block element, and a half-metal that was conducting in the minority spin band. However, while the material does have exotic magnetic behavior, experimental results instead showed an electrically insulating magnetically frustrated system. also displays a Verwey transition where charge ordering ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Trioxide
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty. It is also called boric oxide or boria. It has many important industrial applications, chiefly in ceramics as a flux for glazes and enamels and in the production of glasses. Structure Boron trioxide has three known forms, one amorphous and two crystalline. Amorphous form The amorphous form (g-) is by far the most common. It is thought to be composed of boroxol rings which are six-membered rings composed of alternating 3-coordinate boron and 2-coordinate oxygen. Because of the difficulty of building disordered models at the correct density with many boroxol rings, this view was initially controversial, but such models have recently been constructed and exhibit properties in excellent agreement with experiment. It is now recognized, from experimental and theoretical studies, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
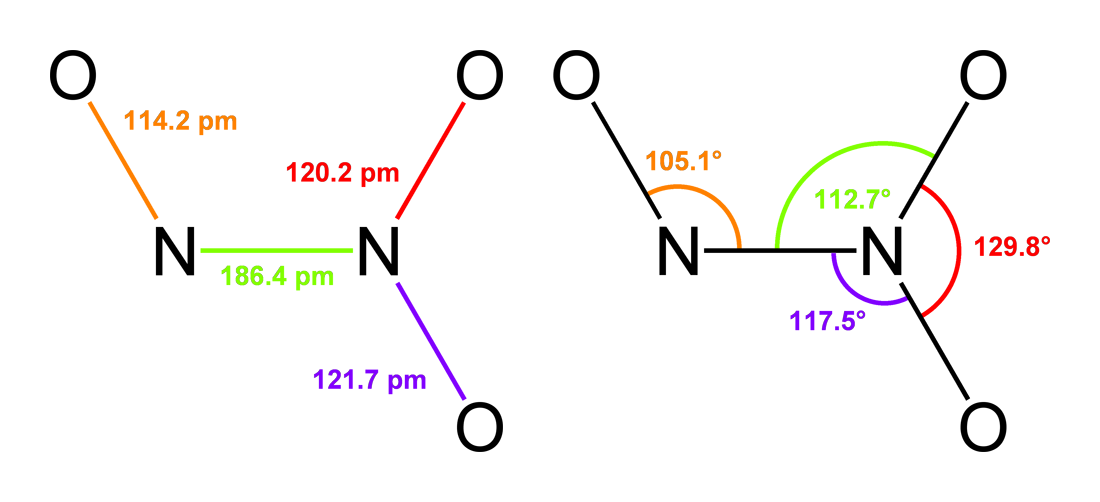
Dinitrogen Trioxide
Dinitrogen trioxide (also known as nitrous anhydride) is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a nitrogen oxide. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21°C (−6°F): : + Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures (i.e., in the liquid and solid phases). In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color. At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with ''KD'' = 193 kPa (25°C). This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical . Structure and bonding Dinitrogen trioxide molecule contains an N–N bond. One of the numerous resonant structures of the molecule of dinitrogen trioxide is , which can be described as a nitroso group attached to a nitro group by a single bond between the two nitrogen atoms. This isomer is considered as the "anhydride" of the unstable nitrous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine Trioxide
Dibromine trioxide is the chemical compound composed of bromine and oxygen with the formula Br2O3. It is an orange solid that is stable below −40 °C. It has the structure Br−O−BrO2 (bromine bromate). It was discovered in 1993. The bond angle of Br−O−Br is 111.7°, the bond angle of O−Br=O is 103.1°, and the bond angle of O=Br=O is 107.6°. The Br−OBrO2 bond length is 1.845 Å, the O−BrO2 bond length is 1.855 Å and the Br=O bond length is 1.612 Å. Reactions Dibromine trioxide can be prepared by reacting a solution of bromine in dichloromethane with ozone at low temperatures. It disproportionates in alkali In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The a ... solutions to Br and BrO. References Bromine(V) compounds Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(III) Oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . It occurs in nature as the mineral hematite, which serves as the primary source of iron for the steel industry. It is also known as red iron oxide, especially when used in pigments. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (), which also occurs naturally as the mineral magnetite. Iron(III) oxide is often called rust, since rust shares several properties and has a similar composition; however, in chemistry, rust is considered an ill-defined material, described as hydrous ferric oxide. Ferric oxide is readily attacked by even weak acids. It is a weak oxidising agent, most famously when reduced by aluminium in the thermite reaction. Structure can be obtained in various polymorphs. In the primary polymorph, α, iron adopts octahedral coordination geometry. That is, each Fe center is bound to six oxygen ligands. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum(III) Oxide
Lanthanum(III) oxide, also known as lanthana, chemical formula , is an inorganic compound containing the rare earth element lanthanum and oxygen. It is used in some ferroelectric materials, as a component of optical materials, and is a feedstock for certain catalysts, among other uses. Properties Lanthanum oxide is a white solid that is insoluble in water, but dissolves in acidic solutions. absorbs moisture from air, converting to lanthanum hydroxide. Lanthanum oxide has p-type semiconducting properties and a band gap of approximately 5.8 eV. Its average room temperature resistivity is 10 kΩ·cm, which decreases with an increase in temperature. has the lowest lattice energy of the rare earth oxides, with very high dielectric constant ε = 27. Structure At low temperatures, has an A- hexagonal crystal structure. The metal atoms are surrounded by a 7 coordinate group of atoms, the oxygen ions are in an octahedral shape around the metal atom and there is one oxygen ion above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Earth Elements
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. The term "rare-earth" is a misnomer because they are not actually scarce, but historically it took a long time to isolate these elements. They are relatively plentiful in the entire Earth's crust (cerium being the 25th-most-abundant element at 68 parts per million, more abundant than copper), but in practice they are spread thinly as trace impurities, so to obtain rare earths at usable purity requires processing enormous amounts of raw ore at great expense; thus the name "rare" earths. Scandium and yttrium are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus(III) Oxide
Phosphorus trioxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula P4O6. Although the molecular formula suggests the name tetraphosphorus hexoxide, the name phosphorus trioxide preceded the knowledge of the compound's molecular structure, and its usage continues today. This colorless solid is structurally related to adamantane. It is formally the anhydride of phosphorous acid, H3PO3, but cannot be obtained by the dehydration of the acid. A white solid that melts at room temperature, it is waxy, crystalline and highly toxic, with garlic odor. Preparation It is obtained by the combustion of phosphorus in a limited supply of air at low temperatures. :P4 + 3 O2 → P4O6 By-products include red phosphorus suboxide. Chemical properties Phosphorus trioxide reacts with water to form phosphorous acid, reflecting the fact that it is the anhydride of that acid. : P4O6 + 6 H2O → 4 H3PO3 It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form H3PO3 and phosphorus trichloride. : P4O6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several Aluminium oxide (compounds), aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, ALOX or alundum in various forms and applications and alumina is refined from bauxite. It occurs naturally in its crystalline Polymorphism (materials science), polymorphic phase (matter), phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire,which have an alumina content approaching 100%. Al2O3 is used as feedstock to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. Natural occurrence Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystallinity, crystalline form of aluminium oxide. ruby, Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium, and chromium. It is a rock (geology), rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparency and translucency, transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gemstone, gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, Sapphire#Padparadscha, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange. The name "corundum" is derived from the Tamil language, Tamil-Dravidian languages, Dravidian word ''kurundam'' (ruby-sapphire) (appearing in Sanskrit as ''kuruvinda''). Because of corundum's hardness (pure corundum is defined to have 9.0 on the Mohs scale), it can scratch almost all other minerals. Emery (rock), Emery, a variety of corundum w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |