|
Sequential High-dose Chemotherapy
Sequential high-dose chemotherapy is a chemotherapy regimen consisting of several (2 to 4) sequential monochemotherapies with only one chemotherapeutic agent per course. The idea behind this approach is that when using single-agent chemotherapy, the doctor can easily escalate the dose of the drug to the maximum tolerable dose by the patient, avoiding additive hematological toxicity from chemotherapeutic combinations, and thus improving efficacy. It is mostly used as consolidation therapy for relapsed or refractory lymphomas and relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma, after DHAP induction. There is also an ongoing trial of this approach in multiple myeloma. Dosing regimen Depending on the patient's performance status, his/her ability to tolerate chemotherapy, the type of lymphoma, the stage of disease and different prognostic factors, one or more courses of the full sequence can be omitted or dose reduced. After completion of the sequence, the patient will usually undergo pre- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy Regimen
A chemotherapy regimen is a regimen for chemotherapy, defining the drugs to be used, their dosage, the frequency and duration of treatments, and other considerations. In modern oncology, many regimens combine several chemotherapy drugs in combination chemotherapy. The majority of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy are cytostatic, many via cytotoxicity. A fundamental philosophy of medical oncology, including combination chemotherapy, is that different drugs work through different mechanisms, and that the results of using multiple drugs will be synergistic to some extent. Because they have different dose-limiting adverse effects, they can be given together at full doses in chemotherapy regimens. The first successful combination chemotherapy was MOPP, introduced in 1963 for lymphomas. The term " induction regimen" refers to a chemotherapy regimen used for the initial treatment of a disease. A " maintenance regimen" refers to the ongoing use of chemotherapy to reduce the cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy regimen, regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a cure, curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim only to prolong life or to Palliative care, reduce symptoms (Palliative care, palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''oncology#Specialties, medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' now means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to induce DNA damage (naturally occurring), DNA damage (so that DNA repair can augment chemotherapy). This meaning excludes the more-selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). Lymphomas, leukemias and myelomas are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for common types of non-Hodgkin lymphomas include autoimmune diseases, HIV/AIDS, infection with human T-lymphotropic virus, immunosuppressant medicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, non-painful lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Persons affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying Reed–Sternberg cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DHAP (chemotherapy)
DHAP in context of chemotherapy is an acronym for chemotherapy regimen that is used for remission induction in cases of relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma. It is usually given for 2-3 courses, then followed by high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation. In combination with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab (Rituxan, Mabthera) it is called R-DHAP or DHAP-R. DHAP regimen consists of: # Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody, directed at B-cell surface antigen CD20 # Dexamethasone, a glucocorticoid hormone # High-dose Ara-C - cytarabine, an antimetabolite; # Platinol (cisplatin), a platinum-based antineoplastic, also an alkylating antineoplastic agent An alkylating antineoplastic agent is an alkylating agent used in cancer treatment that attaches an alkyl group (CnH2n+1) to DNA. Since cancer cells, in general, proliferate faster and with less error-correcting than healthy cells, cancer cells a .... Dosing regimen Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibody, antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, Kidney failure, renal insufficiency, and infections may occur. Complications may include hypercalcemia and amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, age and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma is the result of a multi-step malignant transformation, and almost universally originates from the pre-malignant stage monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). As MGUS evolves into MM, another pre-stage of the disease is reached, known as Smouldering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
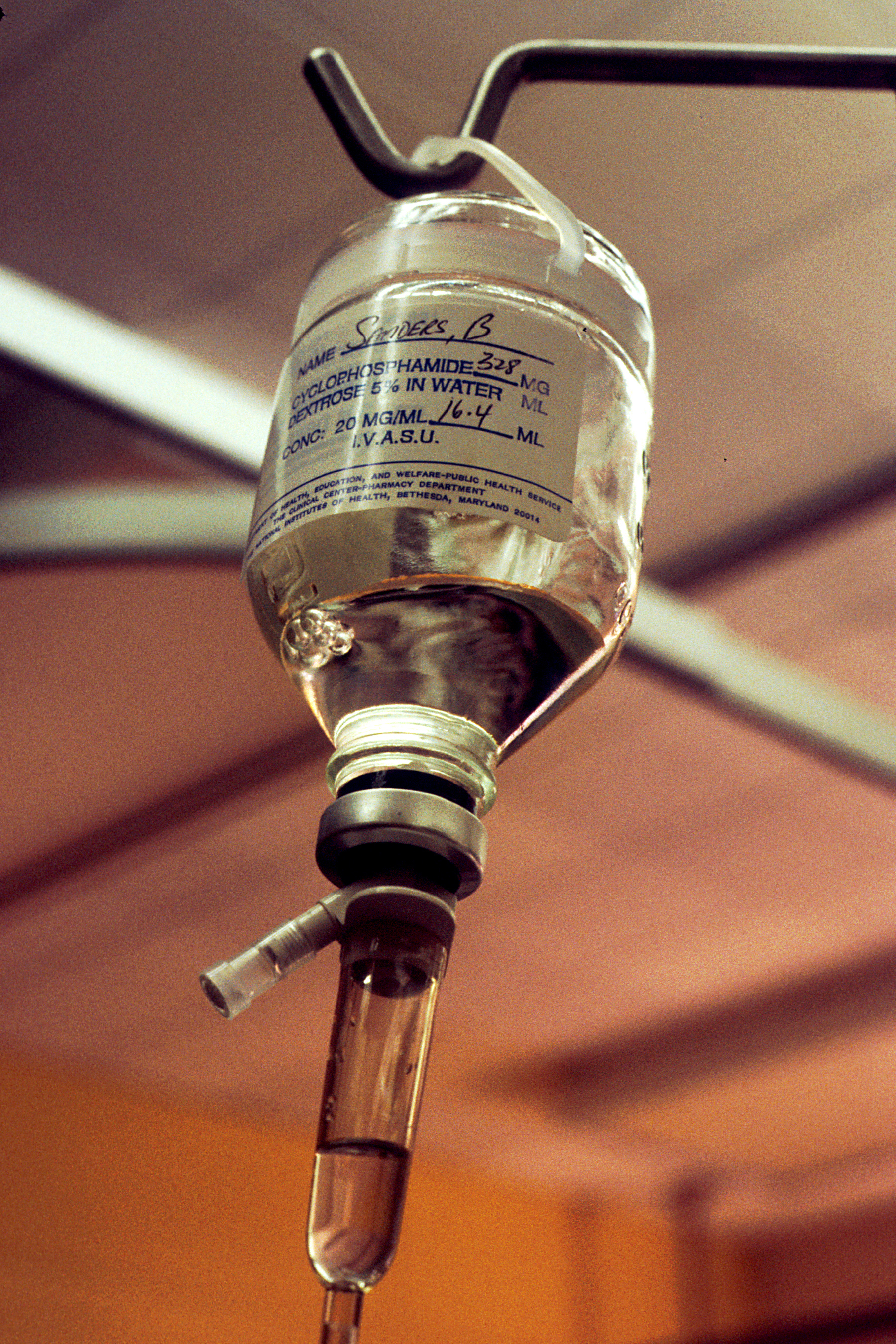
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, ANCA-associated vasculitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Cyclophosphamide was approved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given Oral administration, by mouth or by injection. Common side effects include nausea, feeling tired, fever, increased risk of infection, leukopenia, low white blood cell counts, and ulcerative stomatitis, breakdown of the skin inside the mouth. Other side effects may include liver disease, lung disease, lymphoma, and severe skin rashes. People on long-term treatment should be regularly checked for side effects. It is not safe during breastfeeding. In those with kidney problems, lower doses may be needed. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytarabine
Cytarabine, also known as cytosine arabinoside (ara-C), is a chemotherapy medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by injection into a vein, under the skin, or into the cerebrospinal fluid. There is a liposomal formulation for which there is tentative evidence of better outcomes in lymphoma involving the meninges. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, diarrhea, liver problems, rash, ulcer formation in the mouth, and bleeding. Other serious side effects include loss of consciousness, lung disease, and allergic reactions. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Cytarabine is in the antimetabolite and nucleoside analog families of medication. It works by blocking the function of DNA polymerase. Cytarabine was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1969. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-HDAC
R-HDAC, or R-HD-AraC (rituximab plus high-dose cytosine arabinoside) is a chemotherapy regimen that is used, alternating with R-Maxi-CHOP, as part of so-called "Nordic protocol" of treating mantle cell lymphoma. It consists of monoclonal antibody rituximab and high-dose antimetabolite cytarabine. High-dose Ara-C (HDAC) without rituximab also has several other uses in oncohematology. For example, HDAC, alone or alternating with HD-MTX, is often used for primary CNS lymphoma and for treating CNS involvement in any lymphomas, and also for so-called " CNS prophylaxis" (prophylactic use in those forms of lymphoma which show no signs of CNS involvement at diagnosis but have high chance of CNS relapse or recurrence). HDAC is also used as a consolidation regimen in acute myeloid leukemia Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is also used for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. It is used by mouth or intravenously, injection into a vein. Side effects are very common. They can include cytopenia, low blood cell counts, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, hair loss, and fever. Other severe side effects include allergic reactions and low blood pressure. Use during pregnancy will likely harm the fetus. Etoposide is in the topoisomerase inhibitor family of medication. It is believed to work by damaging DNA. Etoposide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1983. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Etoposide is used as a form of chemotherapy for cancers such as Kaposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation
Autologous stem-cell transplantation (also called autogenous, autogenic, or autogenic stem-cell transplantation and abbreviated auto-SCT) is the autologous transplantation of stem cells—that is, transplantation in which stem cells ( undifferentiated cells from which other cell types develop) are removed from a person, stored, and later given back to that same person. Although it is most frequently performed with hematopoietic stem cells (precursors of blood-forming cells) in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, cardiac cells have also been used successfully to repair damage caused by heart attacks. Autologous stem-cell transplantation is distinguished from allogenic stem cell transplantation where the donor and the recipient of the stem cells are different people. It can be also used as an Assisted reproductive technology to improve the reproductive outcomes. In a first step the bone marrow derived stem cells are mobilized. After that they will be isolated from the peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |