|
Seattle Space Needle
The Space Needle is an observation tower in Seattle, Washington, United States. Considered to be an icon of the city, it has been designated a Seattle landmark. Located in the Lower Queen Anne neighborhood, it was built in the Seattle Center for the 1962 World's Fair, which drew over 2.3 million visitors. At high, the Space Needle was once the tallest structure west of the Mississippi River in the United States. The tower is wide, weighs , and is built to withstand winds of up to and earthquakes of up to 9.0 magnitude, as strong as the 1700 Cascadia earthquake. Elevators take visitors to an observation deck above ground in 41 seconds, which offers panoramic views of the downtown Seattle skyline, the Olympic and Cascade Mountains, Mount Rainier, Mount Baker, Elliott Bay, and various islands in Puget Sound. On April 19, 1999, the city's Landmarks Preservation Board designated the tower a historic landmark. Architecture The architecture of the Space Needle is the result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the county seat of King County, the most populous county in Washington. The Seattle metropolitan area's population is 4.02 million, making it the 15th-most populous in the United States. Its growth rate of 21.1% between 2010 and 2020 made it one of the country's fastest-growing large cities. Seattle is situated on an isthmus between Puget Sound, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and Lake Washington. It is the northernmost major city in the United States, located about south of the Canadian border. A gateway for trade with East Asia, the Port of Seattle is the fourth-largest port in North America in terms of container handling . The Seattle area has been inhabited by Native Americans (such as the Duwamish, who had at least 17 villages a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
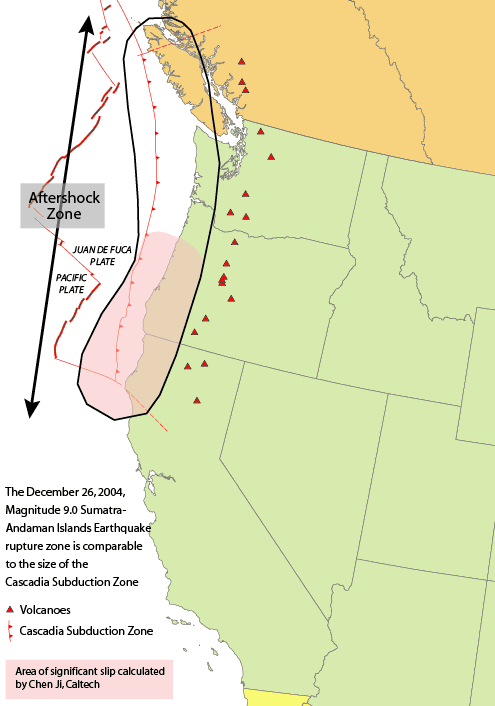
1700 Cascadia Earthquake
The 1700 Cascadia earthquake occurred along the Cascadia subduction zone on January 26, 1700, with an estimated moment magnitude of 8.7–9.2. The megathrust earthquake involved the Juan de Fuca plate from mid-Vancouver Island, south along the Pacific Northwest coast as far as northern California. The plate slipped an average of along a fault rupture about long. The earthquake caused a tsunami which struck the west coast of North America and the coast of Japan. Japanese tsunami records, along with reconstructions of the wave moving across the ocean, put the earthquake at about 9:00 PM Pacific Time on the evening of 26 January 1700. Japanese records The earthquake took place at about 21:00 PT on January 26, 1700 ( NS). Although there are no written records for the region from the time, the timing of the earthquake has been inferred from Japanese records of a tsunami that does not correlate with any other Pacific Rim quake. The Japanese records exist primarily in the moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isthmus
An isthmus (; : isthmuses or isthmi) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus, a narrow stretch of sea between two landmasses that connects two larger bodies of water. Isthmus vs land bridge vs peninsula ''Isthmus'' and ''land bridge'' are related terms, with isthmus having a broader meaning. A land bridge is an isthmus connecting Earth's major land masses. The term ''land bridge'' is usually used in biogeology to describe land connections that used to exist between continents at various times and were important for the migration of people and various species of animals and plants, e.g. Beringia and Doggerland. An isthmus is a land connection between two bigger landmasses, while a peninsula is rather a land protrusion that is connected to a bigger landmass on one side only and surrounded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Saucer
A flying saucer, or flying disc, is a purported type of disc-shaped unidentified flying object (UFO). The term was coined in 1947 by the United States (US) news media for the objects pilot Kenneth Arnold UFO sighting, Kenneth Arnold claimed flew alongside his airplane above Washington (state), Washington State. Newspapers reported Arnold's story with speed estimates implausible for aircraft of the period. The story preceded 1947 flying disc craze, a wave of hundreds of sightings across the United States, including the Roswell incident and the Flight 105 UFO sighting. A National Guard pilot died in pursuit of a flying saucer in 1948, and civilian research groups and conspiracy theories developed around the topic. The concept quickly spread to other countries. Early reports speculated about secret military technology, but flying saucers became synonymous with aliens by 1950. The more general military terms unidentified flying object (UFO) and unidentified anomalous phenomena (UAP) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Graham, Jr
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John (disambigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balloon
A balloon is a flexible membrane bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, or air. For special purposes, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), or light sources. Modern day balloons are made from materials such as rubber, latex, polychloroprene, or a nylon fabric, and can come in many different colors. Some early balloons were made of dried animal bladders, such as the pig bladder. Some balloons are used for decorative purposes or entertaining purposes, while others are used for practical purposes such as meteorology, medical treatment, military defense, or transportation. A balloon's properties, including its low density and low cost, have led to a wide range of applications. The rubber balloon was invented by Michael Faraday in 1824, during experiments with various gases. He invented them for use in the lab. Applications Play Decoration Balloons are used for decorat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Carlson
Edward Carlson (June 4, 1911 – April 3, 1990), was an American hotel and airline executive, and Seattle, Washington civic leader.Carlson, Edward "Eddie" E. (1911-1990) on . Retrieved 2009-10-06. Carlson was born in . As a youth, he helped his single mother make ends meet by working as a gas station attendant, as well as other odd jobs. Carlson entered the University of Washington ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound (geography), sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel. Puget Sound extends approximately from Deception Pass in the north to Olympia, Washington, Olympia in the south. Its average depth is and its maximum depth, off Jefferson Point between Indianola, Washington, Indianola and Kingston, Washington, Kingston, is . The depth of the main basin, between the southern tip of Whidbey Island and Tacoma, Washington, Tacoma, is approximately . In 2009, the term Salish Sea was established by the United States Board on Geographic Names as the collective wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott Bay
Elliott Bay is a part of the Central Basin region of Puget Sound. It is in the U.S. state of Washington, extending southeastward between West Point in the north and Alki Point in the south. Seattle was founded on this body of water in the 1850s and has since grown to encompass it completely. The waterway it provides to the Pacific Ocean has served as a key element of the city's economy, enabling the Port of Seattle to become one of the busiest ports in the United States. History The Duwamish people have lived in the vicinity of Elliott Bay and the Duwamish River for thousands of years and had established at least 17 settlements by the time white settlers came in the 1850s. Among the earliest white settlements was by the Denny Party at New York Alki, which is in the present-day neighborhood of Alki in West Seattle, however after a hard winter they shifted across Elliott Bay near the present-day Pioneer Square, which became Seattle. Over the years the city expanded to cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Baker
Mount Baker (; ), also known as Koma Kulshan or simply Kulshan, is a active glacier-covered andesitic stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the North Cascades of Washington State in the United States. Mount Baker has the second-most thermally active crater in the Cascade Range after Mount St. Helens. About due east of the city of Bellingham, Whatcom County, Mount Baker is the youngest volcano in the Mount Baker volcanic field. While volcanism has persisted here for some 1.5 million years, the current volcanic cone is likely no more than 140,000 years old, and possibly no older than 80–90,000 years. Older volcanic edifices have mostly eroded away due to glaciation. After Mount Rainier, Mount Baker has the heaviest glacier cover of the Cascade Range volcanoes; the volume of snow and ice on Mount Baker, is greater than that of all the other Cascades volcanoes (except Rainier) combined. It is also one of the snowiest places in the world; in 1999, Mount Baker Ski A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Rainier
Mount Rainier ( ), also known as Tahoma, is a large active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range of the Pacific Northwest in the United States. The mountain is located in Mount Rainier National Park about south-southeast of Seattle. With an officially recognized summit elevation of at the Columbia Crest, it is the highest mountain in the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington, the most Topographic prominence, topographically prominent mountain in the contiguous United States, and the tallest in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. Due to its high probability of an eruption in the near future and proximity to a Seattle metropolitan area, major urban area, Mount Rainier is considered one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world, and it is on the Decade Volcano list. The large amount of glacial ice means that Mount Rainier could produce massive lahars that could threaten the entire Puyallup River valley and other river valleys draining Mount Rainier, including the Carbon River, Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |